Podcast
Questions and Answers
What happens to the levels of carbon dioxide in exhaled air as compared to inhaled air?
What happens to the levels of carbon dioxide in exhaled air as compared to inhaled air?
- They remain the same.
- They are eliminated completely.
- They increase. (correct)
- They decrease.
Which component of the breathing system is primarily responsible for the exchange of gases?
Which component of the breathing system is primarily responsible for the exchange of gases?
- Diaphragm.
- Alveoli. (correct)
- Trachea.
- Bronchi.
When air flows into the human breathing system, which sequence correctly describes the pathway taken?
When air flows into the human breathing system, which sequence correctly describes the pathway taken?
- Nose → Bronchi → Larynx → Alveoli.
- Nose → Pharynx → Trachea → Bronchi → Alveoli. (correct)
- Mouth → Trachea → Pharynx → Bronchi → Alveoli.
- Mouth → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchi → Alveoli.
What action occurs in the respiratory system during inhalation?
What action occurs in the respiratory system during inhalation?
Why is it essential for the body to remove carbon dioxide produced by body cells?
Why is it essential for the body to remove carbon dioxide produced by body cells?
What is the primary effect of carbon monoxide on blood?
What is the primary effect of carbon monoxide on blood?
How does smoking lead to decreased efficiency of gas exchange?
How does smoking lead to decreased efficiency of gas exchange?
Which respiratory disease is characterized by the destruction of air sac walls?
Which respiratory disease is characterized by the destruction of air sac walls?
What effect does inflammation have on bronchi and bronchioles in chronic bronchitis?
What effect does inflammation have on bronchi and bronchioles in chronic bronchitis?
What is one consequence of increased mucus secretion in chronic bronchitis?
What is one consequence of increased mucus secretion in chronic bronchitis?
What occurs to the surface area for gas exchange in smokers compared to non-smokers?
What occurs to the surface area for gas exchange in smokers compared to non-smokers?
Which of the following factors is associated with the development of emphysema?
Which of the following factors is associated with the development of emphysema?
What is a common outcome for individuals suffering from emphysema?
What is a common outcome for individuals suffering from emphysema?
What is the initial structure involved in the path of air flow when breathing in?
What is the initial structure involved in the path of air flow when breathing in?
Which structure is primarily responsible for gas exchange in the lungs?
Which structure is primarily responsible for gas exchange in the lungs?
What role do the capillaries play in the air sac during gas exchange?
What role do the capillaries play in the air sac during gas exchange?
What is the correct order of air flow starting from the nasal cavity during inhalation?
What is the correct order of air flow starting from the nasal cavity during inhalation?
Which statement accurately describes the difference between inhaled and exhaled air?
Which statement accurately describes the difference between inhaled and exhaled air?
Which structure helps in the process of breathing by contracting and expanding?
Which structure helps in the process of breathing by contracting and expanding?
What occurs to the temperature of the air as it passes through the air sacs?
What occurs to the temperature of the air as it passes through the air sacs?
What is the primary function of bronchi in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of bronchi in the respiratory system?
Why is the inhaled air moistened by the water on the surface of the air sacs?
Why is the inhaled air moistened by the water on the surface of the air sacs?
During exhalation, which path does air take as it exits the lungs?
During exhalation, which path does air take as it exits the lungs?
What is the primary gas that moves from the air sac into the blood?
What is the primary gas that moves from the air sac into the blood?
What role do capillaries play in the respiratory process?
What role do capillaries play in the respiratory process?
Which of the following statements about air composition is incorrect?
Which of the following statements about air composition is incorrect?
Which part of the respiratory system is primarily involved in producing sound?
Which part of the respiratory system is primarily involved in producing sound?
What effect does gas exchange have on the temperature of exhaled air?
What effect does gas exchange have on the temperature of exhaled air?
What misconception is commonly held regarding inhaled and exhaled air?
What misconception is commonly held regarding inhaled and exhaled air?
What happens to lung tissue when squeezed in water?
What happens to lung tissue when squeezed in water?
Which gas is primarily transported from the air sacs to the blood during inhalation?
Which gas is primarily transported from the air sacs to the blood during inhalation?
What role does carbon dioxide play in the respiratory process?
What role does carbon dioxide play in the respiratory process?
How does blood assist in the gas exchange process?
How does blood assist in the gas exchange process?
What occurs in the air sacs after inhalation?
What occurs in the air sacs after inhalation?
What is the primary purpose of gas exchange in the air sacs?
What is the primary purpose of gas exchange in the air sacs?
Which statement best describes the movement of carbon dioxide during exhalation?
Which statement best describes the movement of carbon dioxide during exhalation?
Flashcards
Exhaled air
Exhaled air
Air breathed out of the lungs.
Inhaled air
Inhaled air
Air breathed into the lungs.
Oxygen content
Oxygen content
Amount of oxygen in the air.
Candle experiment
Candle experiment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Burning candle
Burning candle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Safety spectacles
Safety spectacles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas jar
Gas jar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cover plate
Cover plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Airflow path (inhaling)
Airflow path (inhaling)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Airflow path (exhaling)
Airflow path (exhaling)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breathing In
Breathing In
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breathing Out
Breathing Out
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon Dioxide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lung tissue
Lung tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bubbles from lung tissue
Bubbles from lung tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air sacs
Air sacs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas exchange
Gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen in the air sacs
Oxygen in the air sacs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood carries oxygen
Blood carries oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon dioxide production
Carbon dioxide production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon dioxide removal
Carbon dioxide removal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobalt Chloride Paper Color Change
Cobalt Chloride Paper Color Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why Does Exhaled Air Have More Water Vapor?
Why Does Exhaled Air Have More Water Vapor?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What Happens When You Breathe?
What Happens When You Breathe?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange in Humans
Gas Exchange in Humans
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Breathing System
Human Breathing System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiration
Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide in Exhaled Air
Carbon Dioxide in Exhaled Air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen in Inhaled Air
Oxygen in Inhaled Air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air Sac Function
Air Sac Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange in Air Sacs
Gas Exchange in Air Sacs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhaled Air vs. Inhaled Air
Exhaled Air vs. Inhaled Air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air Sac Moistening
Air Sac Moistening
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air Sac Warming
Air Sac Warming
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillary Role in Gas Exchange
Capillary Role in Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Movement
Oxygen Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide Movement
Carbon Dioxide Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Black tar deposits
Black tar deposits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reduced oxygen carrying capacity
Reduced oxygen carrying capacity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Damaged air sacs
Damaged air sacs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emphysema
Emphysema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is gas exchange less efficient in these diseases?
Why is gas exchange less efficient in these diseases?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the effect of carbon monoxide on the blood?
What is the effect of carbon monoxide on the blood?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do damaged air sacs affect gas exchange?
How do damaged air sacs affect gas exchange?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Gas Exchange in Animals
- Gas exchange occurs in animals as well as plants
- Practical 7.12 investigates carbon dioxide uptake/release by mealworms
- Experiment involves boiling tubes, mealworms, forceps, cotton thread, stoppers, and hydrogencarbonate indicator
- 3 cm³ of hydrogencarbonate indicator is added to two tubes (A and B)
- The initial colour of the indicator in each tube is recorded
- Mealworms are placed in a plastic vial with small holes and put into tube A
- The vial is placed in tube A, ensuring mealworms don't touch indicator
- The tubes are stoppered to prevent air leakage
- The setup is left for one hour
- The colour of the indicator in each tube is recorded after one hour
- Practical 7.13 investigates oxygen uptake/release by mealworms
- The experiment involves boiling tubes, wire gauze, capillary tubes (with colour markers), ruler, soda lime, and mealworms
- In Practical 7.14, inhaled and exhaled air oxygen and carbon dioxide content is compared
- Inhaled air is different from exhaled air, it contains more oxygen and less carbon dioxide
- Practical 7.15 dissects pig lungs to observe their structure
- Your teacher will guide you through the dissection and identification of pig lungs, trachea and bronchi, observe the color in the lungs
- Observe the tissue, and the tracheal differences between those that smoke and those that do not
- Practical 7.3 investigates the effects of smoking on pig lungs
- In the experiment, cigarette smoke is introduced into pig lungs, observing colour and tissue differences
- Tar and other chemicals in cigarette smoke decrease breathing efficiency
- Carbon monoxide reduces oxygen carrying ability in blood
- Smoking damages air sacs, decreasing their surface area for gas exchange
- Smoking causes diseases like emphysema, chronic bronchitis, heart disease, stroke, lung cancer and mouth cancer
- Smoking leads to decreased life expectancy
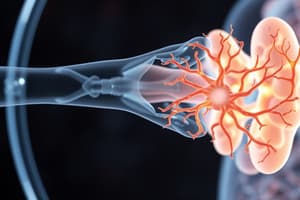
Gas Exchange in Humans
- The human breathing system facilitates gas exchange
- Main parts of the system, such as the nasal cavity, nostrils, trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles, air sacs, diaphragm, and intercostal muscles are involved in bringing oxygen into the body and exhaling carbon dioxide
- Oxygen from the inhaled air enters the blood in the capillaries inside the air sacs
- Carbon dioxide in the blood moves from the capillaries into the air sacs when exhales.
- The air sacs are warmed and moistened by the blood capillaries
- The exhaled air is warmer and contains more water vapor than inhaled air
Gas Exchange at Air Sacs
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between air sacs and the blood in surrounding capillaries
- Inhaled air enters the air sacs, oxygen moves into the bloodstream, and the blood carries oxygen to body cells for respiration
- The body cells produce carbon dioxide; blood carries the carbon dioxide back to the air sacs
- Carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the air sacs; it's removed during exhalation
- Air in the sacs are moisturized by water and warmed by the blood in the capillaries
- Exhaled air is warmer and contains more water vapor than inhaled air
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.