Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a common physical manifestation of chronic tophaceous gout?
What is a common physical manifestation of chronic tophaceous gout?
- Punched out lesions with overhanging edges (correct)
- Symmetrical joint swelling
- Redness and swelling of the entire joint
- Cyst formation in surrounding tissue
Which of the following is considered a primary cause of gout due to overproduction?
Which of the following is considered a primary cause of gout due to overproduction?
- High protein diet (correct)
- Genetic predisposition (correct)
- Use of diuretics
- Chronic kidney disease
Which condition is commonly differentiated from acute gout through synovial fluid analysis?
Which condition is commonly differentiated from acute gout through synovial fluid analysis?
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Pseudogout
- Septic arthritis (correct)
- Osteoarthritis
What is an appropriate first-line treatment option for acute gout if there are no contraindications?
What is an appropriate first-line treatment option for acute gout if there are no contraindications?
What dietary component is specifically encouraged to be avoided to manage gout?
What dietary component is specifically encouraged to be avoided to manage gout?
Which of the following is NOT an indication for urate lowering treatment in gout management?
Which of the following is NOT an indication for urate lowering treatment in gout management?
Which urate lowering drug does NOT require dose reduction in cases of renal impairment?
Which urate lowering drug does NOT require dose reduction in cases of renal impairment?
What factor is most closely associated with underexcretion in the pathophysiology of gout?
What factor is most closely associated with underexcretion in the pathophysiology of gout?
In the treatment of chronic gout, which lifestyle modification is specifically recommended?
In the treatment of chronic gout, which lifestyle modification is specifically recommended?
How should colchicine be administered in patients with acute gout?
How should colchicine be administered in patients with acute gout?
Flashcards
What is Gout?
What is Gout?
Gout is a painful inflammatory condition caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in joints, most commonly affecting the big toe.
Who does Gout affect?
Who does Gout affect?
Gout usually occurs in males, especially older men. It can also happen in women, but is less common.
How does Gout happen?
How does Gout happen?
The accumulation of uric acid in joints can be caused by either the body producing too much uric acid, not getting rid of it properly, or a combination of the two.
What is Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia?
What is Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
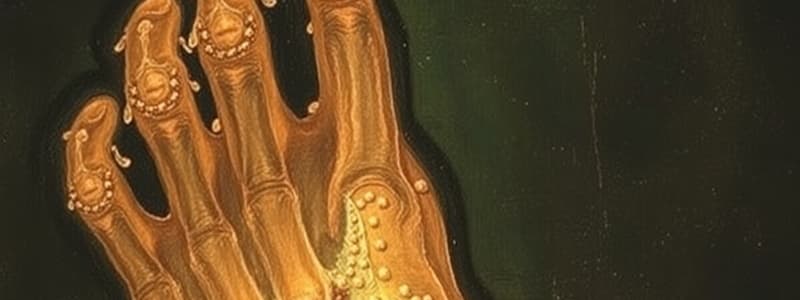
What is Chronic Tophaceous Gout?
What is Chronic Tophaceous Gout?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Acute Gout?
What is Acute Gout?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the intercritical period?
What is the intercritical period?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is acute gout treated?
How is acute gout treated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Urate Lowering Drugs (ULTs)?
What are Urate Lowering Drugs (ULTs)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the two main types of Urate Lowering Drugs?
What are the two main types of Urate Lowering Drugs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Crystal-Associated Arthritis
- Gout
- More common in males
- Can occur in older men, but younger men can also be affected
- Associated with ankylosing spondylitis in some cases
- Causes of Gout
- Overproduction of uric acid
- Acquired
- Dietary factors (hematological, psoriatic, chemotherapy diseases)
- Inherited
- Underexcretion of uric acid
- Renal (90%)
- Combination of overproduction and underexcretion
- Alcohol is a contributing factor
- Uric acid overproduction/underexcretion
- Overproduction of uric acid
Stages of Gout
- Asymptomatic hyperuricemia: no need for treatment
- Acute gout
- Intercritical period: Asymptomatic periods between attacks
- Chronic tophaceous gout: Deformities and bone erosions
- Punched-out appearance with overhanging edges
- Acute gout presentation: Acute monoarthritis (commonly in the first metatarsophalangeal joint)
- Differential diagnosis (DDX): Septic arthritis (differentiation through synovial fluid aspiration with polarized microscopy)
- Findings on microscopy: Needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals
- Treatment of acute gout
- NSAIDs (if no contraindications)
- Colchicine (contraindicated in renal impairment and statin use)
- Steroids (avoid in DM)
- Local steroid injection
- Anakinra (IL-1 agonist)
Treatment of Chronic Gout
- Lifestyle modification (diet)
- Urate-lowering drugs (5 indications)
- Education
- Correction of predisposing factors
- Avoiding hyperuricemic drugs
- Thiazide diuretics
- Loop diuretics (furosemide)
- Niacin (B3)
- Low doses of aspirin
- Foods to avoid
- All meats
- Seafood
- Meat extracts
- Yeast extracts
- Beans
- Lentils
- Peas
- Oats
- Spinach
- Asparagus
- Cauliflower
- Mushrooms
Indications for Urate-Lowering Treatment (ULT)
-
Frequent flares (more than 2-3 flares per year)
-
Renal stones
-
Tophaceous gout (detected on radiographs)
-
Moderate-to-severe CKD
-
Evidence of bone or joint damage
-
The risk of flares can be reduced by using prophylaxis like NSAIDs during the first few months following diagnosis
Urate-lowering drugs
- Allopurinol (available and cheap)
- Febuxostat (no need for dose reduction, Hypersensitivity reaction possible)
- Side effects of Allopurinol (Xanthine oxidase inhibitors)
- Dose Reduction due to renal function test (RFT)
- Uricosuric drugs
- Contraindicated in renal stones and overproducers/renal impairment.
- Uricase (IV)
- Pegloticase (expensive and used in refractory cases)
CPPD (Chondrocalcinosis)
- Causes
- Idiopathic, closely related to osteoarthritis (OA)
- Genetic mutation (early onset CPPD)
- Secondary to other conditions
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Lipomaquesemia
- Hypophosphatemia
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson's disease
- Presentation
- Asymptomatic
- Acute pseudogout (most common)
- Chronic pseudo-RA (knee and wrist, monoarticular in 89%)
- Chronic pseudo-OA
- Diagnosis
- Synovial fluid aspiration under polarized microscopy (Rhomboid shape and positive birefringence)
- X-ray shows chondrocalcinosis (calcium pyrophosphate deposition)
- Knee meniscus
- Wrist triangular
Treatment of Pseudogout
-
Same as acute gout treatment, plus treatment of the underlying cause
-
NSAIDs (if no contraindications)
-
Colchicine (not given in renal impairment and statin use)
-
Steroids (avoid in DM)
-
Local steroid injection(s)
-
Anakinra (IL-1 agonist)
-
Problem in pseudogout: Calcium not uric acid
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.