Podcast
Questions and Answers
What was the evidence presented for the existence of Pangaea?
What was the evidence presented for the existence of Pangaea?
Presented evidence that Pangaea really existed.
Which of the following are major crustal plates? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following are major crustal plates? (Select all that apply)
- Indo-Australian (correct)
- Eurasian (correct)
- Nazca
- Juan de Fuca
Match the following types of crustal plates to their categories:
Match the following types of crustal plates to their categories:
African = Primary Plate Caribbean = Secondary Plate Pacific = Primary Plate Cocos = Secondary Plate
Where is the Sandwich Islands located?
Where is the Sandwich Islands located?
Which of the following oceans separates the Panthalassa Ocean from the Tethys Sea?
Which of the following oceans separates the Panthalassa Ocean from the Tethys Sea?
What are the two types of lithosphere?
What are the two types of lithosphere?
Which rocks are primarily found in the oceanic crust?
Which rocks are primarily found in the oceanic crust?
Who proposed the Continental Drift Theory?
Who proposed the Continental Drift Theory?
Seismic tomography records only anomalies in the oceanic regions.
Seismic tomography records only anomalies in the oceanic regions.
The 'Sandwich Islands' is an old name for the _____ Islands.
The 'Sandwich Islands' is an old name for the _____ Islands.
What keeps tectonic plates in motion according to the Slab Pull Theory?
What keeps tectonic plates in motion according to the Slab Pull Theory?
What is the significance of mantle convection in tectonic plate movement?
What is the significance of mantle convection in tectonic plate movement?
Which of the following is considered a primary tectonic plate?
Which of the following is considered a primary tectonic plate?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
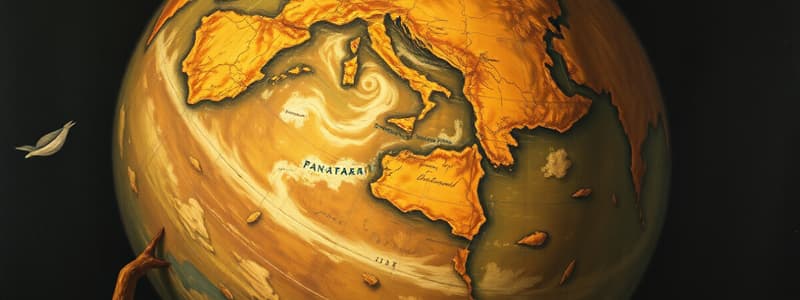
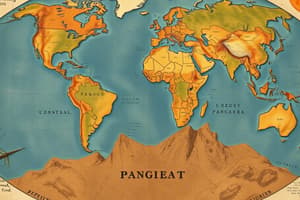
Pangaea and Geological Evidence
- Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed, supported by geological evidence.
- The sequence of continental formations evolved from Rodinia to Pangaea, then divided into Laurasia and Gondwanaland.
- Panthalassa, the vast ocean surrounding Pangaea, and the Tethys Sea acted as major dividing bodies of water.
Crustal Plates
- Earth has over 71 major crustal plates, which include both primary and secondary classifications.
Primary Plates
- African Plate: Covers Africa and parts of the Atlantic Ocean.
- Eurasian Plate: Extends from Europe to Asia, including the area of the Arctic Ocean.
- Indo-Australian Plate: Encompasses India, Australia, and parts of the Indian Ocean.
- North American Plate: Covers North America and extends into the North Atlantic.
- Pacific Plate: The largest tectonic plate, located beneath the Pacific Ocean.
- South American Plate: Covers South America and part of the southeastern Pacific Ocean.
- Nazca Plate: Located off the western coast of South America, often categorized as primary.
Secondary Plates
- Caribbean Plate: Located north of South America, affecting the Caribbean region.
- Nazla Plate: A tertiary designation often associated with tectonics in the Nazca region.
- Philippine Sea Plate: Situated east of the Philippines, impacting local seismic activity.
- Arabian Plate: Covers the Arabian Peninsula, influencing Middle Eastern geology.
- Cocos Plate: Located off the western coast of Central America.
- Scotia Plate: Found between South America and Antarctica, influencing the southern ocean.
- Juan de Fuca Plate: A small plate off the Pacific Northwest, involved in seismic activity.
Sandwich Islands
- The term "Sandwich Islands" is historically attributed to the Hawaiian Islands, situated in the Central Pacific Ocean.
- A separate location with the same name, the South Sandwich Islands, is found near Antarctica in the Southern Atlantic Ocean.
Lithospheric Plates
- Earth’s lithosphere consists of continental and oceanic sections.
- Platforms are areas characterized by new geological formations.
- Basement rocks are the older, foundational rocks beneath the surface.
- Formations refer to cones of volcanic and sedimentary rocks.
- Continental margins are the edges of continents that shift due to plate movements.
- Oceanic crust is primarily composed of basalt and gabbro rocks.
Seismic Tomography
- Seismic tomography creates a "map" to record earth's movements.
- It captures data indicating anomalies beneath the Earth's surface.
Mantle Convection Theory
- This theory explains heat transfer within the Earth’s mantle.
- Heat causes plates to open and shift due to pressure.
- Plates drift in opposite directions as a result of thermal convection.
Slab Pull Theory
- Plate movements are influenced by gravity and subduction of older rocks.
- As older rocks submerge, they create new mountains.
Plate Movement Causes
- Mantle convection drives the movement of tectonic plates.
- Conducting a convection experiment resembles mantle flow using water and food coloring.
Crustal Plates
- The Earth comprises 56 plates, with 15 classified as major tectonic plates.
- Major tectonic plates include Malawak, African, Eurasian, Indo-Australian, North American, Pacific, South American, and sometimes Nazca.
- Secondary plates encompass Oati Langs, Caribbean, Nazca, Philippine Sea, Arabian, Colos, Scotia, and Juan de Fuca.
Tethys Sea
- The Tethys Sea historically separated land masses before the formation of modern continents.
Sandwich Islands
- The "Sandwich Islands" refers to the Hawaiian Islands in the Central Pacific.
- A separate group known as the South Sandwich Islands is located near Antarctica in the Southern Atlantic Ocean.
Plate Tectonics
- The Earth is considered a "fluid of life" due to dynamic continent movements.
- Plate tectonics is linked to volcanic activity and massive earthquakes.
Understanding Through Plate Tectonics
- Studying plate tectonics enhances understanding of Earth's dynamic processes.
- The origin of the term "tectonic" comes from the Greek word "Tekton," meaning carpenter or builder.
Tectonic Plates
- Tectonic plates are perpetually in motion and interact with the asthenosphere.
Continental Drift Theory
- Proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1915, this theory discusses the origins of continents and oceans.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.