Podcast
Questions and Answers
What initiates the depolarization of the heart?
What initiates the depolarization of the heart?
- Gap Junctions
- Sino-atrial Node (correct)
- Purkinje Fibers
- Atrioventricular Node
The AV Node allows electrical activity from the ventricles to affect the atria.
The AV Node allows electrical activity from the ventricles to affect the atria.
False (B)
What is the role of Purkinje Fibers in the heart's conduction system?
What is the role of Purkinje Fibers in the heart's conduction system?
They are responsible for rapid conduction of the impulse through the ventricular myocardium.
The __________ is a unique property of cardiac muscle allowing it to depolarize without external stimuli.
The __________ is a unique property of cardiac muscle allowing it to depolarize without external stimuli.
Match the ECG components with their functions:
Match the ECG components with their functions:
Which structure insulates the ventricles from electrical activity in the atria?
Which structure insulates the ventricles from electrical activity in the atria?
The AV bundle conducts impulses directly from the atria to the lungs.
The AV bundle conducts impulses directly from the atria to the lungs.
The electrical activity in the heart can be monitored using an __________.
The electrical activity in the heart can be monitored using an __________.
What is the importance of the fibrous ring in the heart's conduction system?
What is the importance of the fibrous ring in the heart's conduction system?
How do gap junctions facilitate heart contractions?
How do gap junctions facilitate heart contractions?
Describe the role of the atrioventricular (AV) node in the heart's conduction system.
Describe the role of the atrioventricular (AV) node in the heart's conduction system.
What does the QT interval on an electrocardiogram (ECG) represent?
What does the QT interval on an electrocardiogram (ECG) represent?
How do Purkinje fibers contribute to the efficiency of the heart?
How do Purkinje fibers contribute to the efficiency of the heart?
Explain the significance of the P-wave in an ECG.
Explain the significance of the P-wave in an ECG.
What occurs during the P-Q wave on an ECG?
What occurs during the P-Q wave on an ECG?
How does autorhythmicity affect the heart's function?
How does autorhythmicity affect the heart's function?
The __________ is where depolarization of the heart begins and radiates in all directions.
The __________ is where depolarization of the heart begins and radiates in all directions.
The __________ allows the electrical activity from the atria to affect the ventricles.
The __________ allows the electrical activity from the atria to affect the ventricles.
The __________ connects the atrioventricular node to the ventricles through the bundle branches.
The __________ connects the atrioventricular node to the ventricles through the bundle branches.
Electrocardiograms (ECG) detect the __________ and repolarization waves across the heart.
Electrocardiograms (ECG) detect the __________ and repolarization waves across the heart.
During the P-wave, there is a spread of __________ from the SA node to the cardiac muscle of the atria.
During the P-wave, there is a spread of __________ from the SA node to the cardiac muscle of the atria.
The __________ is responsible for rapid conduction of electrical impulses to the ventricular myocardium.
The __________ is responsible for rapid conduction of electrical impulses to the ventricular myocardium.
The __________ insulates the ventricles from the electrical activity occurring in the atria.
The __________ insulates the ventricles from the electrical activity occurring in the atria.
Gap junctions are housed within __________, allowing depolarization of the heart to move from cell to cell.
Gap junctions are housed within __________, allowing depolarization of the heart to move from cell to cell.
Flashcards
Autorhythmicity
Autorhythmicity
The heart's ability to spontaneously generate electrical impulses that cause its muscle to contract.
Sino-atrial (SA) Node
Sino-atrial (SA) Node
The pacemaker of the heart, where the electrical signal for contraction begins.
Gap Junctions
Gap Junctions
Structures that allow the electrical signal to quickly spread from one heart cell to the next.
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
Signup and view all the flashcards
Purkinje Fibers
Purkinje Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
Signup and view all the flashcards
P-wave (ECG)
P-wave (ECG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
QRS complex (ECG)
QRS complex (ECG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrous Ring
Fibrous Ring
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Conduction Fibers
Cardiac Conduction Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the QRS complex represent on an ECG?
What does the QRS complex represent on an ECG?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the AV node?
What is the purpose of the AV node?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the T-wave?
What is the T-wave?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the QT interval represent?
What does the QT interval represent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the P-wave?
What is the P-wave?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the P-Q segment?
What is the P-Q segment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Conduction System
Cardiac Conduction System
Signup and view all the flashcards
SA Node
SA Node
Signup and view all the flashcards
AV Node
AV Node
Signup and view all the flashcards
ECG: What does the P-wave represent?
ECG: What does the P-wave represent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
ECG: What does the QRS complex represent?
ECG: What does the QRS complex represent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Heart Conduction System
- Simultaneous atrial and ventricular contraction is crucial for proper cardiac function.
- Cardiac muscle has autorhythmicity, meaning it can self-depolarize and contract without external stimuli.
- Sino-atrial (SA) node initiates depolarization, spreading in all directions towards the left side, enabling rapid conduction.
- Depolarization spreads through gap junctions between cardiac muscle cells.
- Fibrous rings isolate atrial and ventricular electrical activity.
- Atrioventricular (AV) node is the only electrical pathway allowing atrial activity to influence ventricles.
- Signals from the AV node are then conducted through the AV bundle, right and left bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers.
- Purkinje fibers rapidly conduct the signal throughout the ventricular myocardium.
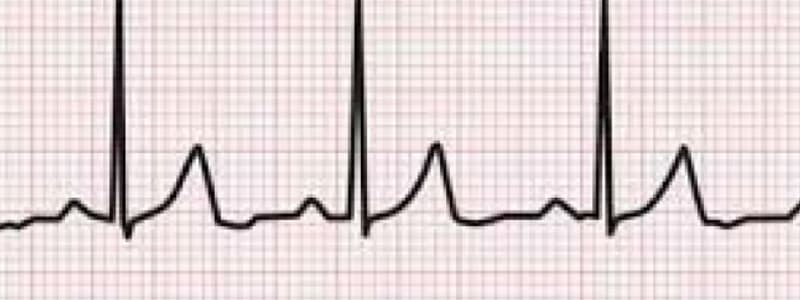
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- ECG measures electrical activity during depolarization and repolarization, detectable at the skin surface.
- Body fluids' high conductivity facilitates detection.
- Three electrodes (right wrist, left wrist, and left leg) are used for lead I.
- Lead I measures the potential difference between two points on the body.
- Positive (red) electrode on the left leg, negative (white) on the right wrist.
- P wave: atrial depolarization.
- PR interval: delay from SA node activity to ventricular excitation.
- QRS complex: ventricular depolarization.
- T wave: ventricular repolarization.
- QT interval: from the start of QRS to end of T, representing ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.