Podcast
Questions and Answers
What term is used for the processes that cause mineral or organic particles to settle and accumulate?
What term is used for the processes that cause mineral or organic particles to settle and accumulate?
- Weathering
- Erosion
- Sedimentation (correct)
- Metamorphism
Which of the following is a type of sedimentary rock?
Which of the following is a type of sedimentary rock?
- Basalt
- Gneiss
- Limestone (correct)
- Granite
What is the main source of scientific knowledge about the Earth's history?
What is the main source of scientific knowledge about the Earth's history?
- Sedimentary rock strata (correct)
- Igneous rock strata
- Metamorphic rock formations
- Fossilized remains
Which agent of denudation is primarily responsible for the transport of sediments by wind?
Which agent of denudation is primarily responsible for the transport of sediments by wind?
What percentage of the Earth's crust is estimated to be made up of sedimentary rocks?
What percentage of the Earth's crust is estimated to be made up of sedimentary rocks?
Which scientific discipline focuses specifically on the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks?
Which scientific discipline focuses specifically on the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks?
What type of stress occurs when rock or sediment is buried?
What type of stress occurs when rock or sediment is buried?
What is the term for the layered structure formed by the deposition of sedimentary rocks?
What is the term for the layered structure formed by the deposition of sedimentary rocks?
What is the primary reason seismologists prefer moment magnitude over Richter magnitude?
What is the primary reason seismologists prefer moment magnitude over Richter magnitude?
How is the largest possible earthquake determined?
How is the largest possible earthquake determined?
What method do geologists use to calculate the distance between an earthquake epicenter and a seismograph?
What method do geologists use to calculate the distance between an earthquake epicenter and a seismograph?
What does the arrival time of seismic waves at a recording station indicate?
What does the arrival time of seismic waves at a recording station indicate?
What happens when a seismograph is located far from the earthquake epicenter?
What happens when a seismograph is located far from the earthquake epicenter?
What does the term 'slip' refer to in the context of an earthquake?
What does the term 'slip' refer to in the context of an earthquake?
Why do different seismic waves arrive at different times at a seismograph?
Why do different seismic waves arrive at different times at a seismograph?
To pinpoint the exact location of an earthquake, how many recording stations do geologists typically compare?
To pinpoint the exact location of an earthquake, how many recording stations do geologists typically compare?
What is the primary characteristic that allows P-waves to travel through various materials?
What is the primary characteristic that allows P-waves to travel through various materials?
Why do P-waves travel faster in the mantle than in the Earth's crust?
Why do P-waves travel faster in the mantle than in the Earth's crust?
What type of motion does a Rayleigh wave exhibit during an earthquake?
What type of motion does a Rayleigh wave exhibit during an earthquake?
Which wave type is specifically unable to travel through liquids?
Which wave type is specifically unable to travel through liquids?
How does a seismograph work during an earthquake?
How does a seismograph work during an earthquake?
What is the term for the record of Earth vibration produced by a seismograph?
What is the term for the record of Earth vibration produced by a seismograph?
What distinguishes S-waves from P-waves in terms of motion?
What distinguishes S-waves from P-waves in terms of motion?
What characterizes Love waves during an earthquake?
What characterizes Love waves during an earthquake?
What is the primary purpose of drawing circles for each seismic station recording an earthquake?
What is the primary purpose of drawing circles for each seismic station recording an earthquake?
What effect does sandy sediment have on structures during an earthquake?
What effect does sandy sediment have on structures during an earthquake?
What is the significance of the time-travel curve in seismology?
What is the significance of the time-travel curve in seismology?
How do engineers prevent structural failure in areas with sandy soil during an earthquake?
How do engineers prevent structural failure in areas with sandy soil during an earthquake?
What is the phenomenon called when water-saturated soil loses its shear strength during an earthquake?
What is the phenomenon called when water-saturated soil loses its shear strength during an earthquake?
Which of the following factors does NOT contribute to earthquake damage in structures built on soil?
Which of the following factors does NOT contribute to earthquake damage in structures built on soil?
In which material can structures be safest from earthquake shaking?
In which material can structures be safest from earthquake shaking?
What happens to the pore water in saturated soil during the sudden shock of an earthquake?
What happens to the pore water in saturated soil during the sudden shock of an earthquake?
What is the primary purpose of borehole geophysics?
What is the primary purpose of borehole geophysics?
What does a well log primarily display?
What does a well log primarily display?
Which of the following is NOT a method to influence the estimation of hydrocarbon reserves?
Which of the following is NOT a method to influence the estimation of hydrocarbon reserves?
What is petrophysical analysis primarily concerned with?
What is petrophysical analysis primarily concerned with?
What characterizes a calibrated petrophysical analysis?
What characterizes a calibrated petrophysical analysis?
How is log analysis typically described?
How is log analysis typically described?
Why might well logs be used beyond oil and gas evaluation?
Why might well logs be used beyond oil and gas evaluation?
What is an effect of compaction on electric current flow?
What is an effect of compaction on electric current flow?
What defines the axial plane in a fold?
What defines the axial plane in a fold?
Which statement about anticlines and synclines is accurate?
Which statement about anticlines and synclines is accurate?
What is the term for the distance that rocks on opposite sides of a fault have moved?
What is the term for the distance that rocks on opposite sides of a fault have moved?
In the context of a fault, what does the term 'hanging wall' refer to?
In the context of a fault, what does the term 'hanging wall' refer to?
How is a normal fault characterized?
How is a normal fault characterized?
What is a fault zone?
What is a fault zone?
What occurs in faults regarding the movement of rocks?
What occurs in faults regarding the movement of rocks?
What happens when rock moves along a fault after it forms?
What happens when rock moves along a fault after it forms?
Flashcards
Igneous Rock Formation
Igneous Rock Formation
The process by which molten rock (magma) cools and solidifies, forming igneous rocks.
Sedimentary Rock Formation
Sedimentary Rock Formation
Rocks formed from the accumulation of sediments, like sand or small pieces of other rocks.
Metamorphic Rock Formation
Metamorphic Rock Formation
Rocks that have been transformed from their original state by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
Weathering
Weathering
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erosion
Erosion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stress
Stress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Confining Stress
Confining Stress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tectonic Forces
Tectonic Forces
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fold Axis
Fold Axis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axial Plane
Axial Plane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anticline
Anticline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Syncline
Syncline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fault
Fault
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slip
Slip
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fault Plane
Fault Plane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hanging Wall
Hanging Wall
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a P-wave?
What is a P-wave?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is an S-wave?
What is an S-wave?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are surface waves?
What are surface waves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Rayleigh wave?
What is a Rayleigh wave?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Love wave?
What is a Love wave?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a seismograph?
What is a seismograph?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a seismogram?
What is a seismogram?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is seismic wave velocity?
What is seismic wave velocity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earthquake Epicenter
Earthquake Epicenter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Time-Travel Curve
Time-Travel Curve
Signup and view all the flashcards
P-Waves
P-Waves
Signup and view all the flashcards
S-Waves
S-Waves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earthquake Location (Triangulation)
Earthquake Location (Triangulation)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earthquake Intensity
Earthquake Intensity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liquefaction
Liquefaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earthquake-Resistant Structures
Earthquake-Resistant Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earthquake Magnitude
Earthquake Magnitude
Signup and view all the flashcards
Richter Scale
Richter Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moment Magnitude Scale
Moment Magnitude Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epicenter
Epicenter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Focus
Focus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seismic Waves
Seismic Waves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Travel Time
Travel Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is well logging?
What is well logging?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a well log?
What is a well log?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is log analysis?
What is log analysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is petrophysics?
What is petrophysics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does lowering the salinity of pore fluid improve oil and gas recovery?
How does lowering the salinity of pore fluid improve oil and gas recovery?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does lithification affect electrical properties of rocks?
How does lithification affect electrical properties of rocks?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does compaction affect electrical properties of rocks?
How does compaction affect electrical properties of rocks?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does removing pore fluid affect electrical properties of rocks?
How does removing pore fluid affect electrical properties of rocks?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
General Geology Course - First Year Students
- Course offered by Prof. Adel Kamel Mohamed
- Intended for first-year students at the Faculty of Education
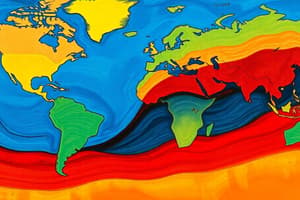
- Image of Earth's tectonic plates with labeled plate boundaries (Ring of Fire highlighted)
The Earth's Layers
- Earthquake waves change speed and direction at depth, revealing interior layers
- Diagram shows Earth layers (crust, upper mantle, lower mantle, liquid outer core, solid inner core)
- Oceanic crust (5-10 km thick) is primarily basalt, rich in iron and magnesium silicates
- Continental crust (20-70 km thick) is primarily granite, with silicon oxides
- Lithosphere includes the crust and upper portion of the mantle—relatively cool, hard, and strong
- Asthenosphere is a weaker, plastic layer beneath the lithosphere
- Mantle (2900 km thick) comprises most of Earth's volume—primarily ultramafic rocks (peridotite)
- Core (Outer core: 2250 km thick, liquid; Inner core: 1220 km thick, solid) is primarily iron and nickel
Review on Rocks
- Sedimentary rocks: Formed from sediment (sand, shale, pebbles). Typically layered, soft, and may contain fossils (e.g., conglomerate, limestone).
- Metamorphic rocks: Formed from existing rocks (pre-existing) under heat and pressure. Often have ribbon-like layers and/or shiny crystals (e.g., gneiss, marble).
- Igneous rocks: Formed from cooling and solidifying magma or lava. Can be intrusive (formed below Earth's surface) or extrusive (formed above Earth's surface) (e.g., granite, basalt).
Geologic Structures
- Stress: A force exerted on an object.
- Confining stress: Compresses rocks equally in all directions.
- Directed stress: Compresses rocks strongly in one direction.
- Compression: Shortens the distance.
- Extension: Lengthens the distance.
- Shear: Causes one part to slide past another.
- Strain: The deformation produced by stress.
- Elastic deformation: Rocks return to original shape.
- Plastic deformation: Rocks retain new shape.
- Brittle fracture: Rocks break.
- Folds: Bends in rock, usually from compressive stress.
- Anticline: Arching upward.
- Syncline: Arching downward.
- Faults: Fractures where rock has moved relative to each other.
- Normal fault: Hanging wall moves down relative to footwall (caused by tension).
- Reverse fault: Hanging wall moves up relative to footwall (caused by compression).
- Thrust fault: Nearly horizontal reverse fault.
- Strike-slip fault: Rocks move horizontally past each other.
- Joints: Fractures where rock has not moved.
Plate Tectonics
- Tectonic plates: Large segments of the lithosphere that move slowly over the asthenosphere.
- Divergent boundaries: Plates move apart, creating new crust (e.g., Mid-Atlantic Ridge).
- Convergent boundaries: Plates move together -
- Oceanic-continental: Denser oceanic plate subducts under continental plate, forming volcanoes and trenches (e.g., Western Aleutians)
- Oceanic-oceanic: Denser oceanic plate subducts under less dense oceanic plate, forming island arcs and trenches (e.g., Western Aleutians).
- Continental-continental: Plates collide, forming mountain ranges (e.g., Himalayas).
- Transform boundaries: Plates slide horizontally past each other (e.g., San Andreas Fault).
Earthquakes
- Earthquakes: Sudden shaking of the Earth's crust caused by the release of stored energy.
- Focus: The point within the Earth where the earthquake originates.
- Epicenter: The point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus.
- Seismic waves: Energy waves that radiate outward from the focus.
- Body waves: Travel through Earth's interior.
- P-waves (primary): Fastest, compressional waves.
- S-waves (secondary): Slower, shear waves.
- Surface waves: Travel along Earth's surface, responsible for most of the damage.
- Liquefaction: The loss of shear strength in water-saturated soil during an earthquake.
Tsunamis
- Tsunamis: Giant waves generated by underwater earthquakes or landslides
- Usually detected in open ocean by flat wave motion
- Wave height increases significantly upon approach to shore
Geophysical Methods
-
Methods used to locate and study the subsurface (magnetic, gravity, seismic, electrical resistivity, borehole logging)
-
Gravity Method-Detecting density differences in subsurface rocks by measuring changes in gravitational acceleration
-
Magnetic Method-Detecting differences in magnetic susceptibility in subsurface materials based on magnetic field anomalies.
-
Electrical Resistivity Method-Measuring varying physical properties in rocks and minerals to estimate subsurface structure via electrical currents.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.