Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following structures is NOT primarily derived from the endoderm?
Which of the following structures is NOT primarily derived from the endoderm?
- Dentine of teeth (correct)
- Epithelial lining of the stomach
- Urinary bladder
- Epithelial lining of the trachea
The exchange of oxygen and nutrients between the mother and the fetus primarily occurs via diffusion across which structure?
The exchange of oxygen and nutrients between the mother and the fetus primarily occurs via diffusion across which structure?
- Umbilical vein
- Amniotic sac
- Umbilical arteries
- Chorionic villi (correct)
Which of the following structures does NOT have an epithelial lining derived from the endoderm?
Which of the following structures does NOT have an epithelial lining derived from the endoderm?
- Pancreas
- Parts of the mouth (correct)
- Tympanic Cavity
- Thyroid
As fetal development progresses, the amniotic sac expands. What is the result of this?
As fetal development progresses, the amniotic sac expands. What is the result of this?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the serous linings of body cavities?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the serous linings of body cavities?
The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta. Which of the following correctly describes the number and type of blood vessels found in the umbilical cord?
The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta. Which of the following correctly describes the number and type of blood vessels found in the umbilical cord?
Which structure plays a critical role in facilitating the indirect connection for nutrient and gas exchange between the mother and the developing fetus?
Which structure plays a critical role in facilitating the indirect connection for nutrient and gas exchange between the mother and the developing fetus?
Based on their endodermal origin, a defect in the development of which organ would most likely also affect the function of glands opening into the digestive system?
Based on their endodermal origin, a defect in the development of which organ would most likely also affect the function of glands opening into the digestive system?
Most of the fetal blood entering via the umbilical vein is shunted to the inferior vena cava through the _________.
Most of the fetal blood entering via the umbilical vein is shunted to the inferior vena cava through the _________.
Normal circulatory changes occurring within the transitional stage at birth include which of the following?
Normal circulatory changes occurring within the transitional stage at birth include which of the following?
Anatomic narrowing of the ductus arteriosus begins in the last trimester by which process?
Anatomic narrowing of the ductus arteriosus begins in the last trimester by which process?
The vitelline veins, common cardinal veins, and umbilical veins all deliver blood into which structure during early fetal heart development?
The vitelline veins, common cardinal veins, and umbilical veins all deliver blood into which structure during early fetal heart development?
Which of the following sequences accurately represents the initial development of the heart?
Which of the following sequences accurately represents the initial development of the heart?
The atrial, ventricular, and bulbus cordis empty into which structure?
The atrial, ventricular, and bulbus cordis empty into which structure?
What is the significance of angiogenic clusters (blood islands) during early embryonic development?
What is the significance of angiogenic clusters (blood islands) during early embryonic development?
Which of the following events occurs around day 28 of gestation?
Which of the following events occurs around day 28 of gestation?
Around what gestational age does unidirectional blood flow begin in the developing heart?
Around what gestational age does unidirectional blood flow begin in the developing heart?
Choose the correct association between the developmental event and its approximate timing.
Choose the correct association between the developmental event and its approximate timing.
At approximately what gestational age is the separation of the aorta and pulmonary artery completed?
At approximately what gestational age is the separation of the aorta and pulmonary artery completed?
Which structure is responsible for nourishing the embryo during early development?
Which structure is responsible for nourishing the embryo during early development?
At what point in fetal development are all four chambers of the heart complete?
At what point in fetal development are all four chambers of the heart complete?
What is the primary role of fetal shunts in circulation?
What is the primary role of fetal shunts in circulation?
Which fetal shunt allows oxygen-rich blood to bypass the liver and flow directly into the inferior vena cava?
Which fetal shunt allows oxygen-rich blood to bypass the liver and flow directly into the inferior vena cava?
What is the primary reason for the high pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) in fetal circulation?
What is the primary reason for the high pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) in fetal circulation?
In fetal circulation, where does blood with the highest oxygen content primarily go after leaving the left ventricle?
In fetal circulation, where does blood with the highest oxygen content primarily go after leaving the left ventricle?
Why does fetal circulation allow the right and left ventricles to pump almost in parallel?
Why does fetal circulation allow the right and left ventricles to pump almost in parallel?
What percentage range of oxygen-rich blood is shunted through the ductus venosus into the inferior vena cava?
What percentage range of oxygen-rich blood is shunted through the ductus venosus into the inferior vena cava?
What is the significance of the placenta having a large vascular surface area in fetal circulation?
What is the significance of the placenta having a large vascular surface area in fetal circulation?
What happens when the umbilical vessels are clamped during the transition to extrauterine life?
What happens when the umbilical vessels are clamped during the transition to extrauterine life?
Which vessel carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus?
Which vessel carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus?
What directly causes a reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) during the first breath of a newborn?
What directly causes a reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) during the first breath of a newborn?
What is the interface for gas, nutrient, and waste exchange between the maternal and fetal organ systems?
What is the interface for gas, nutrient, and waste exchange between the maternal and fetal organ systems?
Which of the following is the third fetal shunt that allows blood within the pulmonary artery to bypass the lungs?
Which of the following is the third fetal shunt that allows blood within the pulmonary artery to bypass the lungs?
How does increased systemic arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2) contribute to the decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance?
How does increased systemic arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2) contribute to the decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance?
What would be the immediate effect of a significant decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) during fetal development?
What would be the immediate effect of a significant decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) during fetal development?
Besides gas exchange, what mechanical factor contributes to the expansion of pulmonary vasculature after birth?
Besides gas exchange, what mechanical factor contributes to the expansion of pulmonary vasculature after birth?
If the ductus venosus failed to properly shunt blood in a fetus, what would be the most likely immediate consequence?
If the ductus venosus failed to properly shunt blood in a fetus, what would be the most likely immediate consequence?
What changes contribute to the closure of the ductus arteriosus after birth?
What changes contribute to the closure of the ductus arteriosus after birth?
What proportion of the fetal cardiac output flows through the umbilical arteries as the fetus matures?
What proportion of the fetal cardiac output flows through the umbilical arteries as the fetus matures?
During heart development, fusion of the heart tubes gives rise to which structures?
During heart development, fusion of the heart tubes gives rise to which structures?
Oxygenated blood travels from the placenta to the fetus via which vessel?
Oxygenated blood travels from the placenta to the fetus via which vessel?
In fetal circulation, the majority of blood entering the main pulmonary artery is shunted to the aorta through which structure?
In fetal circulation, the majority of blood entering the main pulmonary artery is shunted to the aorta through which structure?
Most of the fetal blood that enters via the right atrium is shunted to the left atrium through the:
Most of the fetal blood that enters via the right atrium is shunted to the left atrium through the:
Which statement accurately describes a characteristic of fetal circulation?
Which statement accurately describes a characteristic of fetal circulation?
Which event triggers the systemic circulation to transition from a low-resistance to a high-resistance system after birth?
Which event triggers the systemic circulation to transition from a low-resistance to a high-resistance system after birth?
Which of the following adaptations is crucial for fetal circulation, allowing the lungs to be bypassed?
Which of the following adaptations is crucial for fetal circulation, allowing the lungs to be bypassed?
How does clamping the umbilical cord contribute to the closure of the ductus arteriosus after birth?
How does clamping the umbilical cord contribute to the closure of the ductus arteriosus after birth?
Flashcards
Major Body Cavities
Major Body Cavities
Cavities that house major organs.
Serous Linings
Serous Linings
Serous membranes that line organs within body cavities.
Tooth components
Tooth components
Includes dentine, cementum, and pulp.
Endoderm
Endoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digestive System (Endoderm)
Digestive System (Endoderm)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory System (Endoderm)
Respiratory System (Endoderm)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System (Endoderm)
Urinary System (Endoderm)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glands (Endoderm)
Glands (Endoderm)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angiogenic Clusters (Blood Islands)
Angiogenic Clusters (Blood Islands)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart Tubes
Heart Tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart Tubes Fusion
Heart Tubes Fusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart Begins to Beat
Heart Begins to Beat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Folding, Looping, Ballooning of the Heart
Folding, Looping, Ballooning of the Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atrial Septation Begins
Atrial Septation Begins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricular Septation Starts
Ventricular Septation Starts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocardial Cushions Form
Endocardial Cushions Form
Signup and view all the flashcards
Septum Secundum Starts
Septum Secundum Starts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foramen Ovale Complete
Foramen Ovale Complete
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta's Role
Placenta's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umbilical Vein
Umbilical Vein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Venosus
Ductus Venosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foramen Ovale
Foramen Ovale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Arteriosus
Ductus Arteriosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ascending Aorta (Fetal)
Ascending Aorta (Fetal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
High Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR)
High Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Veins (Fetal)
Pulmonary Veins (Fetal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Shunts Function
Fetal Shunts Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umbilical Vein Function
Umbilical Vein Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal circulatory changes at birth
Normal circulatory changes at birth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anatomic narrowing of the ductus arteriosus
Anatomic narrowing of the ductus arteriosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta expulsion
Placenta expulsion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Arteriosus Function
Ductus Arteriosus Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circulatory Changes at Birth
Circulatory Changes at Birth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umbilical Arteries Function
Umbilical Arteries Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Cardiac Output in Umbilical Arteries
Fetal Cardiac Output in Umbilical Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta Blood Volume
Placenta Blood Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umbilical Vessel Clamping
Umbilical Vessel Clamping
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impact of First Breath
Impact of First Breath
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lung Inflation Effects
Lung Inflation Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Pressure's Effect
Oxygen Pressure's Effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary stretching
Pulmonary stretching
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Ductus Arteriosus
Function of Ductus Arteriosus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Shunts
Fetal Shunts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placenta Vascular Resistance
Placenta Vascular Resistance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic Circulation Transition
Systemic Circulation Transition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Embryological Overview
- Understanding embryology is important for respiratory care practitioners working with newborns
- Need to know normal fetal development to recognize when something goes wrong
- A vascular network develops to circulate nutrients and allow gas exchange to the growing embryo/fetus
- The fetus relies on mother's circulation for this
- Maternal and fetal vascular networks are separate systems, and no blood is shared
- By gestational day 22 the primitive fetal heart begins to beat
- By days 27-29 the heart has myocardial pump function supporting circulation
Fertilization to Implantation
- The zygote (fertilized egg) travels to the uterus, undergoing cell division
- The zygote has no nutrient source at this time
- The ball of developing cells (blastocyst) must implant in the uterine lining for nourishment
- The trophoblast (outer layer of the blastocyst) combines with endometrial tissues
- This forms the chorionic membrane around the blastocyst
Origin of Tissue Systems
- Ectoderm gives rise to the central and peripheral nervous systems
- It also gives rise to sensory epithelia of the eyes, inner ears, and nose
- As well as glandular tissues like the posterior pituitary gland and adrenal medulla
- Also generates epidermal layer of skin, all specializations (sweat, mammary etc) and enamel of teeth
- Mesoderm gives rise to, cardiovascular and lymphatic systems
- Creates all connective tissue, cartilage and bone, and marrow
- It is also needed for all muscle tissue
- Responsible for the dermis and hypodermis
- It is also needed for kidneys and ureters, and the spleen
- Lastly it gives rise to reproductive tissues, lining of body cavities and teeth (dentin, cementum)
- Endoderm makes the digestive system except for parts of the mouth/pharynx and anus
- Also responsible for respiratory system and epithelial lining of trachea and lungs
- Also makes the urinary system, liver/pancreas, tonsils, thymus, thyroid, and epithelial lining of auditory tube/tympanic cavity
- Cells arrange to form the embryonic disk, which forms the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm
- The outer loop forms the amniotic sac while the inner loop forms the yolk sac
- The yolk sac degenerates and is replaced by the growing amniotic sac
- The amniotic sac surrounds the entire embryo, which attaches to the outer layer via the umbilical stalk
Maternal-Fetal Gas Exchange
- Finger-like projections known as chorionic villi extend into the outer lining of the chorion
- A capillary network forms within the chorionic villi and connects to the umbilical stalk
- Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients diffuse through the capillary surface area via indirect connection
- The interface between mother and fetus is then limited to the discus-shaped placenta
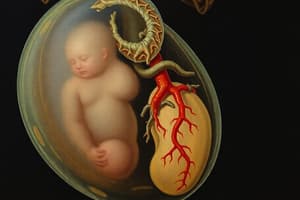
- The umbilical cord connects the placenta to the fetus with one large vein and two smaller arteries
- The vessels tend to spiral and are protected from kinking by Wharton's jelly inside the umbilical cord
Cardiovascular Development
- By the third gestational week, the heart is fully formed, and is the first complete organ formed
- By 8 weeks, the fetal heart is fully functional with all chambers, valves, and major vessels
- The fetal heart must accommodate circulation within a fluid-filled environment
- In early embryonic development, angiogenic clusters supply nutrition to the growing embryo
- Clusters then coalesce to create 2 heart tubes lined with specialized myocardial tissue
- By day 18 the heart tubes fold into the thoracic cavity, fuse, and become the basic structure by day 21
- The cardiovascular system forms from the mesoderm layer and cardiac contractions are detectable by day 22
Chamber Development
- Dramatic changes occur during the fourth week of gestation
- Heart tubes merge into bulbus cordis, ventricular bulge, and atrial bulge
- These empty into the sinus venosus, which receives blood from the vitelline veins, common cardinal veins, and umbilical veins
- These structures continue to bend, fold, and dilate
- As outflow tracts mature, the truncus arteriosus connects the heart to the future arterial system
- Between days 23-28 dextral looping happens, and the ventricular bulge balloons into a C-shape
- This moves the atrial bulge into the superior direction
- The embryonic heart appears as a twisted S-shape
- Ventricular structure merges with the bulbus cordis to form the bulboventricular loop, which dilates
- The septum primum begins separating the primitive atrium and is followed by the growth of endocardial cushions
- This separates the atria from the ventricles
- The left atrium incorporates the primordial pulmonary veins as four pulmonary veins empty into it
- Right horn of the sinus venosus grows and merges into the future right atrium from the vena cavae
- By the fourth week the ventricular spaces fold and force the ventricular septal bud upward.
- By this point, blood flow matures into a unidirectional path.
- During weeks 5-6 the structures mature rapidly
- The septum secundum begins to appear between the atria
- By week 6 the septum secundum and a flap from the septum primum form the foramen ovale (fetal shunt)
- The atrioventricular canal matures and endocardial cushions separate ventricles from the atrium
- The ventricular septum grows as the ventricles dilate
- Ridges appear opposite each other and fuse to form the aorticopulmonary septum
- The atrial heart rate becomes discernible
- At weeks 7 and 8 the ventricles finish forcing the ventricular septum up from its base
- Tissue from the bulbus cordis and endocardial cushions grow to close the ventricular foramen
- The tricuspid and mitral valves form from specialized tissue surrounding the atrioventricular openings
- Aorticopulmonary septum divides the bulbus cordis and truncus into an aortic and pulmonary trunk
- Semilunar valves form at the base of each
- By the eighth week development is complete, cardiac structures are complete, and blood flows normally
- The heart continues to increase in size and length
Fetal circulation and Fetal Shunts
- Fetal circulation differs from an infant because there is no breath
- Fetal circulation lets blood flow shunt around the fetal liver and lungs because mother is respiring for baby
- Blood is shunted through the heart and this allows the proper amount of blood to get to the placenta where there is gas exchange
- Oxygenated blood travels from the placenta through the umbilical vein, which connects to the ductus venosus
- About 30-50% of the umbilical blood is shunted to the IVC via the ductus venosus to by pass the liver
- The amount of shunting through the ductus venosus decreases with age
- The IVC blood mixes with the blood that is coming from the systemic vein
- Most blood passes to the left atrium through the Foramen Ovale, the second fetal shunt
- The remaining blood goes to the right ventircle, it is slightly less oxygenated at this point
- PVR in utero is very high b/c compression of vessels from small lung volumes
- Hypoxic pulmonary vasocontriction also happens, reducing partial pressure of O2
- 13-25% of fetal blood flow goes to lungs
- Then blood goes to the left atrium, then to the left ventricle, then out the aortic valve and to the body
- This blood is going to have higher oxygenation than right side
- High PVR causes the blood of the rigth ventricle to pass through the ductus arteriosus to the aorta so that blood can bypass lungs
Transition to Extrauterine life
- Clamping umbilical cord removes the low pressure system in placenta
- Decreases PVR and icreases pulmobart blood flow because baby inflates lungs
- Increase in PaO2 dilates arterioles, so lungs inflate
- PVR decreases, and pressure on right side decreases, while pressure of left increases
- The foramen ovale closes when pressures of the left atrium become greater than pressures of the right atrium
- This closure facilitates blood flow and facilitates maintaining circulation outside of the womb
- The Functional closure of the Ductus arterious occurs due to increase of PaO2 decreasing PVR
- Reduction of prostaglandins and decrease of prostaglandin receptors in the Ductus aterious
- Constriction happens and 20% close within 24 hours and 80% close in 48
- Anatomic closure of the Ductus Aterious happens in the last Trimester
- Endothelial tissue proliferate intimal mounds, which lead to vasoconstion
- At 204 weeks Anatomic closure is complete
- The Ductus Artiosus becomes the ligamentum arteriosum
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.