Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which bones contribute to the formation of the acetabulum in the hip joint?
Which bones contribute to the formation of the acetabulum in the hip joint?
- Ilum, Ischium, Pubis (correct)
- Pubis, Femur, Ilium
- Ischium, Sacrum, Coccyx
- Ilium, Ischium, Coccyx
What structure bridges the hip joints anteriorly?
What structure bridges the hip joints anteriorly?
- Coccygeal ligament
- Pubic symphysis (correct)
- Sacral promontory
- Ischial tuberosity
Which of the following is NOT part of the obstetric conjugate diameter?
Which of the following is NOT part of the obstetric conjugate diameter?
- Arcuate line of the ilium
- Superior edge of the pubic symphysis
- Inferior ramus of pubis (correct)
- Sacral promontory
Which pelvic structure aids in the passage of the fetus's head during birth?
Which pelvic structure aids in the passage of the fetus's head during birth?
Which part of the pelvis is located posteriorly and articulates with the hip joint?
Which part of the pelvis is located posteriorly and articulates with the hip joint?
What structure surrounds the uterus and is the largest subsection of the broad ligament?
What structure surrounds the uterus and is the largest subsection of the broad ligament?
Which of the following accurately describes the mesovarium?
Which of the following accurately describes the mesovarium?
How long are the fallopian tubes typically?
How long are the fallopian tubes typically?
What is salpingitis?
What is salpingitis?
The term TAH BSO stands for what medical procedure?
The term TAH BSO stands for what medical procedure?
What is another name for a prolapsed bladder?
What is another name for a prolapsed bladder?
What structure holds the vagina open during sexual arousal?
What structure holds the vagina open during sexual arousal?
What layer of the uterus contracts to help expel the fetus during childbirth?
What layer of the uterus contracts to help expel the fetus during childbirth?
What type of innervation is associated with the lower quarter of the vagina?
What type of innervation is associated with the lower quarter of the vagina?
What is the broad ligament primarily composed of?
What is the broad ligament primarily composed of?
What is the length of a normal vagina when relaxed?
What is the length of a normal vagina when relaxed?
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for changing size during pregnancy?
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for changing size during pregnancy?
Which part of the reproductive organs is supported by the broad ligament?
Which part of the reproductive organs is supported by the broad ligament?
The upper three-quarters of the vagina contain which types of innervation?
The upper three-quarters of the vagina contain which types of innervation?
What is the primary function of the perimetrium?
What is the primary function of the perimetrium?
What is the primary role of theca cells in the ovaries?
What is the primary role of theca cells in the ovaries?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does ovulation occur?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does ovulation occur?
What is the primary form of estrogen produced during pregnancy?
What is the primary form of estrogen produced during pregnancy?
Which gland's infection leads to skenitis?
Which gland's infection leads to skenitis?
What is the role of progesterone during pregnancy?
What is the role of progesterone during pregnancy?
Which statement best describes the effects of estrogen on cervical mucus?
Which statement best describes the effects of estrogen on cervical mucus?
What is the relationship between FSH and estrogen levels during the secretory phase?
What is the relationship between FSH and estrogen levels during the secretory phase?
Which structure is primarily responsible for producing hormones during the first ten weeks of pregnancy?
Which structure is primarily responsible for producing hormones during the first ten weeks of pregnancy?
What are the main components of the pelvic diaphragm?
What are the main components of the pelvic diaphragm?
Which of the following describes a function of the pelvic diaphragm?
Which of the following describes a function of the pelvic diaphragm?
What are the apertures found in the pelvic diaphragm?
What are the apertures found in the pelvic diaphragm?
What is the primary role of the perineum?
What is the primary role of the perineum?
What effect does damage to the perineal body have on the pelvic diaphragm?
What effect does damage to the perineal body have on the pelvic diaphragm?
Which of the following conditions can lead to the bulging of the bladder into the vagina?
Which of the following conditions can lead to the bulging of the bladder into the vagina?
What issues may some individuals face due to pelvic floor weakness?
What issues may some individuals face due to pelvic floor weakness?
What is the primary function of the structures beneath the pelvic floor?
What is the primary function of the structures beneath the pelvic floor?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Objectives
- Recognize anatomical structures of the female reproductive system and pelvis.
- Describe the physiology of the menstrual cycle.
Bones of the Pelvis
- The acetabulum, formed by ilium, ischium, and pubis, articulates with the femur's head.
- Hip joints connect anteriorly through the pubic symphysis and posteriorly to the sacrum.
- Key landmarks include superior edge of pubic symphysis, arcuate line of the ilium, and sacral promontory.
Shapes of the Pelvis
- The obstetric conjugate diameter is crucial during childbirth as it is the first point in the maternal pelvis that the fetal head passes.
Pelvic Floor and Perineum
- The pelvic diaphragm comprises levator ani and coccygeus muscles, providing support against intra-abdominal pressure.
- The perineum is a sensitive area between the genitals and anus, crucial for urination, defecation, and copulation.
- Three apertures in the pelvic diaphragm allow for the urinary orifice, vaginal orifice, and anus.
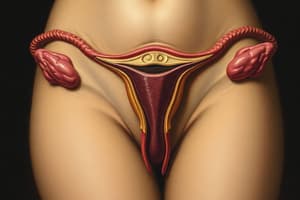
Internal Reproductive Organs
- The vagina is a muscular tube about 8 cm long, innervated differently in its upper and lower portions.
- The uterus is a thick, hollow organ with considerable size variation during pregnancy, comprising endometrium, myometrium, and perimetrium.
Broad Ligament
- A peritoneum fold that supports the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, dividing into mesometrium, mesovarium, and mesosalpinx.
Ovaries and Fallopian Tubes
- Ovaries are almond-shaped, produce oocytes and hormones, and mature oocytes into follicles.
- Each fallopian tube captures the ovulated ovum through fimbriae, potentially inflamed as salpingitis.
External Genitalia
- Comprised of various structures that support reproductive functions.
Glands and Hormones
- Ovaries contain theca and granulosa cells, converting androgens into estrogen.
- Skene's glands and Bartholin glands lubricate the vagina; infections can cause skenitis and bartholinitis, respectively.
Menstrual Cycle Phases
- Menstruation: Days 0-4
- Proliferative Phase: Days 5-13
- Ovulation: Day 14, triggered by the LH surge
- Secretory Phase: Corpus luteum releases estrogen and progesterone, inhibiting GnRH and reducing FSH.
Estrogen
- Three forms: Estrone (E1), Estradiol (E2), and Estriol (E3) tailored for specific life stages.
- Peaks before ovulation, thins cervical mucus to enhance sperm mobility, and keeps vaginal walls thick and lubricated.
Progesterone
- A steroid hormone produced mainly by the ovaries and adrenal cortex, crucial for maintaining uterine health during pregnancy.
- Reduces myometrial contractions to support pregnancy.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.