Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the heating curve represent?
What does the heating curve represent?
- The changes in phases as a sample is heated (correct)
- How different substances absorb heat
- The relationship between temperature and pressure
- The kinetic energy of molecules at various temperatures
At which segments of the heating curve is the temperature constant?
At which segments of the heating curve is the temperature constant?
- Segment AD and Segment BE
- Segment AB and Segment CD
- Segment AE and Segment DF
- Segment BC and Segment DE (correct)
Which statement correctly distinguishes heat from temperature?
Which statement correctly distinguishes heat from temperature?
- Heat refers to the state of matter, while temperature refers to the speed of molecules.
- Heat measures energy transfer, while temperature measures warmth or coldness. (correct)
- Heat is measured in Kelvin, while temperature is measured in Joules.
- Temperature is dependent on mass, while heat is independent.
What is the heat of fusion (Hf)?
What is the heat of fusion (Hf)?
What is the heat of vaporization (Hv)?
What is the heat of vaporization (Hv)?
What happens to the potential energy during a phase change as indicated by the heating curve?
What happens to the potential energy during a phase change as indicated by the heating curve?
Which unit is used to measure heat in chemistry?
Which unit is used to measure heat in chemistry?
During which process does a substance change from solid directly to gas?
During which process does a substance change from solid directly to gas?
Flashcards
Heat of Fusion (Hf)
Heat of Fusion (Hf)
The energy required to change a substance from a solid to a liquid at a constant temperature. It's the energy needed to break the bonds holding the solid together.
Heating Curve
Heating Curve
The graph that shows how a sample changes temperature and phase as heat is added.
Heat of Vaporization (Hv)
Heat of Vaporization (Hv)
The energy required to change a substance from a liquid to a gas at a constant temperature. It's the energy needed to completely overcome intermolecular forces.
Why is the heating curve flat at some points?
Why is the heating curve flat at some points?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heat vs. Temperature
Heat vs. Temperature
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the significance of the Heating Curve?
What is the significance of the Heating Curve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the heating curve look?
How does the heating curve look?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the heating curve?
What is the heating curve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
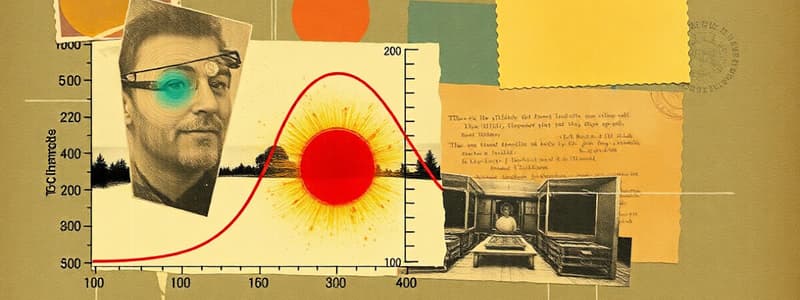
Heating and Cooling Curves
- Heating curves graphically represent how a substance changes phases as heat is added.
- As heat is added, the substance changes temperature and phase.
- The graph plots temperature versus time.
What Happens When Heating a Substance?
- A substance can exist as a solid, liquid, or gas.
- Changes include melting (solid to liquid) and evaporation (liquid to gas).
Defining Heat and Temperature
- Heat is a measure of kinetic energy (in Joules).
- Heat depends on mass, temperature change, and substance-specific heat capacity.
- Temperature is a measure of warmth or coldness, independent of heat.
- Temperature is measured in Kelvin (K) or Celsius (C).
The Heating Curve: A Deeper Look
- The heating curve is a graph showing how a substance changes phases with added heat over time.
- The curve displays segments, each representing a change in state or temperature.
Parts of a Heating Curve
- A: The segment where the substance is in a solid phase and the temperature rises.
- B: The segment represents when the substance starts melting. The temperature stays constant during this phase transition.
- C: Shows the substance fully in a liquid phase and the liquid's temperature increases.
- D: The segment where liquid starts boiling. The heat is used to change the liquid to a gas and temperature stays constant.
- E: The segment where the substance is now fully a gas and its temperature increases.
- F: The final part where the substance exists as a gas at a rising temperature.
Flat Portions of the Heating Curve
- Flat segments on the heating curve indicate that the substance's temperature is constant despite heat input.
- During these periods, energy is used to alter the substance from one state to another (e.g., melting, boiling)
- These flat segments represent the heat of fusion (during melting and freezing) and the heat of vaporization (during boiling and condensation).
Heat of Fusion and Vaporization
- Heat of fusion (Hf) is the energy needed to completely change a solid into a liquid.
- Heat of vaporization (Hv) is the energy needed to completely change a liquid into a gas.
Summary of Heating Curves
- Heating curves are a useful tool in chemistry, showing phase changes and temperature changes of a substance when heat is added.
- They include information about a substance's state, and phase changes (solid, liquid gas).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.