Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the normal angle of the carrying angle in males?
What is the normal angle of the carrying angle in males?
- 5 degrees (correct)
- 15 degrees
- 20 degrees
- 10 degrees
What could be a reason for uneven contours of the clavicles?
What could be a reason for uneven contours of the clavicles?
- Elevated shoulders
- Mal-alignment of a fracture (correct)
- Muscle imbalances
- Normal posture
What is the normal position of the anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS) of the pelvis?
What is the normal position of the anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS) of the pelvis?
- Uneven
- Level (correct)
- Higher on the right side
- Lower on the left side
What is the result of a lateral tilt in the pelvis?
What is the result of a lateral tilt in the pelvis?
What is the normal angle of the carrying angle in females?
What is the normal angle of the carrying angle in females?
What could be a result of an abnormal carrying angle?
What could be a result of an abnormal carrying angle?
What could cause a shift of the thorax?
What could cause a shift of the thorax?
What should be observed in the clavicles?
What should be observed in the clavicles?
What is the main effect of a forward head posture on the cervical extensor muscles?
What is the main effect of a forward head posture on the cervical extensor muscles?
What is the result of an exaggerated lordotic curve in the cervical spine?
What is the result of an exaggerated lordotic curve in the cervical spine?
What is associated with a kyphotic posture?
What is associated with a kyphotic posture?
What is a common feature of a slumped position?
What is a common feature of a slumped position?
What is associated with a retracted shoulder posture?
What is associated with a retracted shoulder posture?
What can be a cause of a protracted shoulder on one side of the body?
What can be a cause of a protracted shoulder on one side of the body?
What is the effect of a forward head posture on the neck?
What is the effect of a forward head posture on the neck?
Which muscle groups may be lengthened in a person with a kyphotic posture?
Which muscle groups may be lengthened in a person with a kyphotic posture?
What is the effect of a kyphotic posture on the thoracic spine extensors and middle and lower fibers of the trapezius?
What is the effect of a kyphotic posture on the thoracic spine extensors and middle and lower fibers of the trapezius?
What can be a natural consequence of pregnancy or a result of increased lumbar lordosis?
What can be a natural consequence of pregnancy or a result of increased lumbar lordosis?
What is suggested by an internally rotated humerus?
What is suggested by an internally rotated humerus?
What can be compressed in the lumbar spine as a result of increased lordosis?
What can be compressed in the lumbar spine as a result of increased lordosis?
What can be a result of restrictions in the muscles and fascia of the chest?
What can be a result of restrictions in the muscles and fascia of the chest?
What can be associated with shortened pectorals, tight intercostals, and shallow breathing?
What can be associated with shortened pectorals, tight intercostals, and shallow breathing?
What can be a characteristic of clients with increased flexibility or hypermobility syndromes?
What can be a characteristic of clients with increased flexibility or hypermobility syndromes?
What can be a consequence of regularly performing an activity that involves external rotation on one side of the body?
What can be a consequence of regularly performing an activity that involves external rotation on one side of the body?
What happens to the lumbar spine when the pelvis tilts anteriorly?
What happens to the lumbar spine when the pelvis tilts anteriorly?
What is a characteristic of a client with hyperextended knees?
What is a characteristic of a client with hyperextended knees?
What may prevent full extension of the knee joint?
What may prevent full extension of the knee joint?
What is a possible consequence of tight quadriceps in a client with hyperextended knees?
What is a possible consequence of tight quadriceps in a client with hyperextended knees?
What happens to the pelvis when the lumbar lordosis is decreased?
What happens to the pelvis when the lumbar lordosis is decreased?
What is associated with a flexed knee position?
What is associated with a flexed knee position?
What is associated with an anteriorly tilted pelvis?
What is associated with an anteriorly tilted pelvis?
What is the relationship between the pelvis and lumbar spine?
What is the relationship between the pelvis and lumbar spine?
What is the characteristic of genu valgum?
What is the characteristic of genu valgum?
What happens to the muscles in genu valgum?
What happens to the muscles in genu valgum?
What is the characteristic of pes planus?
What is the characteristic of pes planus?
What is the possible cause of feet turned out in a ballet-type stance?
What is the possible cause of feet turned out in a ballet-type stance?
What is the characteristic of genu varum?
What is the characteristic of genu varum?
What happens to the muscles in genu varum?
What happens to the muscles in genu varum?
What is the characteristic of pes cavus?
What is the characteristic of pes cavus?
What is the possible cause of feet turned inwards?
What is the possible cause of feet turned inwards?
Study Notes
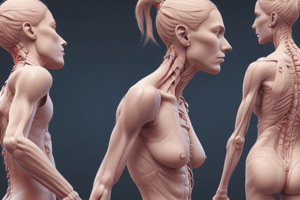
Head Position
- A forward head posture affects the neck, chest, and arms, with the head positioned too far in advance of the body.
- Cervical extensor muscles, such as the levator scapulae, are lengthened and weak, rather than shortened and tight.
- This posture increases the strain on posterior cervical soft tissues, potentially leading to neck, shoulder, and upper back pain.
Cervical Spine
- An exaggerated lordotic curve in the cervical spine often accompanies a kyphotic posture.
- This increases compression on the posterior part of some cervical intervertebral discs and may compress the zygapophyseal joints.
Thoracic Spine
- A kyphotic posture is associated with an exaggerated kyphosis in the thoracic spine, reducing the thoracic cavity.
- This leads to shortened intercostals, pectoralis minor, adductors, and internal rotators of the shoulders.
- Muscles often weak in a kyphotic posture include the thoracic spine extensors and the middle and lower fibers of the trapezius.
Shoulder Position
- Protraction of the shoulders (slumped position) is associated with lengthened and weak rhomboids, tight pectorals, and shortened intercostals.
- Retracted shoulders are associated with shortness in the rhomboid muscles and in the middle fibers of the trapezius, and some parts of the pectoralis major may be lengthened.
- An internally rotated humerus suggests shortness in the muscles of medial rotation, while an externally rotated humerus suggests shortness in muscles such as the infraspinatus and teres minor.
Thorax
- A severely kyphotic posture is associated with shortened pectorals, tight intercostals, and perhaps even shallow breathing due to a depressed chest cavity.
- Thoracic spine extensors, the middle and lower fibers of the trapezius, and the rhomboids may be lengthened and weak.
Abdomen
- Protrusion of the abdomen could be a natural consequence of pregnancy or the result of increased lumbar lordosis, or it could simply be excess adipose tissue due to being overweight.
- Clients with restrictions in the muscles and fascia of the chest may appear to have a protruding abdomen, with a distinct change in shape from the chest area.
Lumbar Spine
- An increased lordotic curve indicates an anteriorly tilted pelvis, potentially leading to pain resulting from compression of soft tissues in this region.
- The correct functioning of the zygapophyseal joints in the lumbar spine may also be compromised if they are compressed.
- The rectus abdominis may be longer and therefore weaker than usual, as may the hip extensors, whereas the muscles responsible for lumbar extension may be shortened.
Pelvis
- An anteriorly tilted pelvis is associated with lengthened but weak hamstrings, plus a lengthened rectus abdominis.
- The psoas may be shortened, and there may be shortened rectus femoris, too.
- A posteriorly tilted pelvis is associated with tightness in the hip extensors and longer, and perhaps weakened, hip flexor muscles.
Knees
- Flexed knees are associated with tight hamstrings and popliteus muscles and weak quadriceps and soleus muscles.
- A flexed knee may accompany an increase in flexion at the hip and an increase in dorsiflexion at the ankle joint.
- Certain pathologies affecting the knee inhibit extension of the joint, while hypermobile clients may hyperextend their knees in standing.
Feet
- Foot arches can appear normal, dropped, or elevated.
- Foot position can be affected by external rotation at the hip joint, lateral tibial torsion, or both.
Anterior Postural Assessment
- Clavicles should have smooth contours and be gently angled upwards away from the sternoclavicular joint.
- Sharply angled clavicles indicate elevated shoulders.
- Uneven contours could indicate a fracture that has healed in mal-alignment or a more recent injury.
Chest
- The thorax may shift laterally or rotate relative to the neck and pelvis.
- Shifts of the chest occur for many reasons, including lateral curvatures in the spine and muscle imbalances.
- When the thorax rotates, compensatory changes occur in the neck and lumbar spine.
Carrying Angle
- The carrying angle is the angle formed between the long axis of the humerus and the long axis of the forearm.
- A normal carrying angle is 5 degrees in males and 10-15 degrees in females.
- An abnormal carrying angle can affect a person's ability to bear weight through the upper limb.
Lateral Pelvis
- The anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS) of the pelvis should be level.
- A lateral tilt in the pelvis corresponds with a lateral curve in the lumbar spine.
Rotated Pelvis
- A rotated pelvis can lead to increased pressure on the lateral or medial side of the foot.
Genu Valgum and Genu Varum
- In genu valgum, there is increased pressure on the lateral side of the knee joint, leading to degenerative changes on that side of the knee.
- In genu varum, there is increased pressure on the medial side of the knee joint.
- Structurally, genu valgum is associated with shorter muscles of the lateral thigh, while genu varum is associated with shorter muscles of the medial thigh.
Foot Position
- Feet turned out in a ballet-type stance could result from external rotation at the hip joint, lateral tibial torsion, or both.
- External hip rotation could indicate shortening of the gluteus maximus and the posterior fibers of the gluteus medius, along with the iliotibial band.
- A client who stands with their feet turned inwards (pigeon-toed) may have shortened internal rotators of the hip, a medially rotated tibia, or both.
Pes Planus and Pes Cavus
- In pes planus, the medial side of the foot might even be touching the floor completely, leaving no gap at all.
- In pes cavus, there will be a greater-than-normal space between the floor and the medial side of the foot.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz assesses your understanding of forward head posture, its effects on the neck, chest, and arms, and the implications on cervical extensor muscles.