Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are common factors that can interfere with the normal function of the gastrointestinal tract?
What are common factors that can interfere with the normal function of the gastrointestinal tract?
- Genetic predispositions
- Excessive physical activity
- Stress and anxiety (correct)
- Bacterial infections
What is the approximate length of the gastrointestinal tract in meters?
What is the approximate length of the gastrointestinal tract in meters?
- 7 to 7.9 m (correct)
- 8 to 9 m
- 5 to 6 m
- 10 to 11 m
Which part of the GI tract is primarily responsible for controlling the opening to the small intestine?
Which part of the GI tract is primarily responsible for controlling the opening to the small intestine?
- The pylorus (correct)
- The body
- The cardia
- The fundus
Which of the following is NOT a type of pathology that can affect the gastrointestinal tract?
Which of the following is NOT a type of pathology that can affect the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the main function of the stomach in relation to digestion?
What is the main function of the stomach in relation to digestion?
Which anatomical feature of the esophagus allows it to pass through the diaphragm?
Which anatomical feature of the esophagus allows it to pass through the diaphragm?
Which part of the GI tract is located under the left lobe of the liver?
Which part of the GI tract is located under the left lobe of the liver?
What typically occurs when there is faulty nervous system control in the gastrointestinal tract?
What typically occurs when there is faulty nervous system control in the gastrointestinal tract?
What role does intrinsic factor play in vitamin B12 absorption?
What role does intrinsic factor play in vitamin B12 absorption?
What is the primary substance responsible for acidity in the stomach?
What is the primary substance responsible for acidity in the stomach?
Which of the following hormones or substances primarily influences gastric motility?
Which of the following hormones or substances primarily influences gastric motility?
What is the major function of the small intestine?
What is the major function of the small intestine?
Which digestive enzyme is responsible for protein digestion in the pancreas?
Which digestive enzyme is responsible for protein digestion in the pancreas?
How long does chyme typically remain in the small intestine?
How long does chyme typically remain in the small intestine?
What is the sphincter called that controls bile flow from the common bile duct into the duodenum?
What is the sphincter called that controls bile flow from the common bile duct into the duodenum?
What type of contractions in the small intestine are responsible for mixing the contents?
What type of contractions in the small intestine are responsible for mixing the contents?
Which mineral is absorbed throughout the length of the small intestine?
Which mineral is absorbed throughout the length of the small intestine?
What is the primary component of feces?
What is the primary component of feces?
What is the primary purpose of colonic secretions?
What is the primary purpose of colonic secretions?
Which part of the small intestine is primarily responsible for bile salts absorption?
Which part of the small intestine is primarily responsible for bile salts absorption?
What function does the ileocecal valve serve?
What function does the ileocecal valve serve?
What is the process by which fats are made easier to absorb?
What is the process by which fats are made easier to absorb?
What primarily contributes to the brown color of feces?
What primarily contributes to the brown color of feces?
Which gas is NOT typically formed in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which gas is NOT typically formed in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which structure's contraction facilitates the elimination of stool?
Which structure's contraction facilitates the elimination of stool?
The gut microbiota begins to colonize the gastrointestinal tract shortly after which event?
The gut microbiota begins to colonize the gastrointestinal tract shortly after which event?
Which of the following factors does NOT affect the composition of normal gut microbiota?
Which of the following factors does NOT affect the composition of normal gut microbiota?
What role does the gut microbiome play in immune function?
What role does the gut microbiome play in immune function?
What is the primary control mechanism for the internal anal sphincter?
What is the primary control mechanism for the internal anal sphincter?
Which of the following symptoms is commonly associated with dyspepsia?
Which of the following symptoms is commonly associated with dyspepsia?
What happens to the external anal sphincter during defecation?
What happens to the external anal sphincter during defecation?
How does aging primarily affect the gastrointestinal system?
How does aging primarily affect the gastrointestinal system?
What type of pain is most commonly associated with gastrointestinal diseases?
What type of pain is most commonly associated with gastrointestinal diseases?
What is the primary action required immediately after excising tissue?
What is the primary action required immediately after excising tissue?
Which of the following is NOT typically necessary before a bowel examination?
Which of the following is NOT typically necessary before a bowel examination?
What is a common trigger for dyspepsia symptoms?
What is a common trigger for dyspepsia symptoms?
During a small bowel procedure, what vital sign aspect would a nurse monitor?
During a small bowel procedure, what vital sign aspect would a nurse monitor?
What is the role of Peyer's patches in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the role of Peyer's patches in the gastrointestinal tract?
What should a nurse monitor the patient for after a bowel examination?
What should a nurse monitor the patient for after a bowel examination?
Which of the following methods is used for visualization of the small intestine?
Which of the following methods is used for visualization of the small intestine?
What is the main purpose of the hydrogen breath test?
What is the main purpose of the hydrogen breath test?
Which test is recommended by the ACS for cancer screening?
Which test is recommended by the ACS for cancer screening?
What should patients avoid before undergoing urea breath testing?
What should patients avoid before undergoing urea breath testing?
What type of imaging does endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) provide?
What type of imaging does endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) provide?
How often should the FIT-fecal DNA test be performed according to the recommendations?
How often should the FIT-fecal DNA test be performed according to the recommendations?
Which of the following is NOT a typical use of abdominal ultrasonography?
Which of the following is NOT a typical use of abdominal ultrasonography?
What is the requirement for dietary restrictions before collecting a stool specimen for a FIT test?
What is the requirement for dietary restrictions before collecting a stool specimen for a FIT test?
What is a key advantage of using abdominal ultrasonography?
What is a key advantage of using abdominal ultrasonography?
Which of the following genetic conditions is associated with Lynch syndrome?
Which of the following genetic conditions is associated with Lynch syndrome?
What is a limitation of abdominal ultrasonography?
What is a limitation of abdominal ultrasonography?
How should a patient prepare for gallbladder studies involving ultrasonography?
How should a patient prepare for gallbladder studies involving ultrasonography?
What is the protocol for genetic counseling for at-risk individuals?
What is the protocol for genetic counseling for at-risk individuals?
What is normally observed in the buccal mucosa during an examination?
What is normally observed in the buccal mucosa during an examination?
What findings on the dorsum of the tongue would be considered normal?
What findings on the dorsum of the tongue would be considered normal?
What is detected by the urea breath test?
What is detected by the urea breath test?
What does an asymmetric rise of the uvula during the phonation of 'ah' indicate?
What does an asymmetric rise of the uvula during the phonation of 'ah' indicate?
Which method is employed to auscultate bowel sounds?
Which method is employed to auscultate bowel sounds?
How is rebound tenderness usually evaluated during an abdominal examination?
How is rebound tenderness usually evaluated during an abdominal examination?
Which part of the assessment evaluates the rectum and perianal region?
Which part of the assessment evaluates the rectum and perianal region?
What should be done if bowel sounds are absent after a minimum of 5 minutes of auscultation?
What should be done if bowel sounds are absent after a minimum of 5 minutes of auscultation?
What differentiates gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) from gastro-esophageal reflux (GER)?
What differentiates gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) from gastro-esophageal reflux (GER)?
What could the presence of white or red plaques in the oral cavity suggest?
What could the presence of white or red plaques in the oral cavity suggest?
What is the importance of inspecting the gums during an oral assessment?
What is the importance of inspecting the gums during an oral assessment?
Which of the following symptoms is commonly associated with excessive flatulence?
Which of the following symptoms is commonly associated with excessive flatulence?
During the inspection of the abdomen, what is the first step to be performed?
During the inspection of the abdomen, what is the first step to be performed?
Nausea can commonly be triggered by which of the following?
Nausea can commonly be triggered by which of the following?
What is the typical sound associated with air in the stomach during percussion?
What is the typical sound associated with air in the stomach during percussion?
What condition is characterized by the forceful emptying of gastric contents through the mouth?
What condition is characterized by the forceful emptying of gastric contents through the mouth?
What does a flat abdominal contour generally indicate?
What does a flat abdominal contour generally indicate?
Which type of stool is likely to indicate bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract?
Which type of stool is likely to indicate bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract?
What is considered an abnormal increase in stool frequency or liquidity?
What is considered an abnormal increase in stool frequency or liquidity?
Which cranial nerve is assessed by evaluating the tongue's symmetry and strength?
Which cranial nerve is assessed by evaluating the tongue's symmetry and strength?
What symptom might accompany constipation?
What symptom might accompany constipation?
What may lead to a change in stool characteristics?
What may lead to a change in stool characteristics?
What could indicate a Mallory-Weiss tear during vomiting?
What could indicate a Mallory-Weiss tear during vomiting?
Which of the following could be a reason for a health care provider to inquire about a patient’s dietary habits?
Which of the following could be a reason for a health care provider to inquire about a patient’s dietary habits?
What is the primary function of the ileocecal valve?
What is the primary function of the ileocecal valve?
The assessment of which area is important during a physical examination of the gastrointestinal system?
The assessment of which area is important during a physical examination of the gastrointestinal system?
What common dietary symptom might indicate gallbladder disease?
What common dietary symptom might indicate gallbladder disease?
Which part of the gastrointestinal tract primarily absorbs nutrients?
Which part of the gastrointestinal tract primarily absorbs nutrients?
What role does salivary amylase play in digestion?
What role does salivary amylase play in digestion?
What should be inspected in a patient during an oral cavity examination?
What should be inspected in a patient during an oral cavity examination?
Which structure prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing?
Which structure prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing?
What is not a typical characteristic of normally formed stool?
What is not a typical characteristic of normally formed stool?
What is the pH level of the gastric fluid secreted in the stomach?
What is the pH level of the gastric fluid secreted in the stomach?
Which blood vessels are primarily responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the intestine?
Which blood vessels are primarily responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the intestine?
Which function is NOT associated with the gastrointestinal tract?
Which function is NOT associated with the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the role of pepsin in the stomach?
What is the role of pepsin in the stomach?
Which of the following statements about the GI tract is correct?
Which of the following statements about the GI tract is correct?
What type of muscle forms the internal and external anal sphincters?
What type of muscle forms the internal and external anal sphincters?
Which section of the small intestine is responsible for the bulk of nutrient absorption?
Which section of the small intestine is responsible for the bulk of nutrient absorption?
What is the primary digestive function of the stomach's acidic secretions?
What is the primary digestive function of the stomach's acidic secretions?
What initiates peristalsis in the esophagus?
What initiates peristalsis in the esophagus?
What is the approximate length of the small intestine?
What is the approximate length of the small intestine?
Which of the following veins contribute to the portal venous system?
Which of the following veins contribute to the portal venous system?
What is the recommended position for performing a rectal examination that many patients find comfortable?
What is the recommended position for performing a rectal examination that many patients find comfortable?
What should the examiner observe for during the external examination of the rectal area?
What should the examiner observe for during the external examination of the rectal area?
What physical response indicates that additional rectal abnormalities may be visible during an examination?
What physical response indicates that additional rectal abnormalities may be visible during an examination?
What is a key nursing intervention for patients undergoing GI diagnostic evaluation?
What is a key nursing intervention for patients undergoing GI diagnostic evaluation?
What kind of tests are commonly performed as initial serum laboratory studies?
What kind of tests are commonly performed as initial serum laboratory studies?
What characteristics are assessed during the inspection of stool specimens?
What characteristics are assessed during the inspection of stool specimens?
What dietary restrictions should patients follow before undergoing guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing?
What dietary restrictions should patients follow before undergoing guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing?
What is indicated when carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is detected in blood tests?
What is indicated when carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is detected in blood tests?
Which condition can both tenderness and inflammation in the rectal area suggest?
Which condition can both tenderness and inflammation in the rectal area suggest?
Why are bowel preparations particularly challenging for older adults during GI evaluations?
Why are bowel preparations particularly challenging for older adults during GI evaluations?
What sort of stool studies require laboratory evaluation beyond basic inspection?
What sort of stool studies require laboratory evaluation beyond basic inspection?
How should stool samples be handled for quantitative studies?
How should stool samples be handled for quantitative studies?
What type of behaviors might be recommended for a patient during an internal examination to reduce discomfort?
What type of behaviors might be recommended for a patient during an internal examination to reduce discomfort?
What is the role of tumor markers like CA 19-9 in cancer management?
What is the role of tumor markers like CA 19-9 in cancer management?
What is a necessary preparation step for a patient scheduled to undergo a barium enema?
What is a necessary preparation step for a patient scheduled to undergo a barium enema?
What condition contraindicates the use of barium enemas?
What condition contraindicates the use of barium enemas?
How can post-procedural complications from an IV contrast agent be minimized?
How can post-procedural complications from an IV contrast agent be minimized?
What is a primary use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in gastroenterology?
What is a primary use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in gastroenterology?
What is a risk associated with the use of IV contrast agents during imaging studies?
What is a risk associated with the use of IV contrast agents during imaging studies?
What is an essential patient preparation step before an MRI?
What is an essential patient preparation step before an MRI?
Why are barium enemas scheduled before any upper gastrointestinal studies?
Why are barium enemas scheduled before any upper gastrointestinal studies?
Which statement is true regarding the CT scan procedure?
Which statement is true regarding the CT scan procedure?
Which of the following is NOT a reason for performing a CT scan?
Which of the following is NOT a reason for performing a CT scan?
What is a common fear that patients may experience during an MRI?
What is a common fear that patients may experience during an MRI?
What is the effect of barium's high osmolarity in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the effect of barium's high osmolarity in the gastrointestinal tract?
What common side effect might some patients experience after receiving a contrast agent?
What common side effect might some patients experience after receiving a contrast agent?
Which of the following describes the process of obtaining CT images?
Which of the following describes the process of obtaining CT images?
What is the main purpose of PET scans in diagnostic imaging?
What is the main purpose of PET scans in diagnostic imaging?
What is the purpose of administering midazolam before a procedure?
What is the purpose of administering midazolam before a procedure?
What is a common disadvantage of virtual colonoscopy?
What is a common disadvantage of virtual colonoscopy?
During gastroscopy, what monitoring is done post-procedure?
During gastroscopy, what monitoring is done post-procedure?
What is one of the goals of colonoscopic polypectomy?
What is one of the goals of colonoscopic polypectomy?
In which position is the patient typically placed during a colonoscopy?
In which position is the patient typically placed during a colonoscopy?
What is the purpose of administering atropine during endoscopic procedures?
What is the purpose of administering atropine during endoscopic procedures?
What complication can occur from medications given during colonoscopy?
What complication can occur from medications given during colonoscopy?
What is the main goal of bowel decompression during colonoscopy?
What is the main goal of bowel decompression during colonoscopy?
What does capsule colonoscopy involve?
What does capsule colonoscopy involve?
Which method is commonly used for effective cleansing of the bowel prior to colonoscopy?
Which method is commonly used for effective cleansing of the bowel prior to colonoscopy?
What is a key consideration for patients after undergoing moderate sedation?
What is a key consideration for patients after undergoing moderate sedation?
What is often monitored continuously during a colonoscopy?
What is often monitored continuously during a colonoscopy?
Why might a patient need a follow-up colonoscopy after capsule colonoscopy?
Why might a patient need a follow-up colonoscopy after capsule colonoscopy?
What does the use of biopsies during colonoscopy achieve?
What does the use of biopsies during colonoscopy achieve?
What is the primary purpose of an upper gastrointestinal (GI) series?
What is the primary purpose of an upper gastrointestinal (GI) series?
What is a common contrast agent used in an upper GI fluoroscopy?
What is a common contrast agent used in an upper GI fluoroscopy?
What is the purpose of the double-contrast method in an upper GI study?
What is the purpose of the double-contrast method in an upper GI study?
How long can the enteroclysis procedure take, even during normal motility?
How long can the enteroclysis procedure take, even during normal motility?
What is recommended for patients regarding dietary changes prior to an upper GI study?
What is recommended for patients regarding dietary changes prior to an upper GI study?
What is the purpose of using a barium enema during a lower GI study?
What is the purpose of using a barium enema during a lower GI study?
Which of the following is NOT considered a nursing intervention prior to an upper GI study?
Which of the following is NOT considered a nursing intervention prior to an upper GI study?
What type of imaging technique has largely replaced the need for double-contrast barium enemas?
What type of imaging technique has largely replaced the need for double-contrast barium enemas?
What adverse effect may a patient experience during a double-contrast barium enema?
What adverse effect may a patient experience during a double-contrast barium enema?
Which bowel-cleansing agent is considered most effective?
Which bowel-cleansing agent is considered most effective?
What is the main benefit of using methylcellulose during enteroclysis?
What is the main benefit of using methylcellulose during enteroclysis?
When is a water-soluble iodinated contrast agent used instead of barium for imaging?
When is a water-soluble iodinated contrast agent used instead of barium for imaging?
Which imaging modality is used to assess lesions or adhesions after an upper GI study?
Which imaging modality is used to assess lesions or adhesions after an upper GI study?
What radioactive isotopes are commonly used in scintigraphy?
What radioactive isotopes are commonly used in scintigraphy?
During gastric emptying studies, which meal component is tagged with radionuclide markers?
During gastric emptying studies, which meal component is tagged with radionuclide markers?
What is the purpose of tagging red blood cells in scintigraphic studies?
What is the purpose of tagging red blood cells in scintigraphic studies?
What is the recommended diet for patients prior to undergoing bowel preparation?
What is the recommended diet for patients prior to undergoing bowel preparation?
How are colonic transit studies conducted?
How are colonic transit studies conducted?
Which patient condition would contraindicate the use of lavage solutions for bowel preparation?
Which patient condition would contraindicate the use of lavage solutions for bowel preparation?
What dosage of sodium phosphate tablets is recommended for colon cleansing?
What dosage of sodium phosphate tablets is recommended for colon cleansing?
What does the use of electronic video endoscopes allow during an upper GI fibroscopy?
What does the use of electronic video endoscopes allow during an upper GI fibroscopy?
What is the expected duration for a patient to pass radionuclide markers in colonic transit studies?
What is the expected duration for a patient to pass radionuclide markers in colonic transit studies?
Which side effects are commonly associated with electrolyte solutions used in bowel preparation?
Which side effects are commonly associated with electrolyte solutions used in bowel preparation?
What is important to monitor in older patients following a bowel preparation?
What is important to monitor in older patients following a bowel preparation?
What is a common indication for performing an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)?
What is a common indication for performing an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)?
What precaution is necessary when performing an upper GI fibroscopy?
What precaution is necessary when performing an upper GI fibroscopy?
What type of patients should consult a cardiologist before a colonoscopy if they have specific devices?
What type of patients should consult a cardiologist before a colonoscopy if they have specific devices?
For what reason might a patient need to be NPO prior to an endoscopic examination?
For what reason might a patient need to be NPO prior to an endoscopic examination?
What is the role of glucagon during a colonoscopy procedure?
What is the role of glucagon during a colonoscopy procedure?
What must be done before performing a colonoscopy to ensure patient safety?
What must be done before performing a colonoscopy to ensure patient safety?
What is the role of sclerosing solutions during therapeutic endoscopy?
What is the role of sclerosing solutions during therapeutic endoscopy?
What method is used to assess gastric motility through non-invasive means?
What method is used to assess gastric motility through non-invasive means?
What is a common position for patients during a flexible sigmoidoscopy?
What is a common position for patients during a flexible sigmoidoscopy?
What can be performed during a flexible sigmoidoscopy if necessary?
What can be performed during a flexible sigmoidoscopy if necessary?
Which of the following is NOT a type of endoscopic procedure for GI tract assessment?
Which of the following is NOT a type of endoscopic procedure for GI tract assessment?
What is the purpose of monitoring vital signs during a colonoscopy procedure?
What is the purpose of monitoring vital signs during a colonoscopy procedure?
What is the primary purpose of scintigraphy in medical diagnostics?
What is the primary purpose of scintigraphy in medical diagnostics?
What technology is involved in capsule endoscopy for assessing the GI tract?
What technology is involved in capsule endoscopy for assessing the GI tract?
After a therapeutic colonoscopy, what should patients be specifically instructed to report?
After a therapeutic colonoscopy, what should patients be specifically instructed to report?
What type of sedation is commonly administered to provide comfort during a colonoscopy?
What type of sedation is commonly administered to provide comfort during a colonoscopy?
What should patients be informed about regarding the side effects of midazolam?
What should patients be informed about regarding the side effects of midazolam?
Flashcards
What is the length of the GI tract?
What is the length of the GI tract?
The GI tract is a long pathway extending from the mouth to the anus, measuring approximately 7 to 7.9 meters (23 to 26 feet) in length.
Where is the esophagus located?
Where is the esophagus located?
The esophagus is situated in the mediastinum, anterior to the spine and posterior to the trachea and heart.
What is the diaphragmatic hiatus?
What is the diaphragmatic hiatus?
The diaphragmatic hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes.
What are the four regions of the stomach?
What are the four regions of the stomach?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the pyloric sphincter?
What is the role of the pyloric sphincter?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is chyme?
What is chyme?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the gastroesophageal junction?
What is the gastroesophageal junction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the stomach?
What is the role of the stomach?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Intestine
Small Intestine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duodenum
Duodenum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Jejunum
Jejunum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ileum
Ileum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ileocecal Valve
Ileocecal Valve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large Intestine
Large Intestine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ascending Colon
Ascending Colon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Colon
Transverse Colon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Descending Colon
Descending Colon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sigmoid Colon
Sigmoid Colon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectum
Rectum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anus
Anus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Portal Venous System
Portal Venous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric Artery
Gastric Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mesenteric Arteries
Mesenteric Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the pyloric sphincter do?
What does the pyloric sphincter do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does digestion begin?
Where does digestion begin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do pancreatic secretions contribute to digestion?
What do pancreatic secretions contribute to digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is bile's role in digestion?
What is bile's role in digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What regulates the flow of bile?
What regulates the flow of bile?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are segmentation contractions?
What are segmentation contractions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is intestinal peristalsis?
What is intestinal peristalsis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to carbohydrates during digestion?
What happens to carbohydrates during digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to proteins during digestion?
What happens to proteins during digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to fats during digestion?
What happens to fats during digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are villi?
What are villi?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the major functions of the colon?
What are the major functions of the colon?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main components of feces?
What are the main components of feces?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main color contributor to feces?
What is the main color contributor to feces?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main gases found in flatus?
What are the main gases found in flatus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is the internal anal sphincter controlled?
How is the internal anal sphincter controlled?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is the external anal sphincter controlled?
How is the external anal sphincter controlled?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the gut microbiota?
What is the role of the gut microbiota?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is the gut microbiota established?
How is the gut microbiota established?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What factors influence the gut microbiota?
What factors influence the gut microbiota?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the gut microbiome?
What is the gut microbiome?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the protective roles of the gut microbiome?
What are the protective roles of the gut microbiome?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the first line of defense against pathogens in the intestines?
What is the first line of defense against pathogens in the intestines?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of Peyer's patches?
What is the role of Peyer's patches?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are common Gl symptoms that might lead to seeking healthcare?
What are common Gl symptoms that might lead to seeking healthcare?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is dyspepsia?
What is dyspepsia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is GERD and how does it relate to dyspepsia?
What is GERD and how does it relate to dyspepsia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
GERD
GERD
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intestinal Gas
Intestinal Gas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bloating
Bloating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nausea
Nausea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vomiting
Vomiting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hematemesis
Hematemesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mallory-Weiss Tear
Mallory-Weiss Tear
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diarrhea
Diarrhea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Constipation
Constipation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melena
Melena
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stool with Mucus
Stool with Mucus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clay-Colored Stool
Clay-Colored Stool
Signup and view all the flashcards
Past Medical History
Past Medical History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Family History
Family History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social History
Social History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
FIT-Fecal DNA Test
FIT-Fecal DNA Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrogen Breath Test
Hydrogen Breath Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urea Breath Test
Urea Breath Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abdominal Ultrasonography
Abdominal Ultrasonography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS)
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lynch Syndrome
Lynch Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic Risk Assessment
Genetic Risk Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic Counseling
Genetic Counseling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preclinical Diagnosis
Preclinical Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prenatal Diagnosis
Prenatal Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric Cancer
Gastric Cancer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lactose Deficiency
Lactose Deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Stensen's duct?
What is Stensen's duct?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the key gum inspections?
What are the key gum inspections?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of assessing the tongue?
What is the purpose of assessing the tongue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the 'V' formation on the tongue's back?
What is the 'V' formation on the tongue's back?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do we inspect the pharynx?
How do we inspect the pharynx?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does a symmetrical rise of the uvula and soft palate indicate?
What does a symmetrical rise of the uvula and soft palate indicate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of abdominal quadrant division?
What is the purpose of abdominal quadrant division?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the key aspects of abdominal inspection?
What are the key aspects of abdominal inspection?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why does auscultation precede percussion and palpation?
Why does auscultation precede percussion and palpation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are normal bowel sounds?
What are normal bowel sounds?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does percussion of the abdomen reveal?
What does percussion of the abdomen reveal?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the two types of palpation?
What are the two types of palpation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the tools needed for rectal examination?
What are the tools needed for rectal examination?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is a rectal examination necessary?
Why is a rectal examination necessary?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the internal and external sphincters?
What are the internal and external sphincters?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the positions used for a rectal examination?
What are the positions used for a rectal examination?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What should the examiner look for during an external rectal examination?
What should the examiner look for during an external rectal examination?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What might tenderness or inflammation during rectal examination indicate?
What might tenderness or inflammation during rectal examination indicate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens during the internal rectal examination?
What happens during the internal rectal examination?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of diagnostic gastrointestinal (GI) studies?
What is the purpose of diagnostic gastrointestinal (GI) studies?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some common GI diagnostic test preparations?
What are some common GI diagnostic test preparations?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some initial serum laboratory studies for GI evaluation?
What are some initial serum laboratory studies for GI evaluation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and its significance?
What is carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and its significance?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is stool examination used for?
What is stool examination used for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT)?
What is guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some factors that can affect gFOBT results?
What are some factors that can affect gFOBT results?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are general nursing interventions for a patient undergoing a GI diagnostic evaluation?
What are general nursing interventions for a patient undergoing a GI diagnostic evaluation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some common GI symptoms that might lead to seeking healthcare?
What are some common GI symptoms that might lead to seeking healthcare?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the gut microbiota, and how is it established?
What is the role of the gut microbiota, and how is it established?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some factors that influence the gut microbiota?
What are some factors that influence the gut microbiota?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper GI Study
Upper GI Study
Signup and view all the flashcards
Barium Sulfate
Barium Sulfate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Bowel Follow-through
Small Bowel Follow-through
Signup and view all the flashcards
Double-contrast Study
Double-contrast Study
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enteroclysis
Enteroclysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower GI Study
Lower GI Study
Signup and view all the flashcards
Barium Enema
Barium Enema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Double-contrast Barium Enema
Double-contrast Barium Enema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water-soluble Contrast Agent
Water-soluble Contrast Agent
Signup and view all the flashcards
NPO (Nil per os)
NPO (Nil per os)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
CT Colonography
CT Colonography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Restrictions Before Imaging
Dietary Restrictions Before Imaging
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follow-up Care After Upper GI Procedure
Follow-up Care After Upper GI Procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissue Handling for Pathology
Tissue Handling for Pathology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Bowel Studies Prep
Small Bowel Studies Prep
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nursing Monitoring During Procedure
Nursing Monitoring During Procedure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Procedure Monitoring
Post-Procedure Monitoring
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small Bowel Studies Recovery
Small Bowel Studies Recovery
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Scintigraphy?
What is Scintigraphy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Scintigraphy show inflammation?
How does Scintigraphy show inflammation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Scintigraphy help find internal bleeding?
How does Scintigraphy help find internal bleeding?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Gastric Emptying Study?
What is Gastric Emptying Study?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Colonic Transit Study work?
How does Colonic Transit Study work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is EGD (Esophagogastroduodenoscopy)?
What is EGD (Esophagogastroduodenoscopy)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is PillCam ESO?
What is PillCam ESO?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)?
What is ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some therapeutic uses of EGD?
What are some therapeutic uses of EGD?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some Nursing Interventions for EGD?
What are some Nursing Interventions for EGD?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Anoscopy?
What is Anoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Proctoscopy?
What is Proctoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Sigmoidoscopy?
What is Sigmoidoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Small-Bowel Enteroscopy?
What is Small-Bowel Enteroscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is midazolam used for during endoscopy?
What is midazolam used for during endoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is the patient positioned in the left lateral position for endoscopy?
Why is the patient positioned in the left lateral position for endoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some signs to monitor for after gastroscopy?
What are some signs to monitor for after gastroscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a virtual colonoscopy?
What is a virtual colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main disadvantage of virtual colonoscopy?
What is the main disadvantage of virtual colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of a colonoscopy?
What is the purpose of a colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the most common use of colonoscopy?
What is the most common use of colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some other uses of colonoscopy?
What are some other uses of colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is colonoscopic polypectomy?
What is colonoscopic polypectomy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is a colonoscopy performed?
How is a colonoscopy performed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some potential complications of colonoscopy?
What are some potential complications of colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is capsule colonoscopy?
What is capsule colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What makes a successful colonoscopy?
What makes a successful colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the methods for bowel preparation before colonoscopy?
What are the methods for bowel preparation before colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the benefits of colonoscopy?
What are the benefits of colonoscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Barium Enema Preparation
Barium Enema Preparation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Barium Enema Contraindications
Barium Enema Contraindications
Signup and view all the flashcards
CT Scan for Abdominal Issues
CT Scan for Abdominal Issues
Signup and view all the flashcards
CT Scan Contrast Agent Risks
CT Scan Contrast Agent Risks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventing Contrast-Induced Nephropathy
Preventing Contrast-Induced Nephropathy
Signup and view all the flashcards
MRI in Gastroenterology
MRI in Gastroenterology
Signup and view all the flashcards
MRI Contraindications and Precautions
MRI Contraindications and Precautions
Signup and view all the flashcards
PET Scan Technique
PET Scan Technique
Signup and view all the flashcards
PET Scan Radioactive Substances
PET Scan Radioactive Substances
Signup and view all the flashcards
Barium Enema Post-Procedure Education
Barium Enema Post-Procedure Education
Signup and view all the flashcards
CT Scan Nursing Interventions
CT Scan Nursing Interventions
Signup and view all the flashcards
MRI Nursing Interventions
MRI Nursing Interventions
Signup and view all the flashcards
MRI Claustrophobia Management
MRI Claustrophobia Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
CT Scan Benefits vs Risks
CT Scan Benefits vs Risks
Signup and view all the flashcards
PET Scan Applications
PET Scan Applications
Signup and view all the flashcards
PET Scan Procedure Overview
PET Scan Procedure Overview
Signup and view all the flashcards
PET Scan Interpretation
PET Scan Interpretation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Split Prep
Split Prep
Signup and view all the flashcards
Low-Residue Diet
Low-Residue Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium Phosphate Tablets
Sodium Phosphate Tablets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electrolyte Solutions
Electrolyte Solutions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lavage Solutions
Lavage Solutions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contraindications for Lavage Solutions
Contraindications for Lavage Solutions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monitoring Older Adults after Bowel Preparation
Monitoring Older Adults after Bowel Preparation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantable Defibrillators/Pacemakers and Colonoscopy
Implantable Defibrillators/Pacemakers and Colonoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contraindications for Colonoscopy
Contraindications for Colonoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prophylactic Antibiotics for Colonoscopy
Prophylactic Antibiotics for Colonoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moderate Sedation for Colonoscopy
Moderate Sedation for Colonoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon for Colonoscopy
Glucagon for Colonoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monitoring During Colonoscopy
Monitoring During Colonoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Colonoscopy Recovery
Post-Colonoscopy Recovery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexible Fiberoptic Sigmoidoscopy
Flexible Fiberoptic Sigmoidoscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
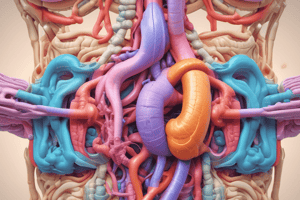
Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Assessment
- GI tract abnormalities encompass various pathologies: bleeding, perforation, obstruction, inflammation, and cancer.
- Factors impacting GI function include congenital, inflammatory, infectious, traumatic, and neoplastic lesions.
- Extrinsic factors (stress, anxiety, fatigue, dietary changes) can also affect GI function.
Anatomic and Physiologic Overview
- The GI tract extends ~7-7.9 m (23-26 feet) from the mouth to the anus.
- The esophagus, ~25 cm (10 inches) long, connects the pharynx to the stomach, passing through the diaphragmatic hiatus.
- The stomach (capacity ~1500mL) stores food, secretes digestive fluids, and propels chyme into the small intestine. Regions: cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus (with pyloric sphincter).
- The small intestine (~70m surface area) is the longest segment, consisting of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum; ending at the ileocecal valve (regulates flow to large intestine). The appendix is attached to the cecum. The common bile duct empties into the duodenum.
- The large intestine includes ascending, transverse, and descending segments, as well as the sigmoid colon, rectum, and anus. Anal sphincters (internal and external) regulate stool elimination (internal is involuntary, external is voluntary).
- Blood supply to the GI tract is about 20% of cardiac output, increasing after meals. Major arteries include gastric, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries. The superior mesenteric vein drains small intestine and parts of large intestine corresponding to those arteries.
- The autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic) innervates the GI tract. Sympathetic nerves inhibit, parasympathetic stimulate activity.
Function of the Digestive System
- Major functions include food breakdown, nutrient absorption (into bloodstream), and waste elimination.
- Secretions help digest, absorb, or eliminate food throughout the GI tract.
Chewing and Swallowing
- Digestion begins with chewing (mechanical breakdown), triggering reflex salivation (1.5L/day from parotid, submaxillary, and sublingual glands).
- Saliva contains enzymes (ptyalin/salivary amylase), water, and mucus to lubricate food for swallowing.
- Swallowing is initially voluntary (controlled by medulla oblongata) then becomes a reflex propelling food through the esophagus.
- Esophageal peristalsis forces food to stomach, and the lower esophageal sphincter prevents reflux.
Gastric Function
- The stomach stores and mixes food with highly acidic fluid (pH ~1, total ~2.4L/day), containing hydrochloric acid (HCl) to break down food and kill bacteria.
- Pepsin (from pepsinogen) is a main protein-digesting enzyme.
- Intrinsic factor, needed for B12 absorption (lack leads to pernicious anemia), is secreted by gastric mucosa.
- Stomach contents (chyme) are mixed and propelled toward pylorus. This process breaks down large particles.
- Food remains in stomach for 30 minutes to several hours based on factors. Hormones, neuroregulators and local substances control gastric secretions and motility.
Small Intestine Function
- Digestive process continues in the duodenum – secretions from pancreas, liver, and gallbladder help.
- Pancreatic juice, has alkaline pH (bicarbonate) to neutralize acidic chyme. Digestive enzymes (trypsin, amylase, lipase) break down protein, starch and fat respectively.
- Bile from liver (stored in gallbladder) emulsifies fats ("breaks them down into smaller pieces"). The sphincter of Oddi regulates bile flow.
- Segmentation contractions mix intestinal contents, and peristalsis moves contents. Nutrients are broken down and absorbed in small intestine for 3 to 6 hours.
- Villi (finger-like projections) increase surface area for absorption. Nutrients (Vitamins, minerals) are absorbed via active transport and diffusion. Specific locations for absorption: Jejunum and duodenum (fats, proteins, carbs, sodium, chloride), ileum (B12 and bile salts), and throughout the small intestine (Mg, phos, potassium).
Colonic Function
- Residual waste from meal enters large intestine (through ileocecal valve).
- Gut microbes help break down undigested food and bile.
- Secretions (electrolytes, bicarbonate solution and mucus) added to waste material.
- Colonic peristalsis reabsorbs water and electrolytes.
- Waste materials enter the rectum typically within 12 hours, though some can remain for 3 days.
Waste Products of Digestion
- Feces consist of undigested food, inorganic materials, water, and bacteria.
- About 75% of feces is fluid, 25% solid.
- Color and odor derive from bile breakdown and gut bacteria.
Elimination of Stool
- Rectal distention initiates reflex contractions and relax sphincters. Defecation is voluntary (external sphincter).
- Abdominal muscle contractions aid in stool elimination. Regular defecation is usually one time a day, although this is variable.
Gut Microbiome
- Gut microbiota plays a role in vitamin synthesis, immune function (against pathogens), innate and adaptive immunity regulation, inflammation, and protection.
- Established by ~2 years old
- Affected by genetics, diet, hygiene, and infections, and aging
Gerontologic Considerations
- Aging has minimal effect on most GI functions, due to functional reserve.
- Some GI disorders (e.g., dysphagia, dyspepsia) may increase in frequency.
- Irritable bowel symptoms may decrease.
Assessment of the Gastrointestinal System
- Assessment includes health history and physical examination (oral cavity, abdomen, and rectum).
Health History
- Question patient about GI symptoms (pain, dyspepsia, gas, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, fecal incontinence, jaundice, and previous GI disease).
Common Symptoms
- GI symptoms leading to healthcare referrals include pain, dyspepsia, gas, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
Pain
- Character, duration, pattern, frequency, location, referred pain, and time of pain are key factors. Meals, rest, activity, and defecation impact pain.
Dyspepsia
- Upper abdominal discomfort after eating, often called heartburn or indigestion, affect ~25% of Americans.
Intestinal Gas
- Gas accumulation (belching and flatulence) can result from issues such as food intolerance or gallbladder disease leading to bloating and distention.
Nausea and Vomiting
- Nausea signals sickness, possibly indicating a pathologic process or caused by odors, activity, medications, or foods.
- Vomiting is forceful emptying of stomach and intestinal contents. Emesis or vomitus may vary in color/content. Acute bright/coffee ground vomitus = potential upper GI bleeding (e.g., Mallory-Weiss tear). Many factors affect vomiting.
Change in Bowel Habits and Stool Characteristics
- Changes relate to colonic issues.
- Diarrhea (increased frequency/liquidity) occurs when contents pass quickly.
- Constipation (decreased frequency or hard/dry stools), linked with discomfort and bleeding.
- Stool color (light to dark brown), consistency, and presence of blood can help diagnose.
Past Health, Family, and Social History
- Evaluate patient’s dental hygiene and routine and nutritional history
- Determine risk factors like tobacco/alcohol use. Consider dietary changes. Assess for weight changes.
Physical Assessment
- Inspect the mouth (lips, gums, tongue, pharynx) for signs of inflammation/lesions. Examine abdomen for skin changes, contour, symmetry, and presence of peristaltic waves. (four or nine quadrants).
- Auscultate for bowel sounds (normal, hyperactive, hypoactive/absent). Listen for vascular sounds and friction rubs.
- Percuss to assess organ size & density, detecting air/fluid/solid masses.
- Rectal examination checks the terminal GI tract (internal/external sphincters and internal organs).
Diagnostic Evaluation
- Multiple modalities assess GI tract (serum tests, stool tests, breath tests, imaging, endoscopic procedures).
- Patient preparation varies depending on the test chosen (diet, medications, etc.).
Serum Laboratory Studies
- Initial tests include complete blood count, complete metabolic panel, clotting times, triglycerides, liver function tests, amylase, lipase, and potentially tumor markers (CEA). Serum tests help diagnose and monitor GI disorders including cancer.
Stool Tests
- Stool examination assesses consistency, color, and presence of occult blood. Collect random/quantitative samples following instructions/dietary restrictions as needed depending on specific test.
- Fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT) is common for initial screening (avoid red meat, aspirin, NSAIDs, vitamin C for 72hrs pre-test) but is not used when hemorrhoidal bleeding is present. Sensitive alternative tests like FIT exist (avoiding factors like gFOBT.)
Breath Tests
- Hydrogen breath test evaluates carbohydrate absorption and bacterial overgrowth. Urea breath test detects H. pylori infection, specific instructions before the test regarding use of medications/antibiotics required.
Abdominal Ultrasonography
- Noninvasive technique using sound waves to image abdominal structures. Assess gallbladder, liver, pancreas, ovaries. Limited by patient body type, bowel gas, operator experience.
Endoscopic Ultrasonography
- Specialized endoscopic procedure for detailed GI imaging, useful for deeper examination.
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Study
- Fluoroscopy views the upper GI tract after contrast agent administration. Identify and rule out abnormalities (ulcers, varices, tumors.) Double-contrast studies for detailed visualization of upper GI tissues. Enteroclysis is used for precise visualization for small bowel issues. Prepare patient with dietary modifications (low residue or clear liquids) and withholding medications and substances. Increased hydration is recommended after procedure.
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Study
- Barium enema visualizes the large intestine. Other methods (double contrast, water-soluble contrast) also used to identify polyps, tumors, and abnormalities. Preparation is critical for visualizing the GI tract.
Computed Tomography (CT)
- Cross-sectional images of abdominal organs using multiple x-rays, digitized, and reconstructed. High-resolution imaging and shorter scan times, and less artifact created, and detection of inflammatory conditions (e.g., appendicitis.) Prepare patient regarding pre-test medications. Consider patient and clinician need for contrast, weigh risk factors. (allergies, kidney function and pregnancy status).
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Uses magnetic fields and radio waves. May use oral contrast to enhance image quality. Useful in GI assessment of soft tissues and blood vessels. Important considerations related to ferromagnetic objects need to be made.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- Detects radiation emitted from radioactive substances after injection to identify areas of heightened metabolism. Used to diagnose malignant/benign tumors and staging.
Scintigraphy (Radionuclide Testing)
- Uses radioactive isotopes. Evaluate organ function, size/shapes, neoplasms. Assess bleeding locations, inflammation. Assess for patient allergies, especially those related to the contrast.
Gastrointestinal Motility Studies
- Radionuclide studies assess gastric emptying and colonic transit time measuring rate substances pass through the parts of the GI tract. Studies used for evaluation of GI motility/obstructions
Endoscopic Procedures
- Various scopes (fibroscopy/EGD, colonoscopy, anoscopy, proctoscopy, sigmoidoscopy) provide direct visualization of GI tract sections. Capsule endoscopy (pillcam ESO) is useful for upper GI tract issues.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) assists in visualization of bile ducts and pancreatic ducts. This procedure can be therapeutic (removing stones, dilating strictures. Important considerations related to patient safety should be addressed.
Nursing Interventions
- Nursing care emphasizes patient education, pre- and post-procedure care, comfort, and addressing patient's risks (especially older adults and patients with comorbities) and patient safety and risks concerning medications, allergies, and complications. Monitor pertinent parameters like vital signs, fluid/electrolyte balance, and oxygen saturation levels.
Genetic Testing
- Recent research has improved risk assessment, preclinical diagnosis, and prenatal diagnosis of genetic GI disorders. Genetic counseling options, and preventing and treating the disease exist, and are available for those detected to be at risk
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.