Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic is unique to cnidarians?
Which characteristic is unique to cnidarians?
- Presence of a coelom for organ development
- Bilateral symmetry in the adult stage
- A complex nervous system with a centralized brain
- Nematocysts used for prey capture and defense (correct)
How does the diploblastic body plan of cnidarians influence their structural organization?
How does the diploblastic body plan of cnidarians influence their structural organization?
- It enables the formation of a true coelom for advanced digestive processes.
- It promotes the development of specialized respiratory organs.
- It restricts tissue development to two layers, limiting organ complexity. (correct)
- It allows for complex organ systems to develop from three germ layers.
What is the primary role of cnidocytes in cnidarians?
What is the primary role of cnidocytes in cnidarians?
- To facilitate gas exchange
- To provide structural support to the body
- To capture prey and defend against predators (correct)
- To aid in locomotion
How do the polyp and medusa body forms optimize cnidarians for different ecological roles?
How do the polyp and medusa body forms optimize cnidarians for different ecological roles?
How does a thicker mesoglea in the medusa form support its lifestyle compared to the polyp form?
How does a thicker mesoglea in the medusa form support its lifestyle compared to the polyp form?
What role does the gastrovascular cavity play in cnidarian digestion and nutrient distribution?
What role does the gastrovascular cavity play in cnidarian digestion and nutrient distribution?
How does the presence or absence of a medusa stage differentiate the Hydrozoa and Anthozoa classes?
How does the presence or absence of a medusa stage differentiate the Hydrozoa and Anthozoa classes?
What is the significance of the velum in some hydrozoan medusae?
What is the significance of the velum in some hydrozoan medusae?
How do the epidermal gonads in Hydrozoa differ from the endodermal gonads in Anthozoa?
How do the epidermal gonads in Hydrozoa differ from the endodermal gonads in Anthozoa?
What structural adaptation allows Anthozoa to increase their surface area for nutrient absorption in the gastrovascular cavity?
What structural adaptation allows Anthozoa to increase their surface area for nutrient absorption in the gastrovascular cavity?
In a freshwater environment, how does the sessile phase benefit hydras?
In a freshwater environment, how does the sessile phase benefit hydras?
How does the tissue-level organization of hydras influence their regeneration capabilities?
How does the tissue-level organization of hydras influence their regeneration capabilities?
How does the location of the hypostome in hydras correlate with their feeding strategy?
How does the location of the hypostome in hydras correlate with their feeding strategy?
What is the functional significance of the nutritive-muscular cells in the gastrodermis of hydras?
What is the functional significance of the nutritive-muscular cells in the gastrodermis of hydras?
How does asexual reproduction via budding in hydras contribute to their population growth in stable environments?
How does asexual reproduction via budding in hydras contribute to their population growth in stable environments?
Under what environmental conditions is sexual reproduction in hydras more likely to occur?
Under what environmental conditions is sexual reproduction in hydras more likely to occur?
What is a colony in the context of Obelia, and how does it influence the organism's survival?
What is a colony in the context of Obelia, and how does it influence the organism's survival?
What is the specific role of reproductive polyps in Obelia colonies?
What is the specific role of reproductive polyps in Obelia colonies?
How does the mobile medusa stage in Obelia's life cycle contribute to the species' distribution?
How does the mobile medusa stage in Obelia's life cycle contribute to the species' distribution?
What is the primary structural difference between Pennaria and Obelia hydroid colonies?
What is the primary structural difference between Pennaria and Obelia hydroid colonies?
How do the filiform tentacles of Pennaria aid in its feeding strategy?
How do the filiform tentacles of Pennaria aid in its feeding strategy?
What unique adaptation allows Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war) to float on the water's surface?
What unique adaptation allows Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war) to float on the water's surface?
How does the division of labor among polyps in a Physalia colony enhance its predatory success?
How does the division of labor among polyps in a Physalia colony enhance its predatory success?
What role do dactylozooids play within a Physalia colony?
What role do dactylozooids play within a Physalia colony?
How does the Aurelia medusa utilize its rhopalium for sensory perception?
How does the Aurelia medusa utilize its rhopalium for sensory perception?
Describe the role of the planula larva in the life cycle of Aurelia.
Describe the role of the planula larva in the life cycle of Aurelia.
What is the significance of the strobila stage in Aurelia's life cycle?
What is the significance of the strobila stage in Aurelia's life cycle?
How does the Cassiopea jellyfish obtain its nutrients?
How does the Cassiopea jellyfish obtain its nutrients?
What unique behavior is exhibited by Cassiopea that distinguishes it from other jellyfish?
What unique behavior is exhibited by Cassiopea that distinguishes it from other jellyfish?
What is the primary ecological role of sea anemones (Actinia) in marine environments?
What is the primary ecological role of sea anemones (Actinia) in marine environments?
What structural feature allows sea anemones to retract their tentacles for protection?
What structural feature allows sea anemones to retract their tentacles for protection?
How does the gastrovascular cavity of Actinia differ from that of Hydrozoa, and what implications does this have for their feeding?
How does the gastrovascular cavity of Actinia differ from that of Hydrozoa, and what implications does this have for their feeding?
What is the composition of the 'house' that corals inhabit and secrete?
What is the composition of the 'house' that corals inhabit and secrete?
What is the ecological importance of corals in marine ecosystems?
What is the ecological importance of corals in marine ecosystems?
In stoney corals, what role do the basal plates play in the overall structure and growth of the coral?
In stoney corals, what role do the basal plates play in the overall structure and growth of the coral?
What is the purpose of the theca in stoney corals?
What is the purpose of the theca in stoney corals?
Flashcards
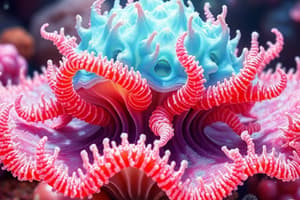
Phylum Cnidaria
Phylum Cnidaria
Phylum of stinging invertebrates characterized by nematocysts, a sac-like diploblastic body, tissue-level organization, radial symmetry and often, a sessile phase.
Cnidocytes
Cnidocytes
Specialized stinging cells in cnidarians containing a fluid-filled capsule with a long, spirally coiled hollow thread used to capture prey and inject paralyzing toxins.
Nematocyst
Nematocyst
A fluid-filled capsule within a cnidocyte that contains a long, spirally coiled hollow thread.
Polyp
Polyp
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medusa
Medusa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrovascular cavity
Gastrovascular cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Velum
Velum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrozoa
Hydrozoa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scyphozoa
Scyphozoa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Body Column (Hydra)
Body Column (Hydra)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pedal Disk
Pedal Disk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Budding
Budding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Obelia
Obelia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feeding Polyps
Feeding Polyps
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reproductive Polyps
Reproductive Polyps
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physalia
Physalia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anthozoa
Anthozoa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sea Anemones
Sea Anemones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corals
Corals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Phylum Cnidaria
- This phylum is characterized by stinging invertebrates.
- They possess nematocysts, which are stinging cells.
- The body plan is a sac-like diploblastic structure formed from two germ layers: endoderm and ectoderm.
- Organization exists at the tissue level.
- These organisms exhibit radial symmetry.
- They all have a sessile phase in their life cycle.
Cnidocytes
- Cnidarians have specialized stinging cells called cnidocytes.
- Each cnidocyte contains a fluid-filled capsule called a nematocyst.
- The nematocyst houses a long, spirally coiled hollow thread.
- When the trigger of the cnidocyte is touched, the nematocyst is discharged to trap prey.
- Some threads can penetrate and inject paralyzing toxins.
Cnidaria Forms
- Cnidarians exist in two forms: polyp and medusa.
- The polyp form is a tube-shaped body with the mouth/anus facing upwards.
- The medusa form resembles an umbrella with the mouth/anus facing downwards.
- Both polyp and medusa have the same body layers.
- The medusa possesses a thicker mesoglea than the polyp.
- Polyps are involved in asexual reproduction through budding
- Medusae are involved in sexual reproduction.
- The gastrovascular cavity is an internal space used for digestion and nutrient distribution.
Cnidaria Classes
- The classes include Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, and Anthozoa.
Hydrozoa
- The polyp stage is dominant.
- Medusa may be present or absent
- Medusa has a velum, which is an inward projecting membrane around the bell margin.
- The mesoglea is noncellular.
- Gonads are epidermal.
- Marine and freshwater forms exist.
- Examples include Hydra, Obelia, Pennaria, and Physalia.
Scyphozoa
- The medusa stage is dominant.
- Examples include Aurelia and Cassiopia
Anthozoa
- The medusa stage is absent.
- Mesoglea is cellular.
- Gonads are endodermal.
- The gastrovascular cavity is partitioned by septa.
- All are marine.
- They can be solitary or colonial.
- Examples include Corals and Actinia.
Hydra
- Hydras are small animals living attached to plants and twigs in freshwaters.
- They have four major body regions including the hypostome.
- The hypostome is where the mouth is located, surrounded by tentacles.
- The body column is divided into a gastric region and peduncle.
- The pedal disk secretes mucus for attachment.
- Asexual reproduction is by budding
- Sexual reproduction involves spermaries and testes
Obelia
- Obelia is a colony that grows by budding and contains feeding and reproducitve polyps
- Feeding polyps capture food
- Reproductive polyps sexually produce medusae.
Pennaria
- Pennaria is a hydrozoa that is a hydroid colony
Physalia
- Physalia, the Portuguese man-of-war, comprises a colony of polyps attached to a gas-filled float that provides buoyancy.
Jellyfishes Aurelia
- They belong to the class Scyphozoa.
Actinia
- The sea anemones belong to the class Anthozoa.
- they are sessile polyps that are attached to a substrate
Corals
- Corals belong to the class Anthozoa.
- They are polyps encased in a calcium carbonate house.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.