Podcast
Questions and Answers
Xylem transports sucrose and amino acids throughout a plant.
Xylem transports sucrose and amino acids throughout a plant.
False (B)
What is the process by which water evaporates from the surface of a plant?
What is the process by which water evaporates from the surface of a plant?
transpiration
The reabsorption of glucose occurs at the ________ convoluted tubule in the kidney.
The reabsorption of glucose occurs at the ________ convoluted tubule in the kidney.
proximal
What is the primary role of ADH in the body?
What is the primary role of ADH in the body?
Match the following structures with their function:
Match the following structures with their function:
Geotropism refers to the response of a plant to light.
Geotropism refers to the response of a plant to light.
Name one of the excretory products of the lungs.
Name one of the excretory products of the lungs.
Flashcards
What are intercostal muscles and what is their function?
What are intercostal muscles and what is their function?
The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs and play a crucial role in breathing. They contract to expand the chest cavity, drawing air into the lungs during inhalation, and relax to reduce the chest cavity volume, expelling air during exhalation.
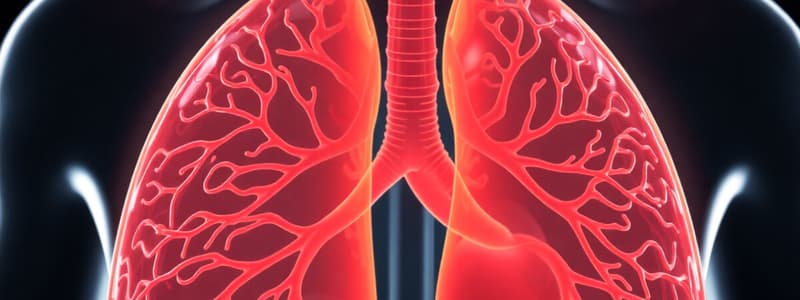
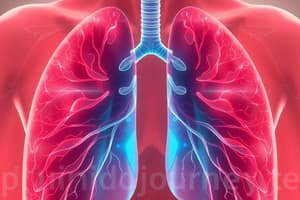
What are alveoli and why are they important for gas exchange?
What are alveoli and why are they important for gas exchange?
The alveoli are tiny air sacs located at the end of the bronchioles in the lungs. They are the primary site for gas exchange, where oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the alveoli to be exhaled.
What is the role of phloem in plants?
What is the role of phloem in plants?
The phloem is a type of vascular tissue in plants that transports sugars, primarily sucrose, produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant where they are needed for growth, storage, or respiration.
What is the role of xylem in plants?
What is the role of xylem in plants?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do root hair cells absorb water?
How do root hair cells absorb water?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is transpiration and how does it work?
What is transpiration and how does it work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the kidneys in the body?
What is the role of the kidneys in the body?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is geotropism and how does it affect plant growth?
What is geotropism and how does it affect plant growth?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Gas Exchange in Animals
-
Thorax Structure: The thorax is a cage-like structure enclosed by ribs. Intercostal muscles lie between the ribs; the diaphragm separates the thorax from the abdomen. The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are part of the airway system. Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs. Pleural membranes line the lungs and thorax, reducing friction during breathing.
-
Ventilation: Intercostal muscles and the diaphragm work together to change the volume of the thoracic cavity, causing air to move in and out of the lungs.
-
Alveoli Adaptation: Alveoli are thin-walled, maximizing the surface area for gas exchange. The blood in surrounding capillaries has a high concentration of carbon dioxide, which diffuses into the alveoli. Oxygen in the alveoli diffuses into the blood.
-
Smoking's Effects: Smoking damages the lungs and circulatory system, leading to conditions such as coronary heart disease.
-
Practical Application: Practical investigations should focus on breathing, carbon dioxide release, and exercise effects.
Transport in Plants
-
Phloem Function: Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids from leaves to other plant parts.
-
Xylem Function: Xylem transports water and mineral ions from roots to the rest of the plant.
-
Water Absorption: Root hair cells absorb water from the soil via osmosis.
-
Transpiration: Transpiration is water evaporation from a plant's surface.
-
Transpiration Factors: Environmental factors like humidity, wind speed, temperature, and light intensity affect the rate of transpiration.
-
Practical Application: Practical investigations should investigate the role of environmental factors on transpiration rates.
Excretion
-
Excretion Organs: Lungs, kidneys, and skin remove waste products from the body.
-
Kidney Function: Kidneys perform excretion and osmoregulation. They filter waste products from the blood.
-
Urinary System: The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urine travels through the system and is expelled.
-
Nephron Structure: Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys. They include the Bowman's capsule, glomerulus, convoluted tubules, loop of Henle, and collecting duct.
-
Ultrafiltration: Fluid is filtered in the Bowman's capsule. The filtrate contains most substances in blood except blood cells and large proteins.
-
Water Reabsorption: Water reabsorption occurs in the collecting duct, controlled by hormones.
-
Glucose Reabsorption: Glucose is selectively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
-
ADH Role: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) regulates water reabsorption in the collecting ducts, balancing water levels in the blood.
-
Urine Composition: Urine consists of water, urea, and ions.
Coordination and Response
-
Plant Responses: Plants respond to stimuli, such as light and gravity.
-
Geotropism and Phototropism: Roots exhibit positive geotropism (growing towards gravity) and negative phototropism (growing away from light). Stems show negative geotropism and positive phototropism.
-
Auxin Role: Auxin is a plant hormone influencing stem growth and phototropism.
-
Central Nervous System: The human central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord. It controls rapid responses.
-
Sensory Input: Receptors in sense organs send electrical signals (impulses) along nerves to the CNS, leading to responses.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.