Podcast
Questions and Answers
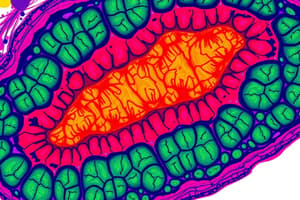
Which of the following diseases is characterized by an infection affecting the small intestine's lamina propria, leading to malabsorption and an increased number of macrophages?
Which of the following diseases is characterized by an infection affecting the small intestine's lamina propria, leading to malabsorption and an increased number of macrophages?
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Scurvy
- Whipple disease (correct)
The mesentery relies on which type of connective tissue for support and to serve as a conduit for vessels and nerves?
The mesentery relies on which type of connective tissue for support and to serve as a conduit for vessels and nerves?
- Loose Connective Tissue (correct)
- Elastic Cartilage
- Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
- Reticular Connective Tissue
How does the primary function of brown adipose tissue differ from that of typical white adipose tissue?
How does the primary function of brown adipose tissue differ from that of typical white adipose tissue?
- Brown adipose primarily generates heat, while white adipose is mainly for energy storage. (correct)
- Brown adipose synthesizes collagen, while white adipose synthesizes elastin.
- Brown adipose produces hormones, while white adipose stores them.
- Brown adipose cushions organs, while white adipose provides structural support.
What is the key characteristic that differentiates brown adipocytes from white adipocytes at a microscopic level?
What is the key characteristic that differentiates brown adipocytes from white adipocytes at a microscopic level?
Thermogenin (UCP-1) is a protein that is found in the mitochondria of brown adipose tissue. What role does it play in generating heat?
Thermogenin (UCP-1) is a protein that is found in the mitochondria of brown adipose tissue. What role does it play in generating heat?
Which of the following characteristics primarily distinguishes smooth muscle from skeletal muscle?
Which of the following characteristics primarily distinguishes smooth muscle from skeletal muscle?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum plays a crucial role in muscle cell function. What is its primary function?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum plays a crucial role in muscle cell function. What is its primary function?
A researcher is examining a muscle tissue sample under a microscope after staining it with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E). The tissue stains red. Which type of muscle tissue is the researcher most likely observing?
A researcher is examining a muscle tissue sample under a microscope after staining it with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E). The tissue stains red. Which type of muscle tissue is the researcher most likely observing?
Skeletal muscle contraction requires nerve synapses. What is the significance of these synapses in muscle function?
Skeletal muscle contraction requires nerve synapses. What is the significance of these synapses in muscle function?
What is the role of muscle satellite cells in skeletal muscle tissue?
What is the role of muscle satellite cells in skeletal muscle tissue?
Which type of gland combines both serous and mucous secretions?
Which type of gland combines both serous and mucous secretions?
In which of the following glands does the entire secretory cell disintegrate to release its product?
In which of the following glands does the entire secretory cell disintegrate to release its product?
Which of the following features distinguishes compound glands from simple glands?
Which of the following features distinguishes compound glands from simple glands?
A researcher is studying a gland that releases its secretions via exocytosis without any loss of cellular material. Which type of secretion mechanism is the gland utilizing?
A researcher is studying a gland that releases its secretions via exocytosis without any loss of cellular material. Which type of secretion mechanism is the gland utilizing?
Goblet cells, found in the lining of the intestines, are examples of what kind of gland, based on morphology?
Goblet cells, found in the lining of the intestines, are examples of what kind of gland, based on morphology?
If a gland has secretory units that are shaped like branched tubules, and branched ducts, how would it be classified?
If a gland has secretory units that are shaped like branched tubules, and branched ducts, how would it be classified?
The mammary gland utilizes which secretion mechanism?
The mammary gland utilizes which secretion mechanism?
A gland that exhibits both acinar and tubular components in its secretory units, along with branched ducts falls under which classification?
A gland that exhibits both acinar and tubular components in its secretory units, along with branched ducts falls under which classification?
Which of the following is the primary function of simple squamous epithelium found in the lining of blood vessels (endothelium)?
Which of the following is the primary function of simple squamous epithelium found in the lining of blood vessels (endothelium)?
In which of the following locations would you most likely find pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
In which of the following locations would you most likely find pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What characteristic distinguishes stratified squamous keratinized epithelium from stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium?
What characteristic distinguishes stratified squamous keratinized epithelium from stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium?
Which type of epithelium is specialized to provide a protective and distensible lining in organs that undergo volume changes, such as the urinary bladder?
Which type of epithelium is specialized to provide a protective and distensible lining in organs that undergo volume changes, such as the urinary bladder?
Which type of epithelium lines the intestine and gallbladder, and what are its primary functions?
Which type of epithelium lines the intestine and gallbladder, and what are its primary functions?
Which of the following features is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following features is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue?
Suppose a patient's thyroid gland is not producing enough hormones. Which type of epithelium is most likely to be affected?
Suppose a patient's thyroid gland is not producing enough hormones. Which type of epithelium is most likely to be affected?
What is the main function of the mesothelium that lines the pleural cavity?
What is the main function of the mesothelium that lines the pleural cavity?
Which of the following epithelia is correctly matched with its location?
Which of the following epithelia is correctly matched with its location?
In the alveoli of the lungs, which type of epithelium facilitates efficient gas exchange?
In the alveoli of the lungs, which type of epithelium facilitates efficient gas exchange?
Which factor primarily dictates the slow rates of fiber contraction in certain muscle types?
Which factor primarily dictates the slow rates of fiber contraction in certain muscle types?
In smooth muscle, what is the role of Myosin Light-Chain Kinase (MLCK)?
In smooth muscle, what is the role of Myosin Light-Chain Kinase (MLCK)?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT associated with slow oxidative muscle fibers?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT associated with slow oxidative muscle fibers?
How is smooth muscle contraction most commonly stimulated?
How is smooth muscle contraction most commonly stimulated?
Which structural component is responsible for enclosing individual smooth muscle fibers?
Which structural component is responsible for enclosing individual smooth muscle fibers?
What is the approximate size range of the nucleus within a smooth muscle cell?
What is the approximate size range of the nucleus within a smooth muscle cell?
Which protein binds to calcium ions in smooth muscle to initiate the contraction process?
Which protein binds to calcium ions in smooth muscle to initiate the contraction process?
Which of the following is a key distinction between skeletal muscle and smooth muscle?
Which of the following is a key distinction between skeletal muscle and smooth muscle?
How does smooth muscle contraction differ from skeletal muscle contraction regarding sarcomere organization?
How does smooth muscle contraction differ from skeletal muscle contraction regarding sarcomere organization?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of cardiac muscle that distinguishes it from skeletal muscle?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of cardiac muscle that distinguishes it from skeletal muscle?
What function do intercalated discs serve in cardiac muscle tissue?
What function do intercalated discs serve in cardiac muscle tissue?
How does physical training lead to muscle enlargement?
How does physical training lead to muscle enlargement?
What is the primary difference between hypertrophy and hyperplasia in the context of muscle tissue?
What is the primary difference between hypertrophy and hyperplasia in the context of muscle tissue?
In Myasthenia Gravis, how do circulating antibodies affect acetylcholine receptors?
In Myasthenia Gravis, how do circulating antibodies affect acetylcholine receptors?
Which of the following characteristics distinguishes smooth muscle from both skeletal and cardiac muscle?
Which of the following characteristics distinguishes smooth muscle from both skeletal and cardiac muscle?
Which factor has the LEAST influence on the variation in diameter observed across different muscle fibers?
Which factor has the LEAST influence on the variation in diameter observed across different muscle fibers?
Flashcards
Loose Connective Tissue (LCT) Function & Location
Loose Connective Tissue (LCT) Function & Location
Connective tissue providing suspension and support for tissues not under strong forces; forms conduits for vessels and nerves.
Whipple Disease
Whipple Disease
A multisystemic disease caused by infection of Tropheryma whippleii, primarily affecting the small intestine.
Brown Adipose Tissue Feature (Multilocular)
Brown Adipose Tissue Feature (Multilocular)
Connective tissue characterized by cells containing many small lipid inclusions.
Brown Adipose Tissue - Function
Brown Adipose Tissue - Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipose Tissue
Adipose Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcoplasm
Sarcoplasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Satellite Cells
Muscle Satellite Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Column Epithelium
Column Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Startified Squamous Epithelium
Startified Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucous Gland
Mucous Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seromucous (Mixed) Gland
Seromucous (Mixed) Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sebaceous Gland
Sebaceous Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Merocrine (Eccrine) Gland
Merocrine (Eccrine) Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apocrine Gland
Apocrine Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocrine Gland
Holocrine Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unicellular Gland
Unicellular Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compound Tubuloacinar Gland
Compound Tubuloacinar Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fiber Contraction Rates
Fiber Contraction Rates
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slow Oxidative Fibers
Slow Oxidative Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle Fibers
Smooth Muscle Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
MLCK and Calmodulin
MLCK and Calmodulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calmodulin
Calmodulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle Control
Smooth Muscle Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle Stimulation
Smooth Muscle Stimulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle Contraction
Smooth Muscle Contraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smooth Muscle: Thin Filament Attachment
Smooth Muscle: Thin Filament Attachment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercalated Discs
Intercalated Discs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Striations
Striations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Fiber Diameter Variation
Muscle Fiber Diameter Variation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcomeres in Smooth Muscle
Sarcomeres in Smooth Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Epithelial Cells
- Avascular tissue lacks direct blood supply
- Derived from Greek words "epi" (upon) and "thele" (nipple)
- Most epithelial tissues continuously renew
- Have distinctive shapes: spherical, elongated, or epileptic
- Nutrients delivered by diffusion from blood vessels in connective tissue
Basic Functions
- Protection from abrasion and injury (e.g., skin and esophagus)
- Absorption of material from lumen (e.g., tubules in kidney, small/large intestine)
- Transportation of material along the surface (e.g., cilia-mediated transport in the trachea)
- Secretion of mucus, hormones, and proteins (e.g., glands)
- Gas exchange (e.g., alveoli in the lungs)
- Lubrication between two surfaces (e.g., mesothelium of the pleural cavity)
Classification of Epithelial Tissue (Polyhedral)
- Simple: One layer of cells
- Stratified: Two or more layers of cells
- Squamous Epithelium: Flat cells
- Cuboidal Epithelium: Cube-like cells
- Columnar Epithelium: Column-like cells
- Transitional Epithelium: Urothelium (seen in urine)
Common Types of Covering Epithelia
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: Facilitates movement of viscera (mesothelium), active transport by pinocytosis and secretion
- Cuboidal Epithelium: Covering of the ovary and thyroid. Covering, secretion
- Columnar Epithelium: Lining of the intestine and gallbladder. Protection, lubrication, absorption, secretion
- Stratified Squamous (keratinized/dry): Epidermis. Protection; prevents water loss
- Stratified Squamous (nonkeratinized/moist): Mouth, esophagus, larynx, vagina, and anal canal. Protection; prevents water loss
- Stratified Cuboidal: Sweat glands, developing ovarian follicles. Protection, secretion
- Transitional: Bladder, ureters, and renal calyces. Protection, distensibility
- Columnar: Conjunctiva. Protection
- Pseudostratified: Lining of trachea, bronchi, and nasal cavity. Protection, secretion. Cilia-mediated transport of particles trapped in mucus out of air passages
Specializations of Epithelial Cells (Apical Domain)
- Cilia: Elongated, motile structures aiding in material transport on the epithelial surface and arise from basal bodies
- Microvilli: Smaller than cilia, composed of actin microfilaments, anchored to a terminal-web structure, aiding in absorption
Specializations of Lateral Surface (Lateral Domain)
- Zonula Occludens (Tight Junction): Completely surrounds apical cell borders to seal the intercellular cleft
- Zonula Adherens (Adhering Junctions): Located beneath tight junctions, forms a bond-like junction to attach adjacent cells
- Desmosomes: Located beneath adhering junctions; assist in cell-to-cell attachment
- Gap Junction: Communicating junctions allow passage of ions and small molecules between adjacent cells
Basal Lamina
- A sheet of material that basal surfaces of all epithelial cells connect with, located next to underlying connective tissue
- Composed of laminin, type IV collagen, entactin (nidogen), and proteoglycans
- Laminin are glycoprotein molecules that self-assemble into a lace-like sheet
- Type IV Collagen are monomers that self-assemble into a sheet associated with the laminin layer
- Entactin (nidogen) is a glycoprotein and proteoglycan that links laminin and type IV collagen sheets
- Reticular Lamina: Located below the Type IV collagen layer and consists of Type III collagen made for anchoring fibrils
Simple Squamous Epithelial Cell
- One-layer of uniform flat cells resting on the basement membrane and are the simplest of epithelial cells
- Smooth apical surfaces with cell width greater than height
- Allows passage of materials, secretes lubricating substances, and is located in lining blood vessels, the posterior surface of the cornea, lymphatic vessels, and lining body cavities
Simple Squamous Epithelial Cell Clinical Significance
- Mesothelioma: A neoplasm from pleural and peritoneal cavities, linked to asbestos exposure or smoking
- Endothelial Cells: They are flattened, elongated, parallel to blood flow, and rest on a basement membrane
- The tunica intima consists of the endothelium, subendothelium connective tissue, and the internal elastic lamina.
- Endothelial cells are linked by junctionals called hemidesmosomes
- Atherosclerosis: Deposits of cholesterol, lipid material, and lipophages; hardened deposits may lead to vascular occlusion, stroke, and are affected by endothelial dysfunction
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial Cell
- Composed on one layer of uniform, cubed cells on a basement membrane
- The cells are equal in height, depth, and width, with centrally located spherical nuclei
- Functions: secretion and absorption
- Location: Distal and collecting tubules of the kidney and some excretory glands
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial Cell Clinical Significance
- Hyperthyroidism (Goiter): Characterized by excess thyroid production, with symptoms like nervousness, tremors, treatable in patients with iodine-131
- Grave's Disease (Diffuse Toxic Goiter): The most common form of hyperthyroidism, an autoimmune disease from antibodies for the TSH receptor, treatable of patients with iodine-131
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: Most common cause of hypothyroidism, associated with thyroid gland enlargement (goiter), characterized by TSH and TPO antibody
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- One layer of cells resting on a basement membrane and are taller in height then they are wide
- Elongated nucleus that are basally-located
- Functions in absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes, and ciliary action
- Location: digestive tract, Fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system, and ductuli efferences testis of the reproductive system
Simple Columnar Epithelial Cell Clinical Significance
- Celiac (coeliac) Disease: Gluten allergy, disorder of the small intestine due to microvilli damage
- Intestinal lining can not absorb, causing anemia and/or bone damage.
- Histologic features include blunting of villi, presence of lymphocytes, and increased lymphocytes within the lamina propria
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- A single layer of non-uniform cells varying in shape and height, can be classified as basal cells or stem cells
- Most widespread type can be found in the respiratory tract with fingerlike motile structure cells
- Functions in secretion, population of mucus, and ciliary action
- Locations: Ciliated variety found in trachea and upper respiratory tract. Nonciliated types found in the male sperm carrying duct
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelial Cell Clinical Significance
- Bronchitis: Acute or chronic inflammation of the bronchial tubes
- Inflammation caused by viral/bacterial infections or by irritants of the bronchi
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Contains multiple cell layers in which top layer is composed of flattened cells
- Protects body from injury abrasion dehydration and infection
- Found: Oral cavity, esophagus, vagina, and true vocal cords (nonkeratinized)
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Clinical Significance
-
Psoriasis: A chronic inflammatory skin disease with pink or salmon plaques with silver scales with the T-lymphocyte-mediated immunologic reaction
-
Barrett Syndrome: A complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease marked metaplasia of the SSE of the distal esophagus
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
- Upper most layer: Columnar, most basal level: cuboidal
- Made of 2-3 layers
- Location: conjuctiva, some exocrine glands
- Blockage from ducts, most common: salivary stone (calculus/calculi), removal of stone may include surgery
Transitional Epithelium
- A stratified epithelium referred to as a urothelium that line excretory channels leading from the kidney such as the renal calyces, ureters, bladder and proximal segment of the urethra
- Surface can be described as "dome shaped" and are called dome cells (they can contain two nucleoli) or umbrella cells (which contain extra membrane)
Glandular Epithelia
- Composed of epithelial cells but are classified based on of how the secretory products leaves the gland
- Endocrine Glands: release products into interstitial fluid or directly into the bloodstream
- Exocrine Glands: secrete products through ducts into the lumen or directly onto the body surfaces
- Serous gland: watery proteinaceous fluid (EX. parotid, von Ebner of the tongue, pancreas, and sweat gland)
- Mucous gland: secretes mucus, a mixture of glycoprotein and water (EX. goblet cells in the small and large intestine, respiratory epithelium, hard and soft palates, stomach epithelium)
- Seromucous (mixed) gland: have both serous and mucous secretion (EX. submandibular, sublingual, tracheal glands)
- Sebaceous gland: produce lipids (skin)
Classification of Exocrine Gland Mechanisms
- Merocrine (eccrine): only releases its secretory product w/o the loss of cell matter
- Apocrine: releases secretory product along with part of the apical cytoplasm
- Holocrine: Releases entire contents when it undergoes disintegration
Glands Classified According to Morphology
- Unicellular glands release product directly onto the the surface of a cell (ex. Goblet cells)
- Multicellular glands have secretory cells that arranges into simple and compound arrangements
Pathologic Terms
- Metastasis: Spread of malignant neoplasm from its origin site to a remote site through blood and lymphatic vessels.
- Dyslipidemia: Lipid imbalances
- Osteomalacia: Softening of bones due to defective mineralization
- Metaplasia: Where cells change shape
- Microabscess: Collection of neutrophils and debri within the parakeratotic scale of some skin in the condition psoriasis.
- Micropostule: Collection of neutrophils within the upper layer of skin
- Parakeratosis: retention of nuclei in the keratinocytes
Connective Tissue
- Mesodermal origin and contains cells, fibers, and ground substance
- Classification and function is depended on the amount of cells and composition
- Functions: provides structure for the body, metabolic support, location for lying down epithelial cells
- Vascular, unlike epithelial tissue
Types of Connective Tissue
- Connective Tissue Proper: Dense regular/irregular tissue, Loose Connective tissue
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Adipose, Reticular,Elastic tissue
- Embryonic Connective Tissue: Mesenchymal, Mucous connective tissue
- Supporting Connective Tissue: Cartilage, Bone
- Hematopoietic Connective Tissue: Blood, Bone Marrow
Cellular Differentiation of Connective Tissue
- Mesenchymal cells: Fixed cells such as adipocytes and fibroblasts
- Hematopoietic stem cells: Wandering cels such mast cells, macrophages, plasma cells, and leukocytes.
- Fibroblasts: Responsible for the the synthesis and maintenance of the extracelluar material
- Macrophages, plasma cells, and leukocytes are responsible for defense and immune function
Connective Tissue Cells
- Fibroblast: Produces fibers and ground substance, provides structural support.
- Plasma cell: Produce antibodies, assists immune system in defensive functions, and their cytoplasm appears basophilic
- Lymphocyte: Produces immunocompetent cells for immune defense and monitoring
- Eosinophilic leukocyte: Aid in inflammation.
- Neutrophilic leukocyte: Destroys foreign substances.
- Macrophage defense: Provides defense by secreting cytokines and other molecules.
- Mast cell and Basophilic: Participates in allergic reactions.
- Adipocyte: Stores nutrients like fat, energy.
- Their pale and obvious that contain well-developed RER and rich Golgi complexes.
Molecules Released from Mast Cells
- Heparin: Acts like a anticoagulant.
- Histamine: Promotes an increased vascular permeability.
- Serine protease: Activates mediators of inflammation
Plasma Cells
- Derived from B lymphocytes of the lymphatic system
- Has a lot of basophilic cytoplasm that contains a eccentrically placed nucleus.
- Can be found within the blood.
- Has "clock-face appearance" of the chromatin in the nucleus
- Has a life time of 10-20 days
Leukocytes
- Considered transient cells (appear briefly) that have the ability to move from blood vessels into connective tissue
- Cardinal indications include: Rubor signs, swelling, increased temperature and/or color.
- There are a mixture of Banded cells from different origins
Fibers
- Three types of conductive tissue fibers are the collagen fibers, reticular fibers, and elastic fibers
- Most important function is to conduct heat
- Most are made of I, II, and III
- Reticular fibers consists of the the collagen the type |||
- Type V collagen can be found in cartilage
- Elastin is important to help restore bone back to shape
- Elastic fibers are stained more darker than collagen with other stains like orcein
Ground Substances
- Ground: Highly hydrated and very transparent.
- Ground Substances, PROTEOGLYCANS, are all important
GAGs
- dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfates, keratan sulfate, and heparan sulfate
Dense Connective Tissue
- Made of thick collagen bundles that's packed with cylinders
- Providing high resistance in tendons and ligaments
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
- Can be found in glands and capsules of organs
- Not greatly vascularized
Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids
- Disorder in collagen
Tendinosis
- Degenerative disease
Loose Tissue
- Provides support for organs
- Conduits used to transmit blood
- Contains a lot of mesentery
Whipple Disease
- Multisystem caused by the bacteria infection of Tropheryma whippleii
Adipose Tissue
- Two: White and Brown tissue
- Brown: Abundant for mitochondria
- Brown: hibernating bland
- White is specialized for long term storage
Brown Tissue
- Contains several small tissues together
- Called multilocular
- Contains thermogenin
Obesity
- Hypertrophic, increase in body fat
- Increases with other conditions like diabetes that could occur
Reticular Tissue
- Delicate tissue
- Provides cellular structure for tissue and organs
Elastic Connective Tissue
- Provides material
- Can be found in vertebrae
- Allow distinction and recall
Marfan Syndrome
- Effects elastic fibers
- Mutation affects those who also long limbs, hands, and feet
Mucous Connective Tissue
- Can be found in the best connective tissue.
- Can be considered Wharton's jelly
Medical Issues (U-P C-N C)
- Urticaria, skin allergic
- Pruritus, itchiness
- Cirrhosis, abnormal liver disease
- Jaundice, yellowing of the skin from bilirubin
- Coagulopathy, effects clotting
- and Necrosis
Muscle Tissue
- Cells optimize universal contractility, and drive organismal movement
- The forces needed are produced between two groups of protein
- Origin: Mesodermal
- Almost all cells differentiate
- Stains Red with H &E
Voluntart versus Involuntart
- Voluntary- Is under conscious control and also describes skeletal muscle contraction
- Invoulntary- response to autonomic control and cardiac or smooth muscle contractions
Sacroplasm
- Muscle cytoplasm
- The greek word "saroks" meaning:flash+plasma
Histological Classification
- Skeletal Muscle- Multinucleated
- Cardiac Muscle- Branched, intercalated discs, includes glycogen
- Smooth Muscle- No striations, nucleic
Skeletal Muscle
- Fibers are arranged
- Enabled the bodies muscle
- Wont work w/o neve synapses
- Striated is long multinucleated
- Muscle satellite calls remains
Development of Skeletal Muscles
- Begins a messenger fuse
- Formed from mesenchymal cells
- Myotubes synthesize protein
- Myofibalmentary light can show cross striations by reflecting protein
Organization of Skeletal Muscles
- Epimysium- an external dense sheet of muscle cells
- perimysium connective tissues layer with fascicle
- Endomysium- is a thin reticular fiber with scattered fibroblasts.
- Fiber, cappilaries in the the endomysium brings O2 and muscle fibers
3 Layers
- All 3 layer form a strong connection
- Highly organized sarcoplasm
- Formed by the Mline and the Hzone
Myofibrils
- Organized by cilindircal
- Consist of several sarcomeres
A band (dark)
- Contains filaments
- Anistrophic polarized
Ibands (light)
- Portions of thin structures
- Do not overlap
Sarcomere and sarcoplasmic
- Appears with the light microscope
- Is the contractile apparatus of the cell and extends fromz dict to district
- Mitochondria and sarcoplasm
Thick Myosin Filament
- 1.6 um long inside the abnd region
Myosin
- Complex with light or heavy light chain molecules (2)
Thick Myosin Tails
- Thin rob together an myosin
Myosin Head
- From filament cross bridges
Actin Filaments-
- Helich shaped and run filaments
Mechanism of Contraction
- Ca2 binds to troponin cells
- Filaments
FAST muscle fibers
- Specialized to contract for a short time
SLOW muscle fibers
- Contain very little glycogen
SKELETAL MUSCLES Tissues
- Muscles adopted slow contraction
- There are few capillaries if without the hormone
Smooth Muscles tissues
- Specialized for short and controlled contractions
- Influences by hormones or autonomic nerves
- Can be found with in Vessle
Smooth Muscle
- Made of small blood volume (20 um) in small areas and 50 um in pregnant woman
- Monoanucleated in central region (5_10 um)
- Lack troponin or tropomyosin with proteins
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Connective tissue by a large area w/ • Involves muscularly functioning fibroids
Cardiac Muscle
- Connected and striated but acts involuntarily
- Responsible for heart beats and contains one nucleic in cell
Hypertrophy
- Variation in muscle (cell size)
- Is the physical training of an individual
- Cell sizes increase
Myasthenia Gravis
- Autoimmune order
- Circulating antibodies
- Interferes receptors
Dystrophin
- Has a large amount of actin-binding proteins
- Involved with myofibrils
- Caused by dystrophin proteins
Ischemia
- Most injury sustained by cardiac muscle
- Heart cannot regenerate
- Can be cause by atherosclerosis
Bones
- Provides a solid support for the body
- Encloses marrow/ red blood cell
- Acts as reservoir
- Connective Tissue : Osteocytes osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Features & Functions
- Osteocytes: Found in lacuna
- Osteoblasts " growing cells
- Osteoclasts: Removes Bone Tissue
Bone Matrix
- Provides a bone harness
- Allows organization
- 50% inorganic, mainly calcium
- 50% organic mainly collagen
Bone's Protective Layers + Development
- Peristeoum & Endosteum are the layers
- Osteogenesis creates new osteoids
- They can be formed by a intramembranous ossification and the preexisiting Hyaline cartilage matrix is then eroded
- Osteoblast then secrete new osteuoids
Epiphyseal
- Consists of 5 zones that help with a Hyaline creation
Calcium
- Raises and stimulate osteoclasts for bone resorption; for bone creation
- Can be mobilize with mobilization with minerals
Joints
- The 3 joint movements include Synarthoses with limited movement, Diarthrotic are movable
- Macrophages is also contained
Medical issues of muscles & bones
- Osteoporesis, is common.
- Osteogenesis, disease; congenital.
- Osteomalacia and osteitis
Rickets
- Calcium efficiency with children's joints or muscle disorders.
Tumors
- Are uncommon
- Can develop
Naming
- Can be named with GH deficiency, for childhood reasons.
Disease
- Related for growth or bone
Cartilage
- Contains collagen elastin cells, and a tough flexible connective tissue. Is high in ECM with glycosaminoglycans
- Providing bone formulation that can be one of three types: Hayline, Elastic, & Fibrocartilage
C-E-F
- Location joints and tensile strength are the key factors
- Functions, that allows them to be smooth
ECM
- Mainly consist of type II collagen
Cell Types
- Chondrocytes: Has small amounts of cells that's high in water composition
- Cartilage contains water for a shock of absorption by making it very dense.
Perichondrium
- Contains a connective tissue that function providing nutrients, and contains progenitor cells
- Two types of growth, intersitail & Appositionial, that chondroblasts form from perichondrium
Healing
- Avascular slow, is the capacity which leads to slow cartilage movement.
- Low mitotic activity of chondrocytes. Making healing hard to do
Applications
- Osteoarthritis
- Aging, repetitive use, lead from the loss of synthesis
Hormones and Gene
- Gene affects synthesis
- Lead joint issues
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.