Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of capacitation in the fertilization process?
What is the primary purpose of capacitation in the fertilization process?
- To allow sperm to penetrate the zona pellucida (correct)
- To promote sperm formation
- To enhance sperm motility
- To initiate acrosome reaction
During the movement of sperm from the cervix to the oviduct, what assists their propulsion?
During the movement of sperm from the cervix to the oviduct, what assists their propulsion?
- Muscle contractions of the uterus
- Chemical signals from the oocyte
- Fluid movements generated by uterine cilia (correct)
- Cilia of the uterine tube
Which key event occurs during the acrosome reaction?
Which key event occurs during the acrosome reaction?
- Exocytosis of the acrosome (correct)
- Sperm membrane fusion with the oocyte
- Activation of sperm motility
- Sperm undergoes capacitation
What is a necessary condition for sperm to fertilize the oocyte?
What is a necessary condition for sperm to fertilize the oocyte?
What happens to sperm motility upon reaching the isthmus during their journey?
What happens to sperm motility upon reaching the isthmus during their journey?
What is the duration of capacitation that sperm must undergo before they can fertilize an oocyte?
What is the duration of capacitation that sperm must undergo before they can fertilize an oocyte?
What is the zona pellucida?
What is the zona pellucida?
What triggers the acrosome reaction in sperm?
What triggers the acrosome reaction in sperm?
What is the primary function of the zona pellucida during fertilization?
What is the primary function of the zona pellucida during fertilization?
What enzyme is primarily released during the penetration of the zona pellucida?
What enzyme is primarily released during the penetration of the zona pellucida?
Which statement accurately describes the process of capacitation?
Which statement accurately describes the process of capacitation?
What initiates the acrosome reaction in sperm?
What initiates the acrosome reaction in sperm?
After the sperm binds to the zona pellucida, what happens to prevent further sperm penetration?
After the sperm binds to the zona pellucida, what happens to prevent further sperm penetration?
Which phase of fertilization involves the sperm penetrating the zona pellucida?
Which phase of fertilization involves the sperm penetrating the zona pellucida?
What changes occur in the zona pellucida once one spermatozoon successfully penetrates the oocyte?
What changes occur in the zona pellucida once one spermatozoon successfully penetrates the oocyte?
What role do integrins on the oocyte play in fertilization?
What role do integrins on the oocyte play in fertilization?
What happens to the oocyte membrane immediately after a spermatozoon enters?
What happens to the oocyte membrane immediately after a spermatozoon enters?
Which process describes the alteration of the zona pellucida to prevent further sperm binding?
Which process describes the alteration of the zona pellucida to prevent further sperm binding?
What is the result of the spermatozoon entering the oocyte regarding the meiotic division?
What is the result of the spermatozoon entering the oocyte regarding the meiotic division?
What happens to the plasma membrane of the spermatozoon upon fusion with the oocyte membrane?
What happens to the plasma membrane of the spermatozoon upon fusion with the oocyte membrane?
What is formed when the male pronucleus is created?
What is formed when the male pronucleus is created?
What is the primary function of the activating factor from the spermatozoon?
What is the primary function of the activating factor from the spermatozoon?
How do the maternal and paternal chromosomes contribute to the zygote after fertilization?
How do the maternal and paternal chromosomes contribute to the zygote after fertilization?
Which of the following correctly describes the pronuclei after the sperm enters the oocyte?
Which of the following correctly describes the pronuclei after the sperm enters the oocyte?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
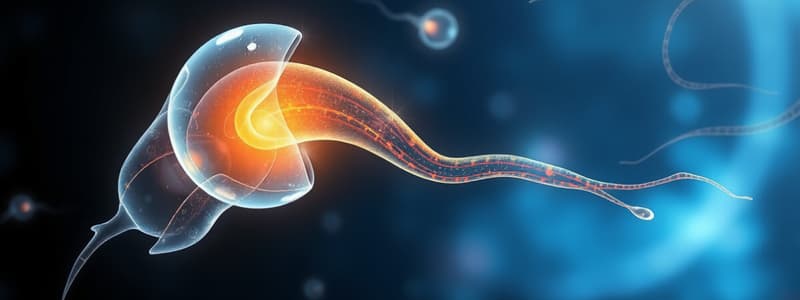
Phases of Fertilization
-
Phase 1: Penetration of the Corona Radiata
- 200-300 million sperm deposited; only 300-500 reach fertilization site.
- Other sperm assist the fertilizing sperm in overcoming barriers.
- Capacitated sperm move through corona cells.
-
Phase 2: Penetration of the Zona Pellucida
- Zona pellucida plays a critical role in sperm binding and triggers the acrosome reaction.
- Binding mediated by zona protein (ZP3).
- Acrosomal enzymes (e.g., acrosin) enable sperm to penetrate zona pellucida.
- Sperm contact with the oocyte alters zona permeability.
- Release of lysosomal enzymes from oocyte cortical granules prevents further sperm penetration and alters zona properties, ensuring only one sperm can fertilize.
-
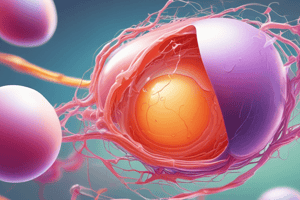
Phase 3: Fusion of Oocyte and Sperm Membranes
- Initial adhesion through integrins on the oocyte and disintegrins on sperm.
- Sperm fusion with the oocyte maintains compatibility for fertilization.
Fertilization Basics
- Fertilization involves the fusion of male and female gametes.
- Occurs in the ampullary region of the uterine tube.
Movement of Spermatozoa
- 1% of sperm deposited in the vagina reach the cervix.
- Sperm rely on propulsion and fluid movement for migration to the oviduct, taking 2-7 hours.
- Sperm become less motile at the isthmus but regain motility at ovulation due to chemo-attractants.
Capacitation
- Process that prepares sperm for zona pellucida penetration.
- Lasts approximately 7 hours, mostly in the uterine tube.
- Involves the removal of glycoprotein and seminal plasma proteins from the sperm's membrane.
Acrosome Reaction
- Exocytosis of the acrosome triggered by zona proteins.
- Plasma membranes of sperm and oocyte fuse, allowing one spermatozoon to penetrate the oocyte.
- Only the head and tail of the sperm enter the oocyte cytoplasm, leaving the plasma membrane on the oocyte’s surface.
Immediate Egg Responses Post-Fertilization
- Cortical and zona reactions ensure the oocyte’s impermeability to additional sperm.
- Resumption of second meiotic division occurs immediately, resulting in a second polar body and the definitive oocyte.
- Activation factors from the sperm initiate metabolic processes in the egg.
Formation of Pronuclei
- Sperm nucleus swells and forms the male pronucleus.
- Male and female pronuclei are morphologically indistinguishable and eventually merge.
DNA Replication in Zygote
- Each pronucleus (haploid) replicates its DNA, preparing for the diploid state.
- 23 maternal and 23 paternal chromosomes split, ensuring zygote receives a normal diploid chromosome number.
Results of Fertilization
- Restoration of diploid chromosome number with half from each parent.
- Creation of a genetically unique zygote.
- Determination of the sex of the new individual based on chromosomal combination.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.