Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic primarily distinguishes continental crust from oceanic crust?
Which characteristic primarily distinguishes continental crust from oceanic crust?
- Density and mineral composition (correct)
- Location relative to sea level
- Proximity to the Earth's core
- Temperature at the deepest parts
What is the typical range of thickness for continental crust?
What is the typical range of thickness for continental crust?
- 15 to 25 kilometers
- 30 to 50 kilometers (correct)
- 60 to 80 kilometers
- 5 to 10 kilometers
Which of the following is a major component of felsic rock commonly found in continental crust?
Which of the following is a major component of felsic rock commonly found in continental crust?
- Feldspar (correct)
- Peridotite
- Pyroxene
- Olivine
Compared to oceanic crust, continental crust has a higher concentration of which element?
Compared to oceanic crust, continental crust has a higher concentration of which element?
At what geological setting is continental crust most commonly formed?
At what geological setting is continental crust most commonly formed?
What is the Mohorovicic discontinuity?
What is the Mohorovicic discontinuity?
Which property of seismic waves is most useful in determining the state of matter within Earth's mantle?
Which property of seismic waves is most useful in determining the state of matter within Earth's mantle?
Although primarily solid, the mantle exhibits properties of a viscous liquid over geological timescales due to:
Although primarily solid, the mantle exhibits properties of a viscous liquid over geological timescales due to:
What is the asthenosphere?
What is the asthenosphere?
The Gutenberg discontinuity marks the boundary between which two layers of the Earth?
The Gutenberg discontinuity marks the boundary between which two layers of the Earth?
Which principle of relative dating states that fossil assemblages are unique to specific geological time periods?
Which principle of relative dating states that fossil assemblages are unique to specific geological time periods?
In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rock layers, where would the oldest fossils generally be located according to the principle of superposition?
In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rock layers, where would the oldest fossils generally be located according to the principle of superposition?
Which type of fossil is formed when minerals replace the original bone or shell material of an organism?
Which type of fossil is formed when minerals replace the original bone or shell material of an organism?
What is the primary difference between relative and absolute dating of fossils?
What is the primary difference between relative and absolute dating of fossils?
What do contour lines on a topographic map connect?
What do contour lines on a topographic map connect?
What are hachures on a topographic map used to indicate?
What are hachures on a topographic map used to indicate?
Which geological process is primarily destructive, leading to the breakdown of existing landforms?
Which geological process is primarily destructive, leading to the breakdown of existing landforms?
What was a key piece of evidence used by Alfred Wegener to support his theory of continental drift?
What was a key piece of evidence used by Alfred Wegener to support his theory of continental drift?
What is the driving force behind the movement of tectonic plates?
What is the driving force behind the movement of tectonic plates?
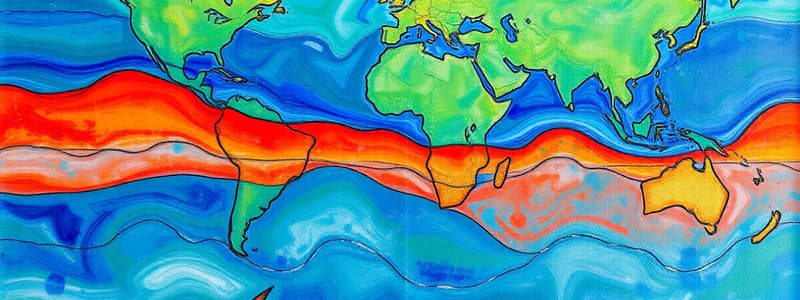
Which type of plate boundary is characterized by tectonic plates moving apart from each other?
Which type of plate boundary is characterized by tectonic plates moving apart from each other?
Which layer of the Earth, based on chemical composition, is directly exposed to the atmosphere?
Which layer of the Earth, based on chemical composition, is directly exposed to the atmosphere?
The Earth's mantle composition is best described as primarily consisting of which type of rock?
The Earth's mantle composition is best described as primarily consisting of which type of rock?
What is the primary driving force behind convection currents in the Earth's mantle?
What is the primary driving force behind convection currents in the Earth's mantle?
Besides convection, which of the following is also a method of heat transfer?
Besides convection, which of the following is also a method of heat transfer?
Which of the following best defines a fossil in the context of paleontology?
Which of the following best defines a fossil in the context of paleontology?
Fossils are most commonly found in which type of rock due to their formation process?
Fossils are most commonly found in which type of rock due to their formation process?
Which type of fossilization process results in the organism's form being preserved as a thin layer of carbon?
Which type of fossilization process results in the organism's form being preserved as a thin layer of carbon?
What is the primary purpose of absolute age dating in geology?
What is the primary purpose of absolute age dating in geology?
Radiocarbon dating is limited in its application to materials younger than approximately how many years?
Radiocarbon dating is limited in its application to materials younger than approximately how many years?
What is the key characteristic of index fossils that makes them useful for correlating rock layers?
What is the key characteristic of index fossils that makes them useful for correlating rock layers?
Where is continental crust primarily located on Earth?
Where is continental crust primarily located on Earth?
How does the thickness of continental crust generally compare to that of oceanic crust?
How does the thickness of continental crust generally compare to that of oceanic crust?
What is the approximate temperature range at the deepest parts of the continental crust?
What is the approximate temperature range at the deepest parts of the continental crust?
Which type of rock is most commonly found in continental crust?
Which type of rock is most commonly found in continental crust?
Compared to oceanic crust, continental crust has a relatively higher concentration of which element?
Compared to oceanic crust, continental crust has a relatively higher concentration of which element?
What geological boundary marks the upper limit of the Earth's mantle, separating it from the crust?
What geological boundary marks the upper limit of the Earth's mantle, separating it from the crust?
In terms of its state of matter, how is the Earth's mantle best described?
In terms of its state of matter, how is the Earth's mantle best described?
What is the primary source of heat that drives convection currents within the Earth's mantle?
What is the primary source of heat that drives convection currents within the Earth's mantle?
Which term describes the ductile and easily deformed portion of the upper mantle?
Which term describes the ductile and easily deformed portion of the upper mantle?
The lithosphere, which is broken into tectonic plates, is composed of which two layers of the Earth?
The lithosphere, which is broken into tectonic plates, is composed of which two layers of the Earth?
Which of the following geological features is most directly associated with a transform plate boundary?
Which of the following geological features is most directly associated with a transform plate boundary?
What is the primary mechanism driving the movement of tectonic plates?
What is the primary mechanism driving the movement of tectonic plates?
In what order are the major tectonic plates listed?
In what order are the major tectonic plates listed?
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of a geological feature located at which type of plate boundary?
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of a geological feature located at which type of plate boundary?
What geological event is described as 'elastic rebound' in the context of earthquakes?
What geological event is described as 'elastic rebound' in the context of earthquakes?
Which of the following is NOT listed as a direct outcome of tectonic plate interaction?
Which of the following is NOT listed as a direct outcome of tectonic plate interaction?
What term is used to describe the fracture in rocks deep underground where movement causes earthquakes?
What term is used to describe the fracture in rocks deep underground where movement causes earthquakes?
What do geologists use to determine that an earthquake has occurred?
What do geologists use to determine that an earthquake has occurred?
How are tectonic plates primarily named?
How are tectonic plates primarily named?
Which of the following best describes the composition of Earth's outer core?
Which of the following best describes the composition of Earth's outer core?
What is the fundamental mechanism driving convection currents within the Earth?
What is the fundamental mechanism driving convection currents within the Earth?
Which statement accurately defines a fossil, according to paleontological standards?
Which statement accurately defines a fossil, according to paleontological standards?
What is the most critical characteristic of index fossils that makes them valuable for correlating rock layers across different geographic locations?
What is the most critical characteristic of index fossils that makes them valuable for correlating rock layers across different geographic locations?
Which of the following absolute age dating methods is LEAST suitable for determining the age of materials older than 100,000 years?
Which of the following absolute age dating methods is LEAST suitable for determining the age of materials older than 100,000 years?
What geological process primarily facilitates the deposition of mantle rock onto the Earth's surface?
What geological process primarily facilitates the deposition of mantle rock onto the Earth's surface?
Edmund Halley's Hollow Earth theory was primarily based on a misinterpretation of which scientific observations and calculations?
Edmund Halley's Hollow Earth theory was primarily based on a misinterpretation of which scientific observations and calculations?
Feeling warmth from a campfire when placing your hand near it is primarily an example of heat transfer through:
Feeling warmth from a campfire when placing your hand near it is primarily an example of heat transfer through:
Fossil formation is most commonly associated with which type of rock due to its formation processes?
Fossil formation is most commonly associated with which type of rock due to its formation processes?
What is the approximate temperature range of the Earth's inner core, located at an average depth of 6470 km?
What is the approximate temperature range of the Earth's inner core, located at an average depth of 6470 km?
Which of the following best describes the primary utility of index fossils in geology?
Which of the following best describes the primary utility of index fossils in geology?
In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rock layers, where would fossils representing more recent organisms typically be found, according to the principle of superposition?
In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rock layers, where would fossils representing more recent organisms typically be found, according to the principle of superposition?
Which type of fossil provides insights into the behaviors and activities of ancient organisms, rather than their physical remains?
Which type of fossil provides insights into the behaviors and activities of ancient organisms, rather than their physical remains?
What is the fundamental distinction between relative dating and absolute dating methods used to determine the age of fossils?
What is the fundamental distinction between relative dating and absolute dating methods used to determine the age of fossils?
What do contour lines on a topographic map represent?
What do contour lines on a topographic map represent?
Erosion is best classified as which type of geological process, based on its primary effect on landforms?
Erosion is best classified as which type of geological process, based on its primary effect on landforms?
Which piece of evidence did Alfred Wegener use to support his theory of continental drift, before the discovery of plate tectonics?
Which piece of evidence did Alfred Wegener use to support his theory of continental drift, before the discovery of plate tectonics?
What geological feature is characteristic of convergent plate boundaries?
What geological feature is characteristic of convergent plate boundaries?
Why is the fossil record considered important for understanding Earth's history?
Why is the fossil record considered important for understanding Earth's history?
What is the primary goal of studying geologic history?
What is the primary goal of studying geologic history?
Flashcards
Continental Crust
Continental Crust
One of Earth's two types of crust, found on land and continents.
Mohorovicic Discontinuity
Mohorovicic Discontinuity
The boundary between the Earth's crust and upper mantle.
Continental Shelf
Continental Shelf
The upper layer of Earth's crust, primarily formed at tectonic plate collisions.
Geothermal Gradient
Geothermal Gradient
Signup and view all the flashcards
Convection Currents
Convection Currents
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mantle
Mantle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Felsic Rocks
Felsic Rocks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subduction
Subduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seismic Waves
Seismic Waves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Relative Dating
Relative Dating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Index Fossils
Index Fossils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Principle of Fossil Succession
Principle of Fossil Succession
Signup and view all the flashcards
Absolute Dating
Absolute Dating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Principle of Superposition
Principle of Superposition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fossils
Fossils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fossil Record
Fossil Record
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trace Fossils
Trace Fossils
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tectonic Plates
Tectonic Plates
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fault
Fault
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rheology
Rheology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thermoluminescence Dating
Thermoluminescence Dating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon Dating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dendrochronology
Dendrochronology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Geodynamo
Geodynamo
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hollow Earth Theory
Hollow Earth Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earth's Crust
Earth's Crust
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the lithosphere?
What is the lithosphere?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a transform boundary?
What is a transform boundary?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is convection?
What is convection?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are tectonic plates?
What are tectonic plates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge?
What is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do earthquakes happen?
How do earthquakes happen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are seismic waves?
What are seismic waves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is elastic rebound?
What is elastic rebound?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the focus of an earthquake?
What is the focus of an earthquake?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the epicenter of an earthquake?
What is the epicenter of an earthquake?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continental crust temperature
Continental crust temperature
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the mantle?
What is the mantle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper mantle behavior
Upper mantle behavior
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continental crust formation
Continental crust formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continental crust composition
Continental crust composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is geologic history?
What is geologic history?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are index fossils?
What are index fossils?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the fossil record?
What is the fossil record?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is relative dating?
What is relative dating?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is absolute dating?
What is absolute dating?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is radiocarbon dating?
What is radiocarbon dating?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is thermoluminescence dating?
What is thermoluminescence dating?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is continental drift?
What is continental drift?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a fault?
What is a fault?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peridotite
Peridotite
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seafloor Spreading
Seafloor Spreading
Signup and view all the flashcards
Convection
Convection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Absolute Age Dating
Absolute Age Dating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Relative Age Dating
Relative Age Dating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transform Boundary
Transform Boundary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lithosphere
Lithosphere
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Rebound
Elastic Rebound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Focus of an Earthquake
Focus of an Earthquake
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epicenter of an Earthquake
Epicenter of an Earthquake
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Continental Crust
- Found at Earth's surface (1 atm pressure)
- Forms continents and extends into oceans as shelves
- Thicker than oceanic crust (30-50 km vs 5-10 km)
- Temperature increases with depth (300-500°C)
- Primarily felsic rock (feldspar, granite, quartz)
- High in silicon and oxygen (about 60% of mass)
- Higher aluminum, sodium, and potassium than oceanic crust
- Iron, magnesium, and calcium are higher in oceanic crust
- Formation primarily at tectonic plate collisions
- Oceanic crust can sometimes subduct, melt, and reform continental crust
- Creation, destruction, and consistency rates of continental crust are still debated by geophysicists.
Mantle
- Largest part of Earth's geosphere (upper and lower mantle)
- Extends from Mohorovicic discontinuity (35 km) to Gutenberg discontinuity (2980 km)
- Primarily solid rock, but behaves like a viscous liquid over geologic time (convection currents)
- Driven by Earth's geothermal gradient (left-over heat and radioactive decay)
- Asthenosphere is the ductile, easily deformed part of the upper mantle
- Mantle material rises, under decompression melts, and can be deposited at mid-ocean ridges as ultramafic rock (peridotite)
- Convection currents can also uplift mantle material to the surface (obduction)
- Seismic wave velocity changes based on the medium through which they pass, this data allows geophysicists to know the state of matter within the Earth's interior.
Earth's Core
- Divided into outer and inner core
- Outer core: mostly liquid iron and nickel
- Inner core: solidified and purified iron
- Inner core temperature: 5400-6000°C, average depth 6470 km
- Rheology (material deformation under stress) is important to understanding the core
- Incorrect theory about a hollow Earth by Edmund Halley due to misunderstanding of magnetic fields and miscalculation of the Moon's density by Isaac Newton (incorrect density calculations implied a need for a hollow Earth).
Earth's Magnetic Field (Geodynamo)
- Movement of ionized material in the outer core (iron pull) is theorized to create the magnetic field
- The exact process and mechanisms are still mysterious.
Heat Transfer
- Three methods: conduction, radiation, and convection
- Convection currents are driven by uneven heating of a fluid (liquid or gas)
- Examples include sea breezes, warmed soup, and campfires. Warmed air rises, cooler air rushes in to replace it, creating convection currents.
Fossils
- Remains or traces of once-living organisms
- Mostly found in sedimentary rock
- Paleontologists study fossils and create timelines
- Types include: petrified, mold/cast, carbon film, trace, preserved remains, compression, impression, and pseudo fossils
- Formed from plant material or hard parts of the organism (soft tissue decays first)
- Used to create a geologic timeline (3.5 billion years old microscopic organisms)
- Index fossils are common, widely distributed, and lived for a short time—important for relative dating
Absolute Age Dating
- Measures the age of materials numerically
- Methods include: thermoluminescence (measuring radiation energy), radiocarbon (measuring carbon isotopes - limited to <75,000 years), and dendrochronology (counting tree rings)
- Applications include dating human remains, ancient pottery, and comparing the age of fallen to healthy Redwood trees.
Index Fossils and Relative Age Dating
- Index fossils are used to establish the relative age of rock layers
- Principle of fossil succession: specific fossils only exist during specific geologic time periods
- Principle of superposition: oldest layers are at the bottom in an undisturbed sequence, younger layers are above
Topographic Maps
- Show elevation using contour lines
- Contour lines connect points of equal elevation
- Index contours have numbers representing the exact elevation
- Contour interval is the elevation change between adjacent lines
- Contour lines close to form circles around hills/depressions
- Hachures indicate depressions on the map
Geologic Processes and History
- Shape Earth's features (creation, destruction, and combinations)
- Geologic history studies past events and their implications
- Biotic and abiotic elements are intricately linked and can affect landscapes and biodiversity
- Geologic processes pose hazards to humans
Continental Drift
- Wegener's theory proposed continents have moved and continue to move
- Supported by similarities in fossils and landforms between continents
- Hess later proved using the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that new land is formed by seafloor spreading.
Tectonic Plates
- Large lithosphere sections that move on mantle convection currents
- Boundaries include:
- Convergent: collision (e.g., Himalayas)
- Divergent: plates pulling apart (e.g., Mid-Atlantic Ridge)
- Transform: plates sliding past each other (e.g., San Andreas Fault)
- Seven major and several minor plates
Earthquakes
- Ground-shaking caused by stress and deformation of rocks underground
- A fault is a fracture where rocks shift releasing stored stress
- Seismic waves from the rock snapping back are felt as ground shaking (elastic rebound).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge on the fundamental differences between continental and oceanic crust. This quiz covers characteristics, formation, and seismic properties, along with geological principles related to Earth's structure. Ideal for geology students looking to enhance their understanding of crustal features.