Podcast
Questions and Answers
What precautions should be taken when handling mealworms?
What precautions should be taken when handling mealworms?
- Rinse them with water before handling.
- Leave them uncovered.
- Wear disposable gloves. (correct)
- Use bare hands.
What is required to prevent air leakage during the experiment?
What is required to prevent air leakage during the experiment?
- Use a larger container.
- Use an open container.
- Leave the tubes partially open.
- Stopper the tubes securely. (correct)
What does a color change in the hydrogencarbonate indicator signify?
What does a color change in the hydrogencarbonate indicator signify?
- Gas exchange occurring. (correct)
- Growth of mealworms.
- Increased gel formation.
- Decrease in temperature.
What is the expected result for tube A if the mealworms are respiring?
What is the expected result for tube A if the mealworms are respiring?
Which of the following would not be a reason for placing tube B in the setup?
Which of the following would not be a reason for placing tube B in the setup?
What condition is essential for the integrity of the measurement in the experiment?
What condition is essential for the integrity of the measurement in the experiment?
What outcome is suggested if the indicator in tube B remains unchanged?
What outcome is suggested if the indicator in tube B remains unchanged?
Why should air leakage be avoided during the experimental setup?
Why should air leakage be avoided during the experimental setup?
What is one of the primary substances in cigarette smoke that negatively impacts gas exchange in pig lungs?
What is one of the primary substances in cigarette smoke that negatively impacts gas exchange in pig lungs?
How does the presence of tar in the lungs affect breathing efficiency?
How does the presence of tar in the lungs affect breathing efficiency?
What role does the large total surface area play in gas exchange?
What role does the large total surface area play in gas exchange?
What visual difference might you observe between the pig lungs exposed to smoke and those not exposed?
What visual difference might you observe between the pig lungs exposed to smoke and those not exposed?
What happens to inhaled air once it reaches the air sacs?
What happens to inhaled air once it reaches the air sacs?
In a comparison of the tracheas from both sets of pig lungs, which statement is likely true?
In a comparison of the tracheas from both sets of pig lungs, which statement is likely true?
Where does gas exchange occur in fish?
Where does gas exchange occur in fish?
What is one consequence of smoking on the respiratory system?
What is one consequence of smoking on the respiratory system?
Which effect does cigarette smoke have on the air sacs in the lungs?
Which effect does cigarette smoke have on the air sacs in the lungs?
What gas is primarily exchanged in the capillaries at the air sacs?
What gas is primarily exchanged in the capillaries at the air sacs?
In which animals does gas exchange occur through both lungs and moist skin?
In which animals does gas exchange occur through both lungs and moist skin?
When observing the smoking pig lungs versus the non-smoking ones, which statement about lung tissue is correct?
When observing the smoking pig lungs versus the non-smoking ones, which statement about lung tissue is correct?
How does exhaled air differ from inhaled air in terms of water vapor content?
How does exhaled air differ from inhaled air in terms of water vapor content?
What unique feature do salamanders use for gas exchange?
What unique feature do salamanders use for gas exchange?
What is a possible consequence of the reduced efficiency of gas exchange due to cigarette smoke?
What is a possible consequence of the reduced efficiency of gas exchange due to cigarette smoke?
What misconception is highlighted regarding inhaled and exhaled air?
What misconception is highlighted regarding inhaled and exhaled air?
Which of the following statements is NOT true about gas exchange structures in animals?
Which of the following statements is NOT true about gas exchange structures in animals?
Which of the following chemicals in cigarette smoke contributes to decreased oxygen absorption in the lungs?
Which of the following chemicals in cigarette smoke contributes to decreased oxygen absorption in the lungs?
What role do capillaries play in the gas exchange process?
What role do capillaries play in the gas exchange process?
In terms of temperature, how do inhaled and exhaled air differ?
In terms of temperature, how do inhaled and exhaled air differ?
Which statement best describes the impact of total surface area on gas exchange efficacy?
Which statement best describes the impact of total surface area on gas exchange efficacy?
Why is it important that air is moistened in the air sacs?
Why is it important that air is moistened in the air sacs?
How many chemicals are inhaled when one smokes?
How many chemicals are inhaled when one smokes?
What is the primary function of air sacs in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of air sacs in the respiratory system?
What is the primary purpose of the practical involving pig lungs?
What is the primary purpose of the practical involving pig lungs?
What should be done to the lungs before and after the practical session?
What should be done to the lungs before and after the practical session?
How do the lungs feel when pressed gently?
How do the lungs feel when pressed gently?
What occurs to the volume of the lungs when air is pumped into them?
What occurs to the volume of the lungs when air is pumped into them?
Upon cutting open the trachea, which structure is directly observed branching off?
Upon cutting open the trachea, which structure is directly observed branching off?
What is the significance of observing the colour of the lungs during the dissection?
What is the significance of observing the colour of the lungs during the dissection?
What tool is used to pump air into the pig lungs during the demonstration?
What tool is used to pump air into the pig lungs during the demonstration?
What happens to the lung tissue when it is placed in water?
What happens to the lung tissue when it is placed in water?
What is the primary difference in gas composition between exhaled air and inhaled air?
What is the primary difference in gas composition between exhaled air and inhaled air?
What role does the human breathing system play in cellular respiration?
What role does the human breathing system play in cellular respiration?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the breathing system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the breathing system?
During the process of breathing in, what happens to the air flow in the human breathing system?
During the process of breathing in, what happens to the air flow in the human breathing system?
What is likely to happen to cobalt chloride paper when exposed to water vapour from exhaled air?
What is likely to happen to cobalt chloride paper when exposed to water vapour from exhaled air?
How does the configuration of the human breathing system assist in effective gas exchange?
How does the configuration of the human breathing system assist in effective gas exchange?
Which mechanism is primarily responsible for the movement of air into and out of the lungs?
Which mechanism is primarily responsible for the movement of air into and out of the lungs?
What should be observed in cobalt chloride paper before exhaling onto a mirror?
What should be observed in cobalt chloride paper before exhaling onto a mirror?
Flashcards
Purpose of tube B
Purpose of tube B
A control group to compare against tube A, letting you see if mealworms produce carbon dioxide.
Gas exchange of mealworms
Gas exchange of mealworms
Mealworms release carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide content change
Carbon dioxide content change
Tube A's indicator will change colour, indicating carbon dioxide production from mealworms in the tube, while tube B's indicator likely stays unchanged, if they were not present
Indicator solution function
Indicator solution function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Experimental setup for observing gas exchange
Experimental setup for observing gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of the control group
Importance of the control group
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gloves in experiment
Gloves in experiment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventing air leakage
Preventing air leakage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhaled air composition
Exhaled air composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas exchange
Gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human breathing system
Human breathing system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inhaled air
Inhaled air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhaled air
Exhaled air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiration
Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobalt chloride paper
Cobalt chloride paper
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breathing system parts
Breathing system parts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas exchange in air sacs
Gas exchange in air sacs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air sac function
Air sac function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillary role in gas exchange
Capillary role in gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moistening inhaled air
Moistening inhaled air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Warming inhaled air
Warming inhaled air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Difference between inhaled and exhaled air
Difference between inhaled and exhaled air
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why exhaled air is warmer and moister
Why exhaled air is warmer and moister
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large surface area in lungs
Large surface area in lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas exchange in fish
Gas exchange in fish
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas exchange in salamanders
Gas exchange in salamanders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas exchange in frogs
Gas exchange in frogs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Smoking's effect on gas exchange
Smoking's effect on gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effects of smoking on breathing system
Effects of smoking on breathing system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventing air leakage in gas exchange experiments
Preventing air leakage in gas exchange experiments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pig lungs after smoking
Pig lungs after smoking
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tar's impact on gas exchange
Tar's impact on gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is gas exchange?
What is gas exchange?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differences in lung color
Differences in lung color
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differences in lung tissue
Differences in lung tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differences in trachea
Differences in trachea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is the control group important?
Why is the control group important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the experiment?
What is the purpose of the experiment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pig lung structure
Pig lung structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pig lung colour
Pig lung colour
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens when air is pumped into the lungs?
What happens when air is pumped into the lungs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trachea branching
Trachea branching
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lung tissue in water
Lung tissue in water
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiration definition
Respiration definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Gas Exchange in Animals
- Gas exchange isn't unique to plants; animals also exchange gases.
- Practical 7.12 investigates carbon dioxide uptake/release by mealworms.
- Materials include boiling tubes, forceps, cotton threads, stoppers, test tube racks, a measuring cylinder, plastic vials with holes, and hydrogencarbonate indicator.
- Procedure involves adding indicator to tubes, placing mealworms in a vial, inserting into one tube, sealing both tubes, waiting, and noting colour changes.
- The hydrogencarbonate indicator changes colour in response to carbon dioxide: red for low CO2, yellow for high CO2.
- Mealworms in tube A (with mealworms) cause the indicator to turn yellow (increase in CO2).
- Tube B (control) stays red (no change in CO2).
- This suggests that mealworms release CO2 during respiration
- Practical 7.13 investigates oxygen uptake/release in mealworms.
Gas Exchange in Humans
-
Humans have a sophisticated breathing system for gas exchange.
-
This system ensures oxygen for cellular respiration and waste CO2 removal.
-
Inhaled air differs from exhaled air in oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour content/concentration.
-
Inhaled v.s. exhaled air: Inhaled air has more oxygen & less CO2, whilst exhaled air has more CO2 and less oxygen
-
Practical 7.14 compares inhaled and exhaled air's compositions.
-
Materials include gas jars, covers, measuring cylinder, mirror, dry cobalt chloride paper, stopwatch, candle, etc..
-
Procedure involves filling gas jars with air, measuring candle burning time, recording differences in burning times for inhaled vs exhaled air, and for colour changes in cobalt chloride paper.
-
Inhaled air supports burning longer than exhaled air (more oxygen).
-
Exhaled air contains more CO2 and water vapour (less oxygen).
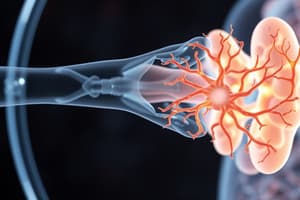
Gas Exchange at Air Sacs
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between air sacs and blood.
- Inhaled air enters air sacs, oxygen diffuses into blood capillaries.
- Blood carries oxygen to body cells. Cellular respiration produces CO2.
- Blood carries CO2 to air sacs; CO2 diffuses out of blood and into air sacs.
- Exhaled air is warmer and contains more water vapour than inhaled air.
- Air is warmed and moistened in the air sacs as it flows through.
Effects of Smoking
- Smoking reduces gas exchange efficiency.
- Tar deposits on air sacs, reducing surface area for exchange.
- Carbon monoxide reduces blood's oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Toxic chemicals damage air sacs, diminishing surface area for gas exchange
- Smoking causes various respiratory diseases.
- Smoking damages nearly every part of the body, including lungs, heart, and mouth
Additional Information
- The lungs' large surface area (about 80 m²) facilitates efficient gas exchange.
- Measurements of inhaled/exhaled air, can be used to determine the presence and quantity of gases in each.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.