Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of body symmetry do cnidarians exhibit?
What type of body symmetry do cnidarians exhibit?
- Bilateral symmetry
- Radial symmetry (correct)
- Asymmetrical
- None of the above
Which of the following statements is true regarding the nervous system of cnidarians?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the nervous system of cnidarians?
- Their nerve cells are only located in the gastrodermis.
- They have no nervous system at all.
- They possess a simple nervous system forming a nerve net. (correct)
- They possess a complex brain and CNS.
What is the primary function of cnidae in cnidarians?
What is the primary function of cnidae in cnidarians?
- Stinging or adhesion (correct)
- Locomotion
- Respiration
- Digestion
In the class Hydrozoa, how is the enteron structured?
In the class Hydrozoa, how is the enteron structured?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the medusa form in Scyphozoa?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the medusa form in Scyphozoa?
What type of reproduction do most polypoid hydrozoans primarily undergo?
What type of reproduction do most polypoid hydrozoans primarily undergo?
What type of skeletal system do Hydrozoa typically possess?
What type of skeletal system do Hydrozoa typically possess?
Which class of cnidarians includes organisms known for their colonial and polymorphic characteristics, like Obelia?
Which class of cnidarians includes organisms known for their colonial and polymorphic characteristics, like Obelia?
What distinguishes scyphomedusa from hydromedusa?
What distinguishes scyphomedusa from hydromedusa?
What feature is notable about Cubozoa medusa?
What feature is notable about Cubozoa medusa?
What type of symmetry do comb jellies exhibit?
What type of symmetry do comb jellies exhibit?
What is unique about the reproductive system of most comb jellies?
What is unique about the reproductive system of most comb jellies?
What type of cells are involved in prey capture in comb jellies?
What type of cells are involved in prey capture in comb jellies?
What is the function of siphonoglyphs in anthozoa?
What is the function of siphonoglyphs in anthozoa?
Which statement is true regarding the mesoglea in both scyphomedusa and anthozoa?
Which statement is true regarding the mesoglea in both scyphomedusa and anthozoa?
What feature enhances the predatory behavior of Cubozoa medusa?
What feature enhances the predatory behavior of Cubozoa medusa?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
General Characteristics of CNIDARIA
- Radially symmetrical, facilitating food capture from all directions.
- Diploblastic structure with epidermis and gastrodermis separated by mesoglea.
- Single gastrovascular cavity functioning as both mouth and anus.
- Absence of a head, brain, and central nervous system; features a simple nerve net.
- Sense organs include statocysts and ocelli.
- Skeletal structures may be horny or calcareous, can be internal or external.
- No specialized structures for respiration, excretion, or transport (except in some jellyfish).
- Unique cnidae in cnidocytes, with nematocysts being the most common type.
- Exhibits polymorphism, existing as solitary or colonial forms (polyp or medusa).
- Four classes identified: Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Cubozoa, and Anthozoa.
Class HYDROZOA
- Enteron is not partitioned by mesenteries.
- Tentacles of polyps typically solid, and mesoglea is acellular.
- Cnidocytes localized only in the epidermis.
- External chitinous skeleton predominates.
- Hydromedusa are smaller and serve as gamete producers with ectodermal gametes.
- Notable genera include Hydra, Gonionemus, and Obelia.
Class SCYPHOZOA
- Medusa form is dominant; differs from hydromedusa due to the absence of velum (acraspedote).
- Tentacles are short and may be notched along the margin.
- Mesoglea contains amoeboid mesenchyme cells.
- Cnidocytes present in both gastrodermis and epidermis, with gastrodermal gametes.
Class CUBOZOA (Box Jelly)
- Medusa is square-shaped with tentacles hanging from the corners.
- Known for strong swimming abilities and being voracious fish predators.
- Possess advanced image-forming eyes for navigation.
- Stings from some species (e.g., Chironex) can be lethal to humans.
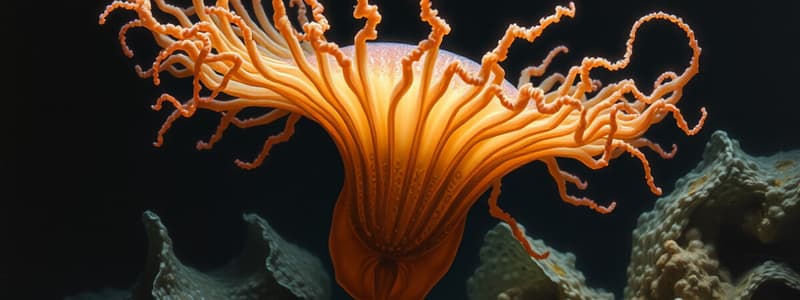
Class ANTHOZOA (Sea Anemones and Coral)
- Only polyp form is predominant, exhibiting limited mobility.
- Oral end expands into a disc with hollow tentacles encircling a slit-like mouth.
- Gastrovascular cavity is compartmentalized by mesenteries, which contain cnidocytes and gonads.
- Mesoglea features amoeboid mesenchyme cells, with a pharynx leading from the mouth.
Class CTENOPHORA (Comb Jelly)
- Features biradial symmetry and is transparent, fragile, acoelomate, and luminescent.
- Bears eight rows of comb-like cilia for movement.
- Largest animals moving via ciliary actions, forming musculature from gelatinous mesenchyme.
- Lacks attached sessile life stages and is typically monomorphic.
- Primarily hermaphroditic, developing through a cydippid larval stage.
- Possesses a complete gut; pharynx leads to branching gastrovascular canal system with small anal pores.
- Tentacles equipped with adhesive cells called colloblasts for trapping prey, lacking stinging nematocysts.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.