Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of genes in living cells?
What is the primary function of genes in living cells?
- Provide information for cell survival and reproduction (correct)
- Regulate cell division
- Control cellular respiration
- Determine cell shape and size
What do gene regulatory sequence regions control?
What do gene regulatory sequence regions control?
- Protein folding
- DNA replication
- Cell division
- Transcription and translation (correct)
What is the foundation of understanding gene annotation, expression, and function?
What is the foundation of understanding gene annotation, expression, and function?
- Understanding protein synthesis
- Understanding genetic mutations
- Understanding gene structure (correct)
- Understanding cell metabolism
What is the role of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) in gene function?
What is the role of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) in gene function?
What do the common elements of gene structure in eukaryotes and prokaryotes largely result from?
What do the common elements of gene structure in eukaryotes and prokaryotes largely result from?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Gene Function and Regulation
- The primary function of genes in living cells is to encode the information necessary for the creation of proteins, which are essential for nearly all cellular processes.
Gene Regulatory Sequence Regions
- Gene regulatory sequence regions control the expression of genes by providing a platform for the binding of transcription factors and other regulatory proteins that modulate gene expression.
Gene Annotation, Expression, and Function
- The foundation of understanding gene annotation, expression, and function is the central dogma, which describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to proteins.
Non-Coding RNA (ncRNA) in Gene Function
- Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) plays a crucial role in gene function by regulating gene expression at various levels, including transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.
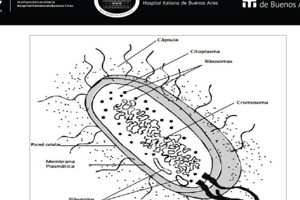
Gene Structure in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
- The common elements of gene structure in eukaryotes and prokaryotes, such as the presence of promoters, coding regions, and terminators, largely result from the shared evolutionary ancestry of these organisms.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.