Podcast
Questions and Answers
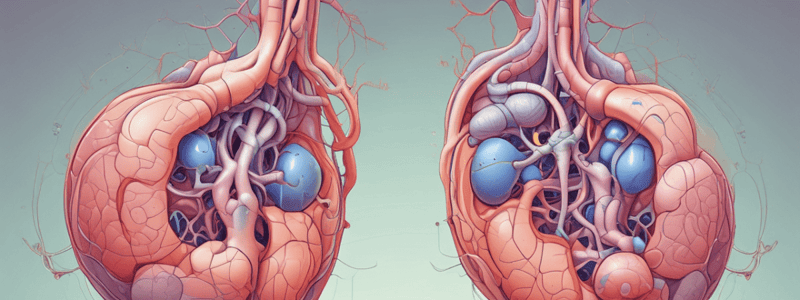
What is the function of smooth muscles in the glomerulus?
What is the function of smooth muscles in the glomerulus?
To regulate blood flow to each glomerulus by closing or opening the afferent and efferent arterioles, thereby adjusting the glomerular filtration rate.
What is the composition of the ultrafiltrate formed in the glomerulus?
What is the composition of the ultrafiltrate formed in the glomerulus?
Water, ions, and small molecules.
What is the purpose of the proximal convoluted tubule in the nephron?
What is the purpose of the proximal convoluted tubule in the nephron?
To add and remove specific substances from the ultrafiltrate.
What is the primary function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
What is the final product of the nephron's processing of the ultrafiltrate?
What is the final product of the nephron's processing of the ultrafiltrate?
What is the significance of the glomerular filtration rate in the kidney?
What is the significance of the glomerular filtration rate in the kidney?
What is the primary function of solutes in the context of body fluids?
What is the primary function of solutes in the context of body fluids?
What is the process called when water moves from an area of high potential to an area of lower potential?
What is the process called when water moves from an area of high potential to an area of lower potential?
What is the approximate solute concentration of seawater in millimoles per kilogram of water?
What is the approximate solute concentration of seawater in millimoles per kilogram of water?
Why do cartilaginous fishes retain urea and other nitrogen-containing compounds in their bodies?
Why do cartilaginous fishes retain urea and other nitrogen-containing compounds in their bodies?
What is the term used to describe the state of body fluids that are in equilibrium with seawater?
What is the term used to describe the state of body fluids that are in equilibrium with seawater?
Why do water flows outward from the blood of marine teleosts and lampreys to the sea?
Why do water flows outward from the blood of marine teleosts and lampreys to the sea?
The ultrafiltrate passes from the glomerular capsule into the ______ convoluted tubule.
The ultrafiltrate passes from the glomerular capsule into the ______ convoluted tubule.
The glomerulus is composed of a leaky ______ capillary tuft encapsulated within a sievelike filter.
The glomerulus is composed of a leaky ______ capillary tuft encapsulated within a sievelike filter.
Blood pressure forces an ultrafiltrate of the blood through the walls of the ______ into the lumen of the glomerular capsule.
Blood pressure forces an ultrafiltrate of the blood through the walls of the ______ into the lumen of the glomerular capsule.
The ultrafiltrate is composed of ______, ions, and small molecules.
The ultrafiltrate is composed of ______, ions, and small molecules.
The blood flow to each glomerulus is regulated by ______ muscles that can close off the afferent and efferent arterioles.
The blood flow to each glomerulus is regulated by ______ muscles that can close off the afferent and efferent arterioles.
The fluid that remains after this processing is ______.
The fluid that remains after this processing is ______.
It is likely that the first vertebrates also had ion levels similar to those in ______.
It is likely that the first vertebrates also had ion levels similar to those in ______.
The presence of solutes lowers the potential activity of ______.
The presence of solutes lowers the potential activity of ______.
In the context of body fluids, a ______ is a small molecule that is dissolved in water or blood plasma.
In the context of body fluids, a ______ is a small molecule that is dissolved in water or blood plasma.
Water moves from areas of high potential to areas of lower potential; therefore, water flows from a ______ solution to a more concentrated solution.
Water moves from areas of high potential to areas of lower potential; therefore, water flows from a ______ solution to a more concentrated solution.
Most marine invertebrates and hagfishes have body fluids that are in ______ equilibrium with seawater.
Most marine invertebrates and hagfishes have body fluids that are in ______ equilibrium with seawater.
Cartilaginous fishes retain ______ and other nitrogen-containing compounds, raising the osmolality of their blood slightly above that of seawater.
Cartilaginous fishes retain ______ and other nitrogen-containing compounds, raising the osmolality of their blood slightly above that of seawater.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying