Podcast
Questions and Answers
During fetal development, what hormonal event primarily determines the development of male reproductive organs from the mesonephric duct?
During fetal development, what hormonal event primarily determines the development of male reproductive organs from the mesonephric duct?
- The absence of testosterone production by the primitive testes.
- The presence of the paramesonephric duct.
- High levels of estrogen produced by the developing ovaries.
- High levels of testosterone produced by the primitive testes between the 7th and 8th week of pregnancy. (correct)
What is the critical timeframe during pregnancy when testosterone levels significantly influence sex differentiation in a fetus?
What is the critical timeframe during pregnancy when testosterone levels significantly influence sex differentiation in a fetus?
- Between the 1st and 2nd week of pregnancy.
- Around the 20th week of pregnancy.
- After the first trimester.
- Between the 7th and 8th week of pregnancy. (correct)
In the absence of sufficient testosterone during fetal development around the 10th week, what developmental path will the gonadal tissues typically follow?
In the absence of sufficient testosterone during fetal development around the 10th week, what developmental path will the gonadal tissues typically follow?
- They will develop into ovaries, and the paramesonephric duct will form female reproductive organs. (correct)
- They will regress, leading to an absence of reproductive organs.
- They will differentiate into testes regardless of testosterone levels.
- They will develop into male reproductive organs.
Which duct regresses in a fetus with high levels of testosterone, leading to the development of male reproductive organs?
Which duct regresses in a fetus with high levels of testosterone, leading to the development of male reproductive organs?
What role does the paramesonephric duct play in fetal development if testosterone is absent around the 10th week of gestation?
What role does the paramesonephric duct play in fetal development if testosterone is absent around the 10th week of gestation?
The term 'obstetric' is historically linked to what role?
The term 'obstetric' is historically linked to what role?
In the context of obstetric care, what does the term 'inter prandial period' refer to?
In the context of obstetric care, what does the term 'inter prandial period' refer to?
A key factor determining the sex-specific development of a fetus is:
A key factor determining the sex-specific development of a fetus is:
A pregnant woman's pelvic inlet is measured. Which anatomical landmarks define the anterior-posterior diameter of the pelvic inlet?
A pregnant woman's pelvic inlet is measured. Which anatomical landmarks define the anterior-posterior diameter of the pelvic inlet?
During a prenatal assessment, a doctor determines the distance between a pregnant woman's ischial spines. What information does this measurement provide?
During a prenatal assessment, a doctor determines the distance between a pregnant woman's ischial spines. What information does this measurement provide?
The fetal head is palpated at 2 cm above the ischial spines. What station is the fetal head located at?
The fetal head is palpated at 2 cm above the ischial spines. What station is the fetal head located at?
During a vaginal examination, the fetal head is determined to be at the level of the ischial spines. What station does this correspond to?
During a vaginal examination, the fetal head is determined to be at the level of the ischial spines. What station does this correspond to?
The fetal head is palpated 3 cm below the ischial spines. What station is the fetal head located at?
The fetal head is palpated 3 cm below the ischial spines. What station is the fetal head located at?
A clinician assesses a pregnant patient and determines the distance between the two ilia. What diameter of the pelvic inlet is being measured?
A clinician assesses a pregnant patient and determines the distance between the two ilia. What diameter of the pelvic inlet is being measured?
During labor, the fetal head is at a +1 station. How far below the ischial spines is the fetal head?
During labor, the fetal head is at a +1 station. How far below the ischial spines is the fetal head?
During an examination, the fetal head is located 2 cm above the ischial spine. Has engagement occurred?
During an examination, the fetal head is located 2 cm above the ischial spine. Has engagement occurred?
If fertilization occurs, what is the primary reason menstruation is prevented?
If fertilization occurs, what is the primary reason menstruation is prevented?
During the second month of pregnancy, what hormonal shift occurs as the placenta develops?
During the second month of pregnancy, what hormonal shift occurs as the placenta develops?
What initiates uterine contractions, leading to labor, as the placenta ages?
What initiates uterine contractions, leading to labor, as the placenta ages?
Considering the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle, what is the role of the hypothalamus?
Considering the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle, what is the role of the hypothalamus?
Which hormone primarily stimulates the ovary to produce estrogen?
Which hormone primarily stimulates the ovary to produce estrogen?
A 48-year-old woman reports absence of menstruation for 11 months and is experiencing hot flashes. What is the most appropriate initial step to confirm menopause?
A 48-year-old woman reports absence of menstruation for 11 months and is experiencing hot flashes. What is the most appropriate initial step to confirm menopause?
A 52-year-old woman, 3 years post-menopause, is considering hormone therapy (HT) to manage persistent hot flashes. Which factor is the MOST significant contraindication to consider before initiating HT?
A 52-year-old woman, 3 years post-menopause, is considering hormone therapy (HT) to manage persistent hot flashes. Which factor is the MOST significant contraindication to consider before initiating HT?
On approximately what day of a typical menstrual cycle does estrogen level typically peak?
On approximately what day of a typical menstrual cycle does estrogen level typically peak?
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between a gland and its hormonal effect during the menstrual cycle?
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between a gland and its hormonal effect during the menstrual cycle?
A woman is diagnosed with premature menopause at age 38. Which of the following is the MOST likely long-term health risk she should be counseled about?
A woman is diagnosed with premature menopause at age 38. Which of the following is the MOST likely long-term health risk she should be counseled about?
What is the role of LHRF (LH-releasing factor) in the menstrual cycle?
What is the role of LHRF (LH-releasing factor) in the menstrual cycle?
A postmenopausal woman reports experiencing vaginal dryness and discomfort during intercourse. Which of the following interventions is MOST appropriate as an initial recommendation?
A postmenopausal woman reports experiencing vaginal dryness and discomfort during intercourse. Which of the following interventions is MOST appropriate as an initial recommendation?
Which statement BEST describes the hormonal changes that occur during menopause?
Which statement BEST describes the hormonal changes that occur during menopause?
A 49-year-old woman is experiencing irregular menstrual cycles, hot flashes, and sleep disturbances. She is concerned about weight gain. What lifestyle modification would be MOST beneficial for managing her symptoms and addressing her concern about weight?
A 49-year-old woman is experiencing irregular menstrual cycles, hot flashes, and sleep disturbances. She is concerned about weight gain. What lifestyle modification would be MOST beneficial for managing her symptoms and addressing her concern about weight?
A patient in the early stages of menopause asks about preventing renal stones. What dietary recommendation is MOST appropriate?
A patient in the early stages of menopause asks about preventing renal stones. What dietary recommendation is MOST appropriate?
A woman who is 46 years old reports hot flashes, night sweats, and irregular periods, and is concerned about bone health. Besides calcium and Vitamin D supplementation, what additional lifestyle change would you recommend?
A woman who is 46 years old reports hot flashes, night sweats, and irregular periods, and is concerned about bone health. Besides calcium and Vitamin D supplementation, what additional lifestyle change would you recommend?
A woman experiences a sharp, localized pain in her lower abdomen midway through her menstrual cycle. This is most likely:
A woman experiences a sharp, localized pain in her lower abdomen midway through her menstrual cycle. This is most likely:
Which characteristic of cervical mucus indicates the highest probability of ovulation?
Which characteristic of cervical mucus indicates the highest probability of ovulation?
What hormonal change is most indicative of the luteal phase following ovulation?
What hormonal change is most indicative of the luteal phase following ovulation?
A woman is using the basal body temperature method to track ovulation. What pattern indicates that ovulation has likely occurred?
A woman is using the basal body temperature method to track ovulation. What pattern indicates that ovulation has likely occurred?
A couple is trying to conceive. The male partner's semen analysis reveals a volume of 1.5 ml. What does this indicate?
A couple is trying to conceive. The male partner's semen analysis reveals a volume of 1.5 ml. What does this indicate?
What does the term “Spinnbarkeit” refer to during ovulation?
What does the term “Spinnbarkeit” refer to during ovulation?
If a hormone has “RF” in its name such as Gonadotropin Releasing Factor (GnRF), where is it released from?
If a hormone has “RF” in its name such as Gonadotropin Releasing Factor (GnRF), where is it released from?
What is Mittelschmerz?
What is Mittelschmerz?
A woman with a consistent 32-day menstrual cycle can expect to ovulate around which day?
A woman with a consistent 32-day menstrual cycle can expect to ovulate around which day?
According to the typical calculations, what is the fertile window for a woman with a 28-day cycle who ovulates on day 14?
According to the typical calculations, what is the fertile window for a woman with a 28-day cycle who ovulates on day 14?
If a woman with a regular 28-day cycle begins her menstruation on the 1st of the month, which days are considered relatively safe for intercourse, assuming she wants to avoid pregnancy and accounting for the menstrual period?
If a woman with a regular 28-day cycle begins her menstruation on the 1st of the month, which days are considered relatively safe for intercourse, assuming she wants to avoid pregnancy and accounting for the menstrual period?
A woman with a 25-day cycle has intercourse on day 4. Considering the typical fertile window, is she likely to conceive?
A woman with a 25-day cycle has intercourse on day 4. Considering the typical fertile window, is she likely to conceive?
Which hormone is predominant during the first half of the menstrual cycle, playing a key role in preparing the uterine lining for ovulation?
Which hormone is predominant during the first half of the menstrual cycle, playing a key role in preparing the uterine lining for ovulation?
A woman who consistently has a 35-day cycle wants to use the rhythm method of contraception. To best avoid pregnancy, she should abstain from intercourse during which approximate timeframe?
A woman who consistently has a 35-day cycle wants to use the rhythm method of contraception. To best avoid pregnancy, she should abstain from intercourse during which approximate timeframe?
A woman tracks her cycle and notices that her luteal phase (from ovulation to menstruation) consistently lasts only 10 days. How might this affect her fertility?
A woman tracks her cycle and notices that her luteal phase (from ovulation to menstruation) consistently lasts only 10 days. How might this affect her fertility?
A woman with irregular cycles finds it difficult to predict her ovulation day using the calendar method. What is the most significant limitation of using cycle length alone to predict ovulation in such cases?
A woman with irregular cycles finds it difficult to predict her ovulation day using the calendar method. What is the most significant limitation of using cycle length alone to predict ovulation in such cases?
Flashcards
Mesonephric Duct
Mesonephric Duct
Male reproductive organs develop from this duct due to high testosterone.
Paramesonephric Duct
Paramesonephric Duct
Regression of this duct occurs in males, leading to the development of male reproductive organs due to high testosterone. Forms female reproductive organs if no testosterone present.
Gonadal Tissues (Female)
Gonadal Tissues (Female)
Develops into ovaries due to lack of testosterone.
Obstetric Nursing
Obstetric Nursing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anteprandial period
Anteprandial period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inter-prandial period
Inter-prandial period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-prandial
Post-prandial
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone Role (Embryo)
Testosterone Role (Embryo)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pelvic Inlet (A-P) Diameter
Pelvic Inlet (A-P) Diameter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pelvic Outlet (A-P) Diameter
Pelvic Outlet (A-P) Diameter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Diameter (Inlet)
Transverse Diameter (Inlet)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Diameter (Outlet)
Transverse Diameter (Outlet)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Engagement
Engagement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Station Zero
Station Zero
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Stations
Negative Stations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Stations
Positive Stations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menopause definition
Menopause definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian function in Menopause
Ovarian function in Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oocyte count
Oocyte count
Signup and view all the flashcards
Average age of Menopause
Average age of Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnosis of Menopause
Diagnosis of Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Symptoms of Menopause
Common Symptoms of Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health Teachings for Menopause
Health Teachings for Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
HRT in Menopause
HRT in Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertile Window
Fertile Window
Signup and view all the flashcards
Safe Days (Menstrual Cycle)
Safe Days (Menstrual Cycle)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen (First Half)
Estrogen (First Half)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone (Second Half)
Progesterone (Second Half)
Signup and view all the flashcards
28-Day Cycle
28-Day Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstruation Phase
Menstruation Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Day (28-Day Cycle)
Ovulation Day (28-Day Cycle)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pregnancy & Corpus Luteum
Pregnancy & Corpus Luteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta's Role (Month 2)
Placenta's Role (Month 2)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta at 9 Months
Placenta at 9 Months
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothalamus stimulates?
Hypothalamus stimulates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
APG stimulates?
APG stimulates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovary affects?
Ovary affects?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gland Stimulating Ovary
Gland Stimulating Ovary
Signup and view all the flashcards
What hormone stimulates APG to produce LH?
What hormone stimulates APG to produce LH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mittelschmerz
Mittelschmerz
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinnbarkeit
Spinnbarkeit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Body Temperature Shift
Basal Body Temperature Shift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Temperature Spike
Ovulation Temperature Spike
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Body Thermometer
Basal Body Thermometer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormone Changes During Ovulation
Hormone Changes During Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation Indicators
Ovulation Indicators
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Volume Evaluation
Sperm Volume Evaluation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
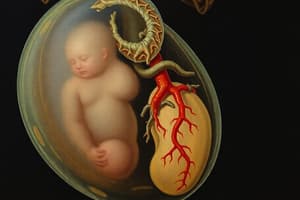
Reproductive Development
- Obstetric Nursing originates from "obstetric," meaning "midwife."
- Midwives care for clients during prandial periods.
- Gonads are reproductive organs: testes in males and ovaries in females.
- Testes produce sperm carrying X and Y chromosomes.
- Ovaries produce eggs carrying XX chromosomes, determining gender.
Sex Determination
- Gender develops around the 5th week of intrauterine life with primitive gonadal tissue.
- Two ducts are present: Mesonephric Duct (male) and Paramesonephric Duct (female).
Role of Testosterone
- Between the 7th and 8th week, high testosterone levels from primitive testes cause the mesonephric duct to develop into male reproductive organs.
- The paramesonephric duct regresses due to high testosterone.
- Absence of testosterone by the 10th week causes gonadal tissues to become ovaries, and the paramesonephric duct develops into female reproductive organs.
- Testosterone presence or absence determines sex.
Early Development Summary
- Primitive gonadal tissues are present at 5 weeks of intrauterine life.
- Primitive testes develop during the 7th-8th week, producing small amounts of testosterone.
- High or low testosterone determines the development of mesonephric or paramesonephric ducts.
- Ovaries produce egg cells with XX chromosomes.
- Testes produce sperm cells with X or Y chromosomes.
- XX sperm fertilizing an egg results in a female (XX) baby.
- Y sperm fertilizing an egg results in a male (XY) baby.
- Mesonephric ducts form male organs, and paramesonephric ducts form female organs if testosterone is low.
Pubertal Development (General)
- Puberty starts around age 9, ends around age 17.
- Secondary sex changes begin between ages 9-17 for both sexes, with average ages varying by sex.
- Growth spurts occur earlier in girls (9–12) and later in boys (12–14).
Hormonal Roles
- In females, the adrenal cortex and ovaries use the hypothalamus as a master clock.
- The hypothalamus triggers the adrenal cortex to produce hormones.
- Ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone.
- In males, adrenal cortex stimulates the testes to produce testosterone.
Female Sexual Development
- Acceleration in linear growth (growth spurt) marks initial development.
- Transverse diameter of the pelvis increases, followed by breast development (thelarche).
- Pubic hair grows (adrenarche), then menstruation begins (menarche), and axillary hair develops.
- Ovulation follows after the other named developments.
- Increase in vaginal secretions also occurs.
- Earliest sign of female secondary sex characteristics is increase in height, or accelerated linear growth.
- Thelarche is the female secondary sign of sex characteristic.
- Pubic hair appears earlier than axillary hair.
Male Sexual Development
- Weight increases, then shoulders broaden.
- Testes grow, followed by face, axillary, and pubic hair, and the voice changes.
- Penile growth then height increase (second to last) and spermatogenesis complete the development.
- Seminal fluid production begins in males around ages 12–14, while sperm production occurs later.
Reproductive Anatomy
- Male and female reproductive anatomy has external and internal structures.
Male External Structures
- The penis contains glands covered by skin known as the prepuce.
- The scrotum hangs from the body and holds the testicles.
- Testicles are outside the body because sperm cells are heat sensitive.
- Scrotal temperature is 1 degree Fahrenheit lower than body temperature.
- An erect penis averages 4 to 5 inches in length.
- The urethra in the penis's tip functions for urination and semen passage.
- The male urethra averages 7 inches in length.
Male Internal Structures
- The testes produce testosterone and are responsible for spermatogenesis in seminiferous tubules.
- The epididymis serves as storage for sperm maturation.
- The vas deferens connects the seminal vesicle and epididymis.
- The seminal vesicle, prostate gland, and Cowper's gland produce seminal fluid.
- 5% of seminal fluid from epididymis, 30% from seminal vesicle, 60% from prostate, 5% from Cowper's gland.
Fluids and Semen
- Sperm travels from the vas deferens to the ampulla.
- Seminal fluid is produced to lubricate the sperm in the ejaculatory duct.
- Sperm route is: testes, then epididymis (5% fluid), then vas deferens, then ampulla, then seminal vesicle (30% fluid), then prostate (60% fluid), then Cowper’s (5% fluid).
Ejaculation and Semen
- Sperm cells are alkaline to survive vaginal acidity.
- Cowper's and prostate glands produce alkaline secretions.
- Forceful ejaculation ensures sperm doesn't stay in the acidic vaginal canal.
- Sperm reaches the cervix in 90 seconds and fallopian tubes in 5 minutes.
- Testosterone and testes are male sex hormones and glands, respectively.
- Vasectomy is surgical sterilization that involves ligating and cutting the vas deferens, and sperm cells die after maturation.
Surgical Sterilization
- After vasectomy, sperm may remain in the vas deferens causing pregnancy, so condoms should be used for 2 months.
- Sperm cells mature for 64 days; testing sperm count ensures sterility.
- Vasectomy doesn't stop erection/spermatogenesis but prevents sperm ejaculation.
- It also doesn't protect from STDs.
Semen Analysis
- Average semen: 3-5 mL, at least 20M sperm/mL, 150M sperm/mL
- Oligospermia: <20M sperm/mL, Aspermia: zero sperm.
- Clomid helps increase sperm production and fertility.
- Average ejaculation: 400M sperm.
- Sperm lifespan: 3-5 days, pH 7-8 alkaline.
Sperm Characteristics
- 30% normal shape/size (so every ejaculation 200M are alive).
- 50% motility (are activley moving).
- 50% Viability
Female External Anatomy
- Mons pubis protects the symphysis pubis.
- Labia majora/minora and the clitoris are present, with the clitoris providing sexual stimulus.
- The vestibule contains urethral meatus and vaginal orifice.
- The female urethra is shorter than the male urethra.
- Clitoris visible for catheterization.
- The fourchette joins labia minora and majora.
- Paraurethral glands and Bartholin's glands are present, with the latter lubricating the vagina.
- Episiotomy is a perineal incision to widen the birth space.
- Mediolateral episiotomy is better than midline.
- Nerve endings are avoided by cutting during contractions.
Female Internal Anatomy
- Size: 3x2x1 inches, pear shaped location
- Location: between bladder and rectum.
- Position: anteflexion, anteverted, retroverted, retroflexion, flexion (abnormal), The uterus assumes a retroverted position during the 2nd trimester.
Uterine Position
- Anteflexion exhibits uterus fundus is leaning sharply forward.
- Discomfort of pregnancy experienced as urinary frequency experienced by pregnant women.
- A pregnant woman is 2 ½ mos pregnant is the uterus already enlarging and anteverted, causing bladder compression.
- This urinary frequency in the 3rd mos. of trimester disappears in 2nd trimester when the uterus position is retroverted.
Uterine Functions
- Implantation site with endometrium; and houses/nourishes products of conception
- Aids in the delivery (promoting contractions).
- Outer perimetrium, middle myometrium and the inner endometrium.
- The uterus as a whole has 4 parts: Fundus, Corpus, Isthmus, Cervix
- Site in fundus, location with the thickest myometrium that gives it the capacity for a strong uterine contraction while downward baby pushes.
Cervix and Ovaries
- Internal os effaces; pregnancy = cervical canal turns into operculum (thickened), which softens because of high estrogen levels.
- External os widens, estrogen makes the cervix soft through Goodell's sign,.
- Purplish/Blueish = Chadwick sign
- Internal os measured by % in delivery and external os by "cm".
- Endometrium best site of implantation in upper segment - posterior, supplied by uterine arteries
- Implamation happen in endometrium, not myometrium, future pregnancy
3 Probable Signs of Pregnancy:
- Chadwicks sign (purplish/blueish color)
- Goodell's sign (softness of cervix)
- Hegar's sign (softening of cervix); GS and HS are the same in function.
- Soft-Non pregnant and earlobe. Late and early = nose tip and earlobe
- Thickned Cervicle mucus(Operculum); acidic vaginal canal with acidity
- Supports the uterus.
Ligaments of the Uterus and Location
- Broad keep the tubes and uterus.
- Round ligament (in midde = important).
- Uterosacral floor ligament/pelvic support(low), allows a retroverted position
- Cardinal (cardinal is not call cardinal, it is not important: stable: cordnal to fundus in 2nd trimester: round
- Uterine nerve is Sensory with the ability to affect motor contractions:
- Epidural affects senosry (with painless delivery.
- 1 Degree differemce between body and S temperature: Sperm=cold
The Fallopian Tubes (Ovaries)
- Pair of tubular Organs; transports ovum once fertilized (w/c
- Is outer thrid) has taken site
- Ampulla allows fertilization, common of ectopic pregnancy
- Fimbriae cath egg -1st day after last mensuration is best time to get tubal ligation 3.4 stay fertilized and Pro (ges): enlargeuterus Estrogen: contractuters Function: produce progesterone and estrogen with epothelium divisions of 3 division.
The Breast
- Mammary Gland in pectoralis muscles, produces milk, storage of milk
- Mammary gland needs stimulus of: Lactin which goes to pituatry and oxytoin to contraract. The best after action of baby because contration remains firm: This will also prevent post bleeding period.
Pelvis
- Support for reproductive and pelivis ogran; has 2 divisions = false and tru
- True= starts at pubis bone : gylnecold, anthropoid, androird(mal), plat(flat) for pregnancy
- Inlet transverse is bigger A then P..Oulter trans smaller, A and P is big Head need to rotate to deliver Baby Mechanism: Defelx, Flex rotate Fetus need pressure and amniotic to move: ballottement.
Ischial Tuberosity
- Sit and weight: Ishical: spine (patay): If pressuring the pelvis baby will get: (t) or not.
- Stationo Zero= pressure to deliver ba; it to low but head not engange, by Bounncine attemp. If head was alwasys engage: its down 5 positve. Ischa Sp is important for delivery. If IE(internal exam) = negative for station: babay may have balllottement Pressure = 3.4 station positive for dialation and contactions
Attitude
- Felx tagala yuko four region of smallness of head
- Suturs to cranial point to space.
- Diamind space called Fotenal Fetal to vagina
- Cephalic, breech and Trasver
- Baby in C head but depend, will still not cause cervical head
Featal Lies and main manament of monapus
Longitudinal, transverse if uterus and parallel to head. This comes down at the same time: E and Pro: but Pro needs to be higher
Pre Menstral Cycle
- GonadoTropins; Ovaries less sensitve, therefore lower E will release
Mamagement of E and Health
- E replacement, hot flash, vagina
- Prevet mood and ostersioosis.. you get younger. cant with fam history breast cancer. after last P Calcium(vitD) will hel renal stones. Regular exercise hel[
Menstration
- Discharge blood from uterus; normal aver= 60cc, heavy; palos Menstration perios only three to fire 7 days, cycle 23 to maxim 40 day: ave 28 day First to 17 , safe:
OVARY
Cycle ovulation: release 2 , and you get pregnant; or if not 8-10 day 3rd: Hormonal, estogen(first), prog(latter), day of cycle If the day cycle does not exist ever month, irriregular, this can cause for infertile cycle. Days are fertile day, not, Note; Longest you do not go more them 35 day; You can do 30 so u set it urself. E is 1st then APG; APG(2), then ovary.. High level
- 4 dates: then P and ovulation hel for pregnancy If your have not had intercourse a B can be very in heat cycle..then its pro and prog is ready to high 7-7 32
Ovarian Fallopian
3d: Low E, stimulation :Est will help 20+ to stim uterus. 1st day menses. 13day: Will releas HRF:stim E then the ovary will increase
Female ovulation
- 2 weeks long then. Corpus lumun. then help contract uterine.
- 3-5ml liquid of sperm, 1ml =5-10m sperms; .4 ml (1 tsp = 1 ml) are active
- Test in lab before Follpoian has fllopain tubule and out is fimbre; which in turn in inter.. If outter = preg outside
Q to ask
7days : pro help fert, and enlarge Es: help contr. E; 8-10 preg get test 4 in total are regulare for ferti If 8/9 = low E = get preggo.
- 2 main layer of ovum to find radita and zona 4= Then ZONA Is tough: made gly 12 35
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.