Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of a food exchange list in the context of meal planning for individuals?
What is the primary function of a food exchange list in the context of meal planning for individuals?
A tool for quick estimation of the energy and macronutrients for use in planning meals.
Besides quick estimation of energy and macronutrients, what other purposes does a food exchange list serve in nutrition and dietetics?
Besides quick estimation of energy and macronutrients, what other purposes does a food exchange list serve in nutrition and dietetics?
Meal planning, diet instruction, and estimating the macronutrient content of normal and therapeutic diets.
Briefly differentiate between "Edible Portion" (E.P.) and "As Purchased" (A.P.) in food terminology.
Briefly differentiate between "Edible Portion" (E.P.) and "As Purchased" (A.P.) in food terminology.
E.P. is the portion of food served after cooking, while A.P. is the raw state of food before any processing.
Identify the government agency in the Philippines responsible for developing the Food Exchange List.
Identify the government agency in the Philippines responsible for developing the Food Exchange List.
In the Vegetable Exchange List, what is the general approach for calculating the nutritional content of Group A vegetables when more than one exchange is used?
In the Vegetable Exchange List, what is the general approach for calculating the nutritional content of Group A vegetables when more than one exchange is used?
How does the fruit exchange list contribute to a balanced diet, particularly regarding vitamin C intake?
How does the fruit exchange list contribute to a balanced diet, particularly regarding vitamin C intake?
Within the milk exchange list, what implications does the fat content have on the categorization of milk subgroups in the list?
Within the milk exchange list, what implications does the fat content have on the categorization of milk subgroups in the list?
Explain how the Rice Exchange List is used for managing carbohydrate intake, especially in terms of grams and their caloric equivalent.
Explain how the Rice Exchange List is used for managing carbohydrate intake, especially in terms of grams and their caloric equivalent.
How does the Meat and Fish Exchange List assist in managing dietary fat intake?
How does the Meat and Fish Exchange List assist in managing dietary fat intake?
What is the significance of the Fat Exchange List in calculating total caloric intake from fats, and what is the caloric value of one exchange?
What is the significance of the Fat Exchange List in calculating total caloric intake from fats, and what is the caloric value of one exchange?
In the Sugar Exchange List, what does one exchange signify in terms of grams of carbohydrate and corresponding calories?
In the Sugar Exchange List, what does one exchange signify in terms of grams of carbohydrate and corresponding calories?
How are "free foods" defined in the context of the food exchange list, and what conditions apply to their consumption?
How are "free foods" defined in the context of the food exchange list, and what conditions apply to their consumption?
What is the primary purpose of including the Beverage List in the appendices of a food exchange list?
What is the primary purpose of including the Beverage List in the appendices of a food exchange list?
Describe how the Composition of Selected Processed Foods in Exchanges appendix is used for calculating meal components.
Describe how the Composition of Selected Processed Foods in Exchanges appendix is used for calculating meal components.
In creating a meal plan, what three macronutrients should be considered, and how are these represented in meal planning?
In creating a meal plan, what three macronutrients should be considered, and how are these represented in meal planning?
What is the key dietary focus for GROUP 1 in the laboratory activity according to the guidelines provided?
What is the key dietary focus for GROUP 1 in the laboratory activity according to the guidelines provided?
In the given recipe adjustments, what is the objective for calculating the total energy (in kcal) per meal?
In the given recipe adjustments, what is the objective for calculating the total energy (in kcal) per meal?
In the vegetable exchange lists, what is the serving size for Asparagus tips?
In the vegetable exchange lists, what is the serving size for Asparagus tips?
In the vegetable exchange lists, what is the serving size for the vegetable baby corn?
In the vegetable exchange lists, what is the serving size for the vegetable baby corn?
Provide at least three examples of Group A vegetables.
Provide at least three examples of Group A vegetables.
According to the fruit exchange list, what is the Edible Portion (E.P.) weight of an Anonas?
According to the fruit exchange list, what is the Edible Portion (E.P.) weight of an Anonas?
According to the fruit exchange list, what is the Edible Portion (E.P.) weight of a Saba?
According to the fruit exchange list, what is the Edible Portion (E.P.) weight of a Saba?
According to the milk exchange list, what is the measure for the serving size of Milk, fresh carabao's.
According to the milk exchange list, what is the measure for the serving size of Milk, fresh carabao's.
According to the rice exchange list, how many measure of the rice gruel (lugaw) with the "thin consistency"?
According to the rice exchange list, how many measure of the rice gruel (lugaw) with the "thin consistency"?
What measure of beef would be acceptable for someone on a low fat meat and fish exchange diet?
What measure of beef would be acceptable for someone on a low fat meat and fish exchange diet?
What is portion size should you consume of Sitsaron based on the fat exchange list?
What is portion size should you consume of Sitsaron based on the fat exchange list?
What is the serving amount of chewing gum to be considered as sugar-free?
What is the serving amount of chewing gum to be considered as sugar-free?
What amount of Halo-halo is equivalent for having 4 sugar exchanges?
What amount of Halo-halo is equivalent for having 4 sugar exchanges?
Can carbonated water be included in a meal plan according to the Food Exchange List guidelines?
Can carbonated water be included in a meal plan according to the Food Exchange List guidelines?
What amount of Soft drink is equivalent for having 5 sugar exchanges?
What amount of Soft drink is equivalent for having 5 sugar exchanges?
What amount of Buko meat (fruit) is equivalent for having 1 fruit and 1 fat exchanges?
What amount of Buko meat (fruit) is equivalent for having 1 fruit and 1 fat exchanges?
How many exchanges are in 30 g of biscocho?
How many exchanges are in 30 g of biscocho?
According to the Meal Plan for a Normal Diet, how many fat exchanges should be taken during lunch?
According to the Meal Plan for a Normal Diet, how many fat exchanges should be taken during lunch?
In the Meal Plan for a Normal Diet, what meal distributions have more fat exchanges?
In the Meal Plan for a Normal Diet, what meal distributions have more fat exchanges?
In the laboratory activity, how many members each for lunch or breakfast in the group can prepare the meal plan?
In the laboratory activity, how many members each for lunch or breakfast in the group can prepare the meal plan?
Approximately how many calories per day should be consumed by a Filipino woman, according to the instructions for the laboratory activity?
Approximately how many calories per day should be consumed by a Filipino woman, according to the instructions for the laboratory activity?
What should be listed under Ingredients of the Laboratory Activity?
What should be listed under Ingredients of the Laboratory Activity?
In the Meal Activity No. 2, what parts should be written in the output?
In the Meal Activity No. 2, what parts should be written in the output?
Flashcards
Food Exchange List
Food Exchange List
Tool for rapid estimation of energy and macronutrients for individual meal planning.
Food exchange list
Food exchange list
Basic nutrition tool for meal planning, diet instruction, and estimating energy and macronutrient content.
Edible Portion (E.P.)
Edible Portion (E.P.)
Edible portion of food served to a customer after cutting and cooking.
As Purchased (A.P.)
As Purchased (A.P.)
Signup and view all the flashcards
FNRI - Food and Nutrition Research Institute
FNRI - Food and Nutrition Research Institute
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vegetables
Vegetables
Signup and view all the flashcards
Group A Vegetables
Group A Vegetables
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fruits
Fruits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Milk allowance
Milk allowance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meat and Fish exchange list
Meat and Fish exchange list
Signup and view all the flashcards
List 6 – Fat Exchange List
List 6 – Fat Exchange List
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sugar Exchange List
Sugar Exchange List
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free Foods
Free Foods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- A food exchange list assists in quickly gauging energy and macronutrient levels when planning meals.
- Nutrition utilizes a food exchange list as a basic tool for planning meals, instructing on diets, and determining the amount of energy and macronutrients in both normal and therapeutic diets.
- The FNRI and DOST created the food exchange list.
Terminology
- Edible Portion (E.P.) refers to the part of food served to a customer after being cut and cooked, representing the weight of the food without inedible parts.
- As Purchased (A.P.) is the food portion in its raw state before any cutting, processing, or cooking occurs.
- Food and Nutrition Research Institute (FNRI) serves as the main research division of the government for food and nutrition, operating as a research and development institute under DOST.
Vegetable Exchange List
- Vegetables offer crucial minerals and vitamins.
- It is recommended to aim for two to three portions a day, including dark green and yellow vegetables.
- Each exchange provides varied amounts of carbohydrates, protein, fat, and energy
Group A Vegetables
- These contain minimal carbohydrates, protein, and energy.
- When two exchanges of Group A vegetables are utilized, they are calculated like one Group B Vegetable.
- One vegetable exchange portion: 1 cup raw (25 g) or ½ cup cooked (45 g). Examples of vegetables:
- Acelgas (Chinese cabbage), Alagaw leaves, Amapalaya
- Saluyot, tomato, upo
Group B Vegetables
- One exchange: ½ cup raw (40 g) or ½ cup cooked (45 g). Examples of vegetables:
- Carrot, kamansi, squash fruit
Processed Vegetable Measures & Weights
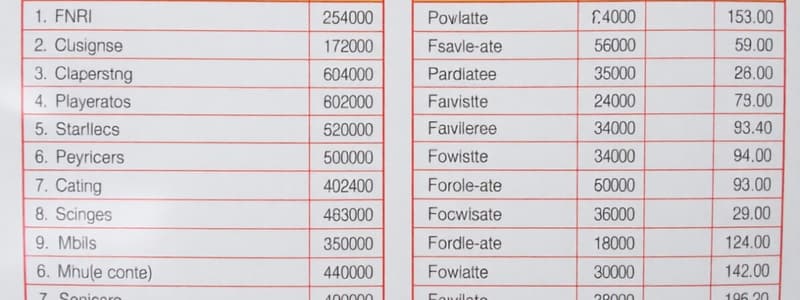
- Asparagus tips: 90 grams or 1 cup.
- Baby corn: 15 grams or 2 pieces (8 cm long x 5-1/2 circumference each).
- Canned tomato juice: 60 grams or 1/2 cup undiluted
Fruit Exchange List
- Fruits are vital for vitamins, minerals, and fiber, include them in the diet two to three times daily, focusing on vitamin C-rich choices.
- One exchange equals 10 grams of carbohydrates or 40 kcalories.
- The fruit weight and measure is different whether it has been purchased and prepared
Fresh Fruit Measures & Weights
- Apple: ½ of 86 grams A.P. or 65 grams E.P. is equal to 1/2 of 8 cm diameter or 1 (6 cm diameter)
- Banana (Bungulan): 60 grams A.P. or 40 grams E.P. equals ½ of 15 x 4 cm
Milk Exchange List
- Milk can be a drink, with cereal, and in coffee or tea.
- Each exchange contains:
- 12 grams CHO
- 8 grams PRO
- Varied amounts of Fat
- Varied amounts of energy
Milk Exchange Examples
- Whole milk: 125 grams E.P. or 1/2 cup.
- Evaporated milk: 125 grams or 1/2 cup.
Rice Exchange List
- 1 exchange is 23 grams of carbohydrate and 2 grams of protein or 100 kcalories.
- Lists specify the kinds and amounts of rice products for one exchange.
Rice Exchange Examples
- Rice cooked: 80 grams E.P. or 1/2 cup, packed.
- Rice gruel (lugaw) thin consistency: 705 grams E.P. or 4-1/2 cups (1/2 cup cooked rice + 5 cups water)
- Native kakanin: 25 grams E.P. or 3 (p x x3-1/2 x 2 cm each)
Meat and Fish Exchange List
- Meat and fish list has 3 groups, determined by the amount of fat and calories: low, medium, and high fat.
- Low fat: 8 grams PRO, 1 gram fat, and 41 kcalories.
- Medium fat: 8 grams PRO, 6 grams fat, and 86 kcalories.
- High fat: 8 grams PRO, 10 grams fat, and 122 kcalories.
- The list shows the kinds and amounts of food for 1 low fat meat and fish exchange.
Examples of Meat and Fish Exchanges
- Beef (Shank): 30 grams E.P. cooked is 1 slice with a matchbox size of (5 x 3-1/2 x 1-1/2 cm)
- Carabeef (shank): 30 grams E.P. cooked is 1 slice with a matchbox size of (5 x 3-1/2 x 1-1/2 cm)
- Lean pork (tenderloin): 30 grams E.P. cooked is 1 slice with a matchbox size of (6-1/2 x 3 x 1-1/2 cm)
Fat Exchange List
- 1 exchange of Fat = 5 grams fat = 45 kcalories.
- Lists show the kinds and amounts of fat for a fat exchange.
Fat Exchange Examples
- Bacon: 10 grams E.P. or 1 strip (10 x 3 cm).
- Butter: 5 grams E.P. or 1 teaspoon.
- Sitsaron: 10 grams E.P. or 2(5 x 3 cm each)
Sugar Exchange List
- 1 exchange = 5 grams carbohydrate = 20 kcalories.
- One teaspoon of sugar is 1 exchange.
- List shows the kinds and amounts for a sugar exchange
Sugar Exchange Examples
- Banana chip: 5 grams E.P. or 1 (6 x 3-1/2 cm).
- Honey: 5 grams E.P. or 1 teaspoon.
Common Sugar Equivalents
- Halo-halo: 410 grams E.P., which is 2-1/3 cups, 4 sugar exchanges, and 80 Kcalories.
- Kundol Matalamis: 20 grams E.P., which is 1(7 x 5 cm), 4 sugar exchanges, and 80 Kcalories.
Appendix A: Free Foods
- These foods can be used freely unless the physician says otherwise.
- They can be with other foods.
- Bagoong, bouillon, carbonated drinks, sugar free foods, carbonated water, and sugar free candy.
Appendix B: Beverage List
- Beverage lists' values are shown for sugar equivalent and nutritional composition.
- Soft drink (237ml): equal to 5 sugar exchanges and 100 Kcalories.
- Fruit Flavored drink concentrate (5ml): equal to 1 sugar exchange and 20 Kcalories.
Appendix C: Composition of selected processed foods in exchanges
- Buko meat (100 grams E.P.): is equal to 1 fruit and 1 fat, and equal to 85 kcalories.
- Biscocho (30 grams E.P.): is equal to 1 rice and ½ fat, and equal to 122 kcalories.
Meal Plan
- Laboratory activity requires a meal plan to be prepared for breakfast and lunch. The meal plan for Filipino women is to equal 1,500kcal and Filipino men is to equal 2,000kcal. Group members are to delegate tasks.
- The meal plans should be arranged in food tray. The cooking for the meal plan, is to be done by the student. The tasks involved in cooking shall be rotated on a rotation basis.
- Group member should be assigned to tasks, such as meal planning, meal preparation, video recording etc.
- For example, a Group needs to write a meal plan, list ingredients, include the amount of carbohydrate, the amount of protein and fat and equal 530 kcalories
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.