Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the fluid that surrounds cells but is not inside blood vessels called?
What is the fluid that surrounds cells but is not inside blood vessels called?
- Interstitial fluid (correct)
- Intracellular fluid
- Transcellular fluid
- Intravascular fluid
Which of the following is another name for intravascular fluid?
Which of the following is another name for intravascular fluid?
- Lymph
- Blood plasma (correct)
- Saliva
- Cerebrospinal fluid
Where is intravascular fluid located?
Where is intravascular fluid located?
- Inside blood vessels (correct)
- Between cells
- Within the brain
- Inside lymph vessels
Interstitial fluid is a component of which larger fluid category?
Interstitial fluid is a component of which larger fluid category?
What is the primary location of interstitial fluid?
What is the primary location of interstitial fluid?
What is the primary use of albumin?
What is the primary use of albumin?
In which condition is albumin commonly used?
In which condition is albumin commonly used?
Albumin is administered when which of the following is needed?
Albumin is administered when which of the following is needed?
What effect does albumin have on blood pressure when administered?
What effect does albumin have on blood pressure when administered?
What might a condition like a burn indicate a necessity for?
What might a condition like a burn indicate a necessity for?
What happens to the mediastinum in tension pneumothorax?
What happens to the mediastinum in tension pneumothorax?
What is the primary problem in tension pneumothorax?
What is the primary problem in tension pneumothorax?
Which of the following treatments is required for tension pneumothorax?
Which of the following treatments is required for tension pneumothorax?
What is a treatment option for tension pneumothorax?
What is a treatment option for tension pneumothorax?
What condition necessitates immediate intervention with needle thoracostomy or chest tube?
What condition necessitates immediate intervention with needle thoracostomy or chest tube?
What is a common use for a portable E tank?
What is a common use for a portable E tank?
Which type of oxygen tank is typically stationary and serves as a main source?
Which type of oxygen tank is typically stationary and serves as a main source?
What is a key recommendation for managing asthma through lifestyle adjustments?
What is a key recommendation for managing asthma through lifestyle adjustments?
What is the focus of lifestyle guidance for individuals with asthma?
What is the focus of lifestyle guidance for individuals with asthma?
In what form is oxygen stored in a portable container as an alternative to gas?
In what form is oxygen stored in a portable container as an alternative to gas?
What is the primary purpose of using smaller, portable oxygen tanks?
What is the primary purpose of using smaller, portable oxygen tanks?
What is the most appropriate recommendation regarding physical activity for an asthmatic patient?
What is the most appropriate recommendation regarding physical activity for an asthmatic patient?
What should an asthmatic patient always carry with them, according to the information?
What should an asthmatic patient always carry with them, according to the information?
What is a key feature of containers used for storing liquid oxygen?
What is a key feature of containers used for storing liquid oxygen?
What is the primary goal of lifestyle guidance for asthmatic patients?
What is the primary goal of lifestyle guidance for asthmatic patients?
What is characterized by fluid accumulation in the lungs?
What is characterized by fluid accumulation in the lungs?
What is the primary concern associated with cerebral edema?
What is the primary concern associated with cerebral edema?
In which organ does pulmonary edema primarily occur?
In which organ does pulmonary edema primarily occur?
What is the main characteristic of cerebral edema?
What is the main characteristic of cerebral edema?
Which of the following conditions involves fluid accumulating specifically in the brain?
Which of the following conditions involves fluid accumulating specifically in the brain?
What is the term for widespread swelling throughout the body?
What is the term for widespread swelling throughout the body?
Which type of edema leaves an indentation after pressure is applied?
Which type of edema leaves an indentation after pressure is applied?
Which condition is most likely to cause anasarca?
Which condition is most likely to cause anasarca?
What is the key characteristic of pitting edema?
What is the key characteristic of pitting edema?
In which area of the body is anasarca likely to be observed?
In which area of the body is anasarca likely to be observed?
What class of medication is albuterol?
What class of medication is albuterol?
What type of medication should an asthmatic patient always carry?
What type of medication should an asthmatic patient always carry?
Why should an asthmatic patient carry a rescue medication?
Why should an asthmatic patient carry a rescue medication?
What is another name for a quick-relief bronchodilator?
What is another name for a quick-relief bronchodilator?
Albuterol is typically administered via which route?
Albuterol is typically administered via which route?
Which of the following is a key component in patient evaluation?
Which of the following is a key component in patient evaluation?
What aspect of a patient's care should be considered alongside medication?
What aspect of a patient's care should be considered alongside medication?
Which intervention is important for managing a patient's condition?
Which intervention is important for managing a patient's condition?
Why is it important to educate patients and their families?
Why is it important to educate patients and their families?
What should patients understand about medications they are taking?
What should patients understand about medications they are taking?
When fluid analysis is conducted following a thoracentesis, what are clinicians hoping to achieve?
When fluid analysis is conducted following a thoracentesis, what are clinicians hoping to achieve?
In which scenario would a thoracentesis be considered a therapeutic intervention?
In which scenario would a thoracentesis be considered a therapeutic intervention?
A patient with lung cancer develops a large pleural effusion, leading to significant shortness of breath. What is the MOST appropriate intervention?
A patient with lung cancer develops a large pleural effusion, leading to significant shortness of breath. What is the MOST appropriate intervention?
What key information can be gained from analyzing the fluid removed during a diagnostic thoracentesis?
What key information can be gained from analyzing the fluid removed during a diagnostic thoracentesis?
A patient with congestive heart failure experiences increased shortness of breath due to pleural effusion. Besides addressing the underlying heart condition, what immediate intervention can provide symptomatic relief?
A patient with congestive heart failure experiences increased shortness of breath due to pleural effusion. Besides addressing the underlying heart condition, what immediate intervention can provide symptomatic relief?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) in the body?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) in the body?
A patient is experiencing significant dehydration. How would this likely affect the distribution of fluid between the intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) compartments?
A patient is experiencing significant dehydration. How would this likely affect the distribution of fluid between the intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) compartments?
How would a medication that causes significant intracellular swelling primarily affect the fluid distribution between ICF and ECF?
How would a medication that causes significant intracellular swelling primarily affect the fluid distribution between ICF and ECF?
A patient with heart failure is retaining excess fluid, leading to increased ECF volume. What compensatory mechanism would the body likely employ to try and restore fluid balance between the ECF and ICF?
A patient with heart failure is retaining excess fluid, leading to increased ECF volume. What compensatory mechanism would the body likely employ to try and restore fluid balance between the ECF and ICF?
A patient is given an IV infusion of a hypertonic saline solution. What immediate shift in fluid distribution between the ICF and ECF would you expect to observe?
A patient is given an IV infusion of a hypertonic saline solution. What immediate shift in fluid distribution between the ICF and ECF would you expect to observe?
Flashcards
Interstitial Fluid
Interstitial Fluid
Fluid between cells, not in blood vessels, part of ECF.
Intravascular Fluid
Intravascular Fluid
Fluid inside blood vessels, also known as blood plasma, part of ECF.
What is Extracellular Fluid (ECF)?
What is Extracellular Fluid (ECF)?
The fluid outside the cells.
What are the two sub-divisions of ECF?
What are the two sub-divisions of ECF?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Blood Plasma?
What is Blood Plasma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Albumin?
What is Albumin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why use Albumin?
Why use Albumin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Albumin raise blood pressure?
How does Albumin raise blood pressure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Albumin cause pulmonary edema?
How does Albumin cause pulmonary edema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does Albumin increase urination?
How does Albumin increase urination?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tension pneumothorax definition
Tension pneumothorax definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tension pneumothorax treatment
Tension pneumothorax treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mediastinal Shift
Mediastinal Shift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Needle thoracostomy
Needle thoracostomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chest tube
Chest tube
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthma & Exercise
Asthma & Exercise
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventing Exercise-Induced Asthma
Preventing Exercise-Induced Asthma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Healthy Behaviors for Asthma
Healthy Behaviors for Asthma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asthma Rescue Medication
Asthma Rescue Medication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Asthma Rescue Medication
Common Asthma Rescue Medication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compressed gas oxygen
Compressed gas oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
H Cylinder
H Cylinder
Signup and view all the flashcards
E Tank
E Tank
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulated portable container
Insulated portable container
Signup and view all the flashcards
Generalized edema
Generalized edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anasarca
Anasarca
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pitting edema
Pitting edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does pitting edema indicate?
What does pitting edema indicate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common causes of generalized edema
Common causes of generalized edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Edema
Cerebral Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Pulmonary Edema
Alveolar Pulmonary Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interstitial Pulmonary Edema
Interstitial Pulmonary Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Capillary Pressure & Edema
Pulmonary Capillary Pressure & Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient Monitoring
Patient Monitoring
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient Education
Patient Education
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electrolyte-Altering Drugs
Electrolyte-Altering Drugs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Therapeutic Diet
Therapeutic Diet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid management
Fluid management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rescue Bronchodilator
Rescue Bronchodilator
Signup and view all the flashcards
SABA (Example: Albuterol)
SABA (Example: Albuterol)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Carrying a SABA
Importance of Carrying a SABA
Signup and view all the flashcards
How SABAs work
How SABAs work
Signup and view all the flashcards
Albuterol
Albuterol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main Fluid Compartments
Main Fluid Compartments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnostic Fluid Aspiration
Diagnostic Fluid Aspiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Therapeutic Fluid Aspiration
Therapeutic Fluid Aspiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conditions Treated by Aspiration
Conditions Treated by Aspiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shortness of Breath
Shortness of Breath
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Analysis
Fluid Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Antibiotics Causing Electrolyte Imbalances
- Certain antibiotics, like vancomycin, can cause hyperkalemia (high potassium).
- Zosyn (piperacillin/tazobactam) may lead to hypernatremia (high sodium).
Nursing Assessment of Electrolyte Imbalances
Assessment
- Monitor intake and output
- Hypo or Hypervolemia (Hypo=Too little volume; Hyper=To much volume)
- Daily weights. Monitor daily weight
Fluid Compartments
- Body fluid is divided into intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF).
- Intracellular fluid is inside cells, about two-thirds of total body.
- Extracellular fluid is outside cells, about one-third of total body water.
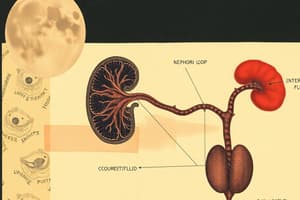
- The extracellular fluid is interstitial fluid that's between cells but not inside blood vessels, intravascular fluid or blood plasma, and transcellular fluids in epithelial-lined cavities like cerebrospinal, synovial, pleural, and peritoneal fluids.
- The distribution and composition of these fluid compartments is regulated in order to maintain function, transport nutrients, remove wastes, and provide the optimal internal environment.
Third Spacing
- Third spacing is when fluid shifts from intravascular space into interstitial space or body cavities.
- This can occur in conditions such as ascites, pleural effusions, intestinal obstructions, and severe burns. Trapped fluid outside of the vascular system leads to a relative decrease in intravascular volume that can result in hypovolemic shock.
- Clinically presents as edema or fluid accumulation in areas like the abdomen or extremities.
Electrolytes and Their Abnormal Signs and Symptoms
Sodium (Normal range: 135-145 mEq/L)
- Hyponatremia (<135 mEq/L) symptoms - Nausea, confusion, fatigue, muscle cramps, seizures.
- Hypernatremia (>145 mEq/L) symptoms - Extreme thirst, confusion, muscle twitches, seizures
Calcium (Normal range: 8.5-10.2 mg/dL)
- Hypocalcemia (<8.5 mg/dL) symptoms - Muscle cramps, numbness, seizures, arrhythmias.
- Hypercalcemia (>10.2 mg/dL) symptoms - Nausea, vomiting, confusion, kidney stones.
Potassium (Normal range: 3.5-5.0 mEq/L)
- Hypokalemia (<3.5 mEq/L) symptoms - Muscle weakness, cramping, arrhythmias.
- Hyperkalemia (>5.0 mEq/L) symptoms - Muscle paralysis, Peaked T-waves on ECG, arrhythmias.
Magnesium (Normal range: 1.8-2.4 mg/dL)
- Hypomagnesemia (<1.8 mg/dL) symptoms - Muscle cramps, tremors, arrhythmias, seizures.
- Hypermagnesemia (>2.4 mg/dL) symptoms - Nausea, vomiting, lethargy, respiratory depression.
Bicarbonate (Normal range: 22-28 mEq/L)
- Low levels symptoms - Metabolic acidosis - nausea, fatigue, Kussmaul respirations.
- High levels symptoms - Metabolic alkalosis - confusion, arrhythmias, muscle twitching.
Albumin (Normal range: 3.5-5.0 g/dL)
- Hypoalbuminemia (<3.5 g/dL) symptoms - Edema, ascites, poor wound healing.
- Hyperalbuminemia (>5.0 g/dL) symptoms - Dehydration, rarely symptomatic.
Isotonic, Hypertonic, and Hypotonic Solutions
- Isotonic solutions have the same osmotic pressure as blood plasma and cells and cause no fluid shift between compartments. Examples 0.9% normal saline and 5% dextrose in water (D5W), and LR.
- Hypertonic solutions have higher osmotic pressure than blood plasma and cells and pull water out of cells, causing them to dehydrate and shrink. Examples are 3-5% saline solution, D10W, D5 in 0.9% NS, DD5 in 0.45% NS, D5 in LR.
- Hypotonic solutions have lower osmotic pressure than blood plasma and cells which causes water to move into cells, leading to cellular swelling and potentially rupture if severe. Examples are 0.45% saline and LR.
Use of Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic Solutions as Treatment
- Isotonic solutions like 0.9% normal saline are used to replace fluid losses and maintain intravascular volume.
- Hypertonic solutions like 3% saline are used to treat severe hyponatremia by raising the sodium concentration in the extracellular fluid while pulling water out of cells.
- Hypotonic solutions like 0.45% saline are used to treat hypernatremia by diluting the extracellular fluid and allowing water to move into cells.
Colloids and Crystalloids
- Colloids contain larger insoluble molecules like proteins or starches suspended in a crystalloid solution. They are used when plasma volume expansion is needed, such as in hypovolemic shock, burns, or during surgery. Examples are albumin, dextran, and hydroxyethyl starches. Colloids pull fluid into the vascular space from the interstitial space due to their higher oncotic pressure.
- Colloid-Albumin is hyper-oncotic and it expands the plasma volume by about four times its volume.
- Crystalloids are aqueous solutions of electrolytes or other water-soluble molecules and are given for fluid resuscitation in conditions like dehydration, hypovolemia, and shock. Examples include normal saline, Ringer's lactate, and dextrose solutions
How Albumin Affects Blood Pressure, Pulmonary Edema and Urination
- Albumin increases blood pressure by expanding the plasma volume (the increased blood volume leads to increased venous return to the heart, increasing cardiac output and blood pressure) when administered intravenously.
- Albumin administration can potentially cause pulmonary (if too much fluid enters the pulmonary vasculature, increasing hydrostatic pressure and leading to fluid leakage into the lung interstitium and alveoli) edema.
- Albumin shifts fluid from of the interstitial spaces into the vascular space due to its oncotic properties and is shift can increase renal perfusion and glomerular filtration rate, resulting in increased urination.
Signs and Symptoms of Fluid Volume Deficit
- Thirst and dry mucous membranes.
- Decreased skin turgor and dry skin.
- Sunken eyeballs.
- Orthostatic hypotension (dizziness upon standing).
- Oliguria (decreased urine output).
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate).
- Fatigue and weakness, headache, muscle cramps.
- Concentrated urine with high specific gravity.
- Elevated BUN and hematocrit levels.
- Weight loss.
- Severe cases can progress to hypovolemic shock with cool, clammy skin, altered mental status, oliguria or anuria, and hypotension.
Signs and Symptoms of Fluid Volume Excess
- Weight gain.
- Edema (swelling) in the legs, feet, hands
- Distended neck veins.
- Shortness of breath
- Crackles or wheezing in the lungs.Ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen)
- Increased blood pressure
- Decreased hematocrit and plasma protein levels.
- Oliguria (decreased urine output).
- Fluid can accumulate in the lungs causing pulmonary edema with pink and frothy sputum and lead to congestive heart failure.
Edema and Its Types
- Edema is the accumulation of excessive fluid in the interstitial spaces between cells or body tissues.
- Types-Localized Edema, generalized edema, pitting Edema, non-pitting edema, peripheral edema, pulmonary edema, cerebral Edema.
Hormonal Regulators of Fluid Intake
- ADH stored in posterior pituitary gland, release in response to changes in blood osmolarity.
- Aldosterone (released by adrenal cortex) is a sodium conserver.
- RAA system is to combat hypovolemia.
- Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) released by the heart.
Organs Releasing Hormonal Regulators
- Hypothalamus produces antidiuretic hormone (ADH), increased by the kidneys.
- Kidneys release renin, which initiates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
- Adrenal Cortex releases aldosterone and increasing blood levels.
- Heart Atria produces atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and reduces blood volume
Fluid and Electrolyte Evaluation
- Serum electrolytes, hematocrit, hemoglobin, BUN, Creatinine.
- Compare Serum electrolyte tests with:Measure sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate levels. Hemoglobin
Causes of Acidosis and Alkalosis
- Acidosis can be caused by:
- Metabolic causes: Diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis due to poor perfusion, renal failure leading to acid retention, ingestion of acidic substances.
- Respiratory causes: Hypoventilation and carbon dioxide retention.
- Alkalosis cause:
- Vomiting and loss of hydrochloric acid.
- Diuretic use, hypokalemia.
- Excessive bicarbonate intake.
- Respiratory causes:Hyperventilation and excessive carbon dioxide loss.
Nursing Monitor: Fluid/Electrolyte Assessment/Labs
- Monitor Intake and output
- Hypo or Hypervolemia (Hypo=Too little volume; Hyper=To much volume)
- Hematocrit
- Monitor Laboratory Test:BUN, Creatinine, Urine Specific gravity
- Monitor Serum sodium, Serum osmolality daily weight
- Monitor:Assess Communication,
- Asses:Thermoregulation,Elimination-Monitor Intake of Sodium
- Fluids/Foods
Causes of Acidosis and Alkalosis
- Acidosis can be caused by:
- Metabolic causes: Diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis due to poor perfusion, renal failure leading to acid retention, ingestion of acidic substances.
- Respiratory causes: Hypoventilation and carbon dioxide retention.
- Alkalosis cause:
- Vomiting and loss of hydrochloric acid.
- Diuretic use, hypokalemia.
- Excessive bicarbonate intake.
- Respiratory causes:Hyperventilation and excessive carbon dioxide loss
Signs and Symptoms of Acidosis
- Headache, lethargy, confusion, coma, Kussmaul respirations (rapid, deep breathing),
- Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, Dysrhythmias, hypotension, muscle weakness, cramping, fatigue, restlessness.
Signs and Symptoms of Alkalosis
- Dizziness, headache, confusion, seizures, tetany (muscle twitching/cramping), Shallow, slow breathing, arrhythmias, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, weakness, hyperreflexia, paresthesias (numbness/tingling around mouth and extremities).
Arterial Blood Gases
- Compensated acidosis: pH is normal (7.35-7.45), PaCO2 and HCO3¯ are BOTH abnormal and the respiratory system has compensated for the metabolic acidosis by lowering PaCO2.
- Compensated alkalosis: pH is normal (7.35-7.45), PaCO2 and HCO3¯ are BOTH abnormal and the respiratory system has compensated for the metabolic alkalosis by raising PaCO2.
- Partially compensated acidosis: pH is abnormal as well as both PaCO2 and HCO3¯ are abnormal, partial respiratory compensation.
- Partially compensated alkalosis: pH is abnormal as well as both PaCO2 and HCO3,¯ are abnormal, partial respiratory compensation.
- Uncompensated acidosis: pH is abnormal (acidic < 7.35 or alkaline > 7.45) and only one system (PaCO2 or HCO3) is abnormal.
- Uncompensated alkalosis: pH is abnormal (acidic < 7.35 or alkaline > 7.45) and only one system (PaCO2 or HCO3) is abnormal.
- Uncompensated acidosis:
- PACO2 abnormal, HCO3- normal, Only one system abnormal
- Respiratory: Compensation and tachypnea or hyperventilation.
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance Factors
- Excessive fluid losses (Vomiting, diarrhea, high output fistulas or drains, excessive sweating, burns, or polyuria can lead to dehydration and electrolyte deficits)
- Impaired ability due to kidney function (kidney disease)
- Endocrine (diabetes insipidus, SIADH, Addison's disease) severe illnesses
- Medications like diuretics, chemotherapy, steroids
- Severe injuries
- Gastro intestinal losses
- Liver functions
Nurse Procedures for Determining Fluid Balance
- Measure and record accurate intake and output (I&O), which includes oral, IV and tube feeding, as well as urine output, vomiting, diarrhea, and drainage from tubes/wounds.
- Weigh patient, daily and at the same time using the the same equipment. Use ABGs
- Assess skin/turgor
- ABGs
- Inspect Edemas
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance in Older Adults
- Dehydration, and higher kidney risk. impaired
- hyponatremia and kidney issues, can result and seizures
- Edemas, and causes liver conditions
- Older adults are at high risk for fluid/electrolyte imbalances from age-related physiological changes. Health Outcomes:, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and fluid overload
Reasons for Developing Fluid Deficits/Excesses
- Older adults
- High Risk/Drive is a side affect
- immobility is a contributing
Explain which system compensates the fastest for altered arterial blood gases.
- The kidneys take the longest time.
- The RESPIRATORY SYSTEM compensates the fastest for altered arterial blood gases. Changes in the rate and depth of breathing can rapidly adjust the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) to compensate for acid-base disturbances.
Types of Lung Sounds
- Vesicular breath sounds are the normal soft, breezy sounds heard over lung fields during inhalation and exhalation, which indicate air is moving freely through the airways.
- Crackles (rales) are discontinuous, non-musical, interrupted sounds that can be fine or coarse. Fine crackles (hair rubbing together) may suggest airway secretions or abnormal opening of small airways. Rhonchi are caused by mucus may suggest plugging
Causes, Interventions for Pneumothorax, Tension Thorax, and Hemothorax
- Tension pneumothorax occurs when air enters pleural space but cannot escape, increasing pressure and shifting mediastinum, emergent needle throcosomy
Signs and Symptoms of asthma
• Wheezing • Dyspnea
- SOB elevated heart rate
Nursing Education for Asthma.
Teaching:
- includes educate on proper inhaler technique for bronchodilators and coriticosteroids- Expain what is involved on adjustings .
- Triggers for avoidance includes identify allergens, irritants, viral infections, stress, and other personal asthma triggers. Enviromental/regular testing
Medication used to treat asthma (Classification, side effects patient teaching):
- Steriods-Prednisone the patients must to stop abruplty
- bronchodilators-albuterol should not exeed
- Achlinerig Better rinsh after a use
- Long time
Oxygenation Complications of COPD
Pulmonary hypertension: Increased blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries from chronic hypoxemia and destruction of lung vasculature.
Tuberculosis
- Teaching about what to expect
- To social distance.
- Remind the patient to avoid exposure.
Managing Pneumonia
- Proper nutrtion
- Sputtm
- Lung functions
Medications for Pneumonia
- (zirhomycin ), allergies Educate the family
Calculate MAP
- The Mean Arterial Pressure average vitals with brian heart and kidneys
Teach blood transfusion to Family
What does it mean for blood types
What Does Transfuson Means.
Alloegenic- for the body
Transfuson Reatctions (EXPALINING)
- Family will be with a actions
- Hypoallegeric
- Reactions
- (Trall, acitiutes
- Educate Familys what signs to look for - Clincial fatigue- shortness, low blood cells
- Taught Family
- Avoid / prevent crisis
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.