Podcast
Questions and Answers
What color do Gram-positive bacteria typically stain during the Gram staining process?
What color do Gram-positive bacteria typically stain during the Gram staining process?
- Purple (correct)
- Green
- Yellow
- Pink
Which component is primarily responsible for the purple coloration in Gram-positive bacteria after staining?
Which component is primarily responsible for the purple coloration in Gram-positive bacteria after staining?
- Peptidoglycan (correct)
- Lipoproteins
- Phospholipids
- Teichoic acid
What is the main purpose of using stains in microscopy?
What is the main purpose of using stains in microscopy?
- To make bacteria visible (correct)
- To increase bacteria growth
- To kill the bacteria
- To alter bacteria structure
Which type of stain has a negative charge and is used for staining backgrounds?
Which type of stain has a negative charge and is used for staining backgrounds?
Which statement accurately describes differential staining?
Which statement accurately describes differential staining?
What is the purpose of using a basic stain in bacterial staining?
What is the purpose of using a basic stain in bacterial staining?
What is the primary characteristic of Gram-positive bacteria compared to Gram-negative bacteria?
What is the primary characteristic of Gram-positive bacteria compared to Gram-negative bacteria?
Which method would you use to prepare a smear from solid media?
Which method would you use to prepare a smear from solid media?
What distinguishes differential staining from simple staining?
What distinguishes differential staining from simple staining?
What is the appearance of Gram-negative bacteria after Gram staining?
What is the appearance of Gram-negative bacteria after Gram staining?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
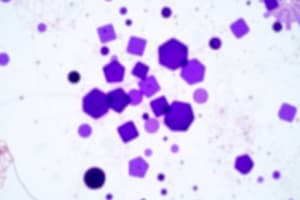
Gram Stain
- Gram stain was developed by Christian Gram in 1884 to stain bacteria in tissues.
- Gram-positive bacteria stain purple, while Gram-negative bacteria stain pink.
- The differences in staining are due to the structural differences in their cell walls.
- Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer and large amounts of teichoic acid.
- Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane made of phospholipids, lipopolysaccharides, lipoproteins, and proteins.
- Gram-negative bacteria are decolorized by alcohol.
- Gram-positive bacteria retain the initial stain (crystal violet) after decolorization.
- The counterstain (safranin) gives Gram-negative bacteria a pink/red appearance.
Staining
- Staining is used to enhance contrast in microscopic images.
- Stains are classified based on their charge:
- Basic stains have a positive charge and are used to stain negatively charged molecules like bacterial cell surfaces.
- Acidic stains have a negative charge and are used to stain positively charged molecules like bacterial capsules.
- Neutral stains have both charges.
- Stains are also classified based on their function:
- Simple staining uses one dye and does not differentiate between bacteria.
- Differential staining uses more than one dye and differentiates between bacteria based on their cell wall structure (e.g., Gram stain).
- Special staining uses more than one dye and visualizes specific structures like capsules or spores.
Preparing Smears
- For liquid media:
- Sterilize a loop with a Bunsen flame.
- Cool the loop.
- Withdraw a loopful of broth culture.
- Spread the broth culture evenly on a clean slide to form a thin film.
- Sterilize the loop.
- Allow the smear to air dry.
- Fix the smear by passing it through a Bunsen flame 3-4 times.
- Allow the slide to cool before staining.
- For solid media:
- Sterilize a loop with a Bunsen flame.
- Cool the loop.
- Place a loopful of clean water on a clean slide.
- Sterilize the loop again.
- Transfer a small portion of bacterial growth to the water on the slide.
- Mix the growth with water thoroughly and spread evenly on the slide.
- Allow the smear to air dry.
- Fix the smear by passing it through a Bunsen flame 3-4 times.
- Allow the slide to cool before staining.
Simple Staining
- This procedure uses a single basic dye like crystal violet, methylene blue, or safranin to stain bacteria.
- Bacteria will simply take on the color of the dye.
Differential Staining
- This procedure uses more than one dye solution.
- The dyes are added in multiple steps according to the procedure.
- Gram staining is used to stain bacteria.
- It helps differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.