Podcast
Questions and Answers
What structures separate the lateral supratentorial compartments in the cranium?
What structures separate the lateral supratentorial compartments in the cranium?
- Arachnoid granulations
- Falx cerebelli (correct)
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Pia mater
How are dural sinuses formed?
How are dural sinuses formed?
- By separation of falx cerebri from the cranium
- By separation of the meningeal and periosteal dura at the tentorium cerebelli
- By joining of two layers of arachnoid mater
- By joining of two layers of meningeal dura at the free edges of dural septa (correct)
Which artery is a primary example of vessels that run between the periosteum and periosteal dura in the cranium?
Which artery is a primary example of vessels that run between the periosteum and periosteal dura in the cranium?
- Basilar artery
- Internal jugular artery
- Vestibulocochlear artery
- Middle meningeal artery (correct)
Where does the blood collect in the dural sinuses from?
Where does the blood collect in the dural sinuses from?
What can disrupt the middle meningeal artery and lead to dissection of connective tissue layers?
What can disrupt the middle meningeal artery and lead to dissection of connective tissue layers?
What forms an area of reduced adherence between the dura and the arachnoid?
What forms an area of reduced adherence between the dura and the arachnoid?
Which structure consists of areas where the meningeal portion of the dura folds inward to separate the cranial cavity into compartments?
Which structure consists of areas where the meningeal portion of the dura folds inward to separate the cranial cavity into compartments?
What can dissect the plane of weakness between the dura mater and arachnoid, leading to a subdural hematoma?
What can dissect the plane of weakness between the dura mater and arachnoid, leading to a subdural hematoma?
What restricts the movement of the brain in the cranial cavity by separating it into compartments?
What restricts the movement of the brain in the cranial cavity by separating it into compartments?
Which structure is responsible for adding some support but also restricting brain movement in compartments within the cranial cavity?
Which structure is responsible for adding some support but also restricting brain movement in compartments within the cranial cavity?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater?
The pia mater is derived from which of the following meningeal layers?
The pia mater is derived from which of the following meningeal layers?
In the spinal cord, what is the relationship between the meningeal dura and the vertebral periosteum?
In the spinal cord, what is the relationship between the meningeal dura and the vertebral periosteum?
What is the function of arachnoid granulations?
What is the function of arachnoid granulations?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the composition of the meningeal layers?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the composition of the meningeal layers?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
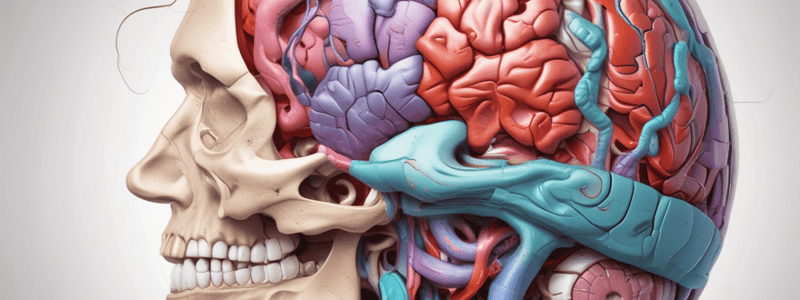
Dural Compartments
- The dural septi form compartments in the cranial cavity, including lateral supratentorial compartments separated by the falx cerebri and an infratentorial compartment bordered by the tentorium cerebelli.
- These rigid compartments limit the expansion of cranial contents and an expanding mass can push contents between compartments.
Dural Sinuses
- Dural sinuses are venous structures formed by two mechanisms: separation of meningeal and periosteal dura at junctions with the skull, and joining of two layers of meningeal dura at the free edges of dural septa.
- Blood collects in dural sinuses from connecting veins from the cortical surface and internal structures.
Dura-Blood Supply
- The vascular supply for the dura in the cranium originates from several branches of the internal carotid artery.
- In the spinal cord, the supply is from multiple sources located close to the vertebral column.
- Vessels in the cranium run between the periosteum and the periosteal dura, often in grooves on the skull.
- The middle meningeal artery is a primary example.
Skull Fractures and Hematomas
- Skull fractures can disrupt arteries, producing dissection of the connective tissue layers and an expanding, space-occupying hematoma (epidural hematoma).
Meningeal Relationships
- In adults, the meninges consist of three primary layers from the skull inward: dura mater (pachymeninx), arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
- These layers consist of fibroblasts and extracellular collagen in various orientations and densities.
Dura Mater
- The ectomeninx eventually divides into periosteal (endosteal) dura (outer layer) and meningeal dura (inner layer).
- In the spinal cord, the ectomeninx is initially continuous with the vertebral periosteum during development, but later separates, leaving an epidural space between the vertebral periosteum and the meningeal dura.
Dural Border Cell Area
- The dural border cell area between the dura and arachnoid is a third, thinner and weaker dural layer.
- This layer forms an area of reduced adherence between the dura and the arachnoid and a potential space.
Bleeding and Hematomas
- Bleeding, typically by a cerebral vein, can dissect the plane of weakness between the dura mater and the arachnoid (subdural hematoma).
- When the brain is removed from a cadaver, the arachnoid may split away from the dura at this layer.
Dural Septa
- The dura has extensions directed away from the skull into the cranial cavity, forming compartments that restrict the movement of the brain.
- Injuries such as an expanding lesion or bleeding can force areas of the brain between compartments.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.