Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which indicator would be appropriate to measure interstitial fluid?
Which indicator would be appropriate to measure interstitial fluid?
- 2Na and 125I albumin
- 3H20 and Na
- 3H20 and 125I albumin (correct)
- 125I albumin
Infusion of isotonic saline would primarily alter which of the following?
Infusion of isotonic saline would primarily alter which of the following?
- Extracellular fluid osmolarity
- Intracellular fluid volume
- Extracellular fluid volume (correct)
- All of the above
What factor would decrease interstitial protein concentration if the capillary reflection coefficient is 1?
What factor would decrease interstitial protein concentration if the capillary reflection coefficient is 1?
- Decreasing capillary hydrostatic pressure
- Increasing capillary hydrostatic pressure (correct)
- Increasing capillary oncotic pressure
- Increasing interstitial hydrostatic pressure
Which infusion would cause the greatest increase in plasma osmolarity?
Which infusion would cause the greatest increase in plasma osmolarity?
Infusion of 15 L of isotonic saline would result in what after equilibration?
Infusion of 15 L of isotonic saline would result in what after equilibration?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
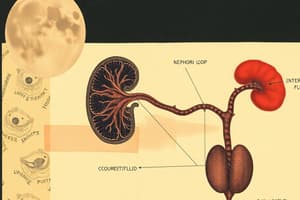
Measurement of Interstitial Fluid
- Indicators for measuring interstitial fluid include 3H2O and Na or 125I-albumin.
- 125I-albumin is a specific marker used in assessing interstitial fluid concentrations.
Effects of Isotonic Saline Infusion
- Infusion of isotonic saline alters extracellular fluid volume, having no significant change to intracellular fluid volume.
- Extracellular fluid osmolarity remains stable during isotonic saline infusion.
Decrease in Interstitial Protein Concentration
- Increasing capillary hydrostatic pressure decreases interstitial protein concentration.
- Increasing interstitial hydrostatic pressure or capillary oncotic pressure also affects protein concentration.
Plasma Osmolarity Increases
- The greatest increase in plasma osmolarity is caused by increasing plasma Na+ by 10 mEq/L.
- Other solutes like K+, glucose, and urea produce smaller osmolarity changes.
Fluid Shifts and Infusions
- Hypotonic fluids cause fluid shifts from extracellular to intracellular compartments.
- Isotonic and hypertonic fluids do not lead to significant fluid shifts in this direction.
Outcomes of Isotonic Saline Infusion
- Infusion of 15 L isotonic saline leads to increased plasma Na+ after equilibration.
- It results in fluid shifts from intracellular to extracellular fluid compartments and expands extracellular fluid volume.
Effects of Glucose Addition
- Adding 500 mEq of glucose to plasma increases extracellular fluid volume after equilibrating.
- It also causes a decrease in plasma Na+ and elevates plasma osmolarity.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.