Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary reason for the pressure difference between the left and right sides of the fetal heart in-utero?
What is the primary reason for the pressure difference between the left and right sides of the fetal heart in-utero?
- The lung is not functional and there is no breathing in or out of air (correct)
- The umbilical vein is not properly connected to the placenta
- The ductus arteriosus is constricted
- The foramen ovale is not allowing proper blood flow
Which of the following vessels carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava?
Which of the following vessels carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava?
- Pulmonary artery
- Umbilical vein (correct)
- Ductus venosus
- Superior vena cava
What is the fate of the umbilical vein after birth?
What is the fate of the umbilical vein after birth?
- It remains functional and continues to supply oxygenated blood
- It becomes a pulmonary vein
- It disintegrates and becomes the Ligamentum Teres (correct)
- It becomes a major artery
Where does the blood from the right atrium flow to after mixing with oxygenated blood?
Where does the blood from the right atrium flow to after mixing with oxygenated blood?
What is the primary reason for the pressure change in the fetal heart after birth?
What is the primary reason for the pressure change in the fetal heart after birth?
What is the function of the ductus arteriosus in the fetal circulation?
What is the function of the ductus arteriosus in the fetal circulation?
What is the path of oxygenated blood from the placenta to the body?
What is the path of oxygenated blood from the placenta to the body?
What is the difference between the fetal circulation and the adult circulation?
What is the difference between the fetal circulation and the adult circulation?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
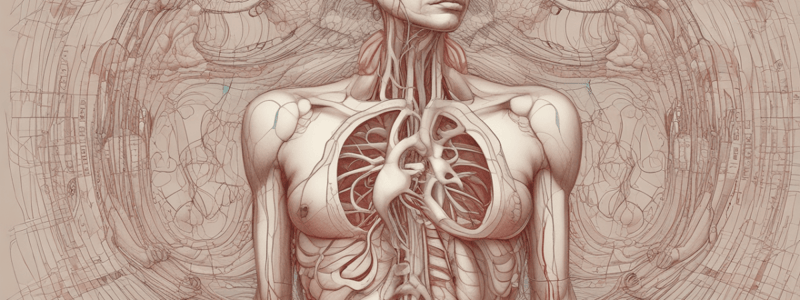
Fetal Circulation: In-Utero
- In-utero, the lung is not functional, and the fetus receives nutrients from the placenta.
- Hypoxic vasoconstriction of pulmonary arteries occurs due to lack of oxygen.
- Pressure is higher in the right side of the heart compared to the left side.
Fetal Circulation: Oxygenated Blood
- Oxygenated blood from the placenta is carried by the umbilical vein to the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava (IVC).
- The ductus venosus shunts blood from the umbilical vein into the IVC.
- Blood passes from the IVC to the right atrium, then through the foramen ovale to the left atrium.
- Blood flows from the right to left atrium due to higher pressure in the right side, allowing for more oxygenated blood.
- Blood then passes from the left atrium to the left ventricle, aorta, and body.
- Some blood passes into the right ventricle, pulmonary trunk, and arteries, and then through the ductus arteriosus shunt into the aorta.
Fetal Circulation: Deoxygenated Blood
- Deoxygenated blood is carried by the superior vena cava (SVC) to the right atrium.
- Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mixes in the right atrium.
- Blood passes from the right atrium to the right ventricle, pulmonary arteries, and then through the ductus arteriosus shunt into the aorta.
- Blood then flows from the descending aorta to the internal iliac artery, and then through the two umbilical arteries to the placenta.
Fetal Circulation: After Birth
- After birth, the lung becomes functional, and hypoxic vasoconstriction of pulmonary arteries ceases.
- Pressure is lower in the right side of the heart compared to the left side.
- The blood level in pulmonary arteries increases, and pulmonary veins empty blood into the left atrium, establishing the adult system.
Fate of Fetal Shunts
- The umbilical vein disintegrates and becomes the Ligamentum Teres after birth.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.