Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the fimbriae in the oviducts?
What is the primary function of the fimbriae in the oviducts?
- To produce estrogen and progesterone
- To implant the embryo in the uterine lining
- To propel the egg slowly through the oviduct
- To sweep over the ovaries and guide the egg into the oviduct (correct)
What is the typical location of the uterus in relation to the urinary bladder?
What is the typical location of the uterus in relation to the urinary bladder?
- Above and tipped over the urinary bladder (correct)
- Below and behind the urinary bladder
- To the side of the urinary bladder
- In front of the urinary bladder
What is the usual width of the uterus in its usual state?
What is the usual width of the uterus in its usual state?
- 2 cm
- 5 cm (correct)
- 10 cm
- 15 cm
Where does implantation of the embryo usually occur?
Where does implantation of the embryo usually occur?
What is the function of the cilia that line the oviducts?
What is the function of the cilia that line the oviducts?
What is the name of the structure that contains the opening to the uterus?
What is the name of the structure that contains the opening to the uterus?
What is the function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
What is the function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
What is the purpose of the muscular walls of the uterus?
What is the purpose of the muscular walls of the uterus?
What is the main function of the endometrium during embryonic and fetal development?
What is the main function of the endometrium during embryonic and fetal development?
What is the purpose of the functional layer of the endometrium?
What is the purpose of the functional layer of the endometrium?
What is the angle at which the vagina lies to the small of the back?
What is the angle at which the vagina lies to the small of the back?
What is the purpose of the acidic environment in the vagina?
What is the purpose of the acidic environment in the vagina?
How many eggs does a female produce on average per month during her reproductive years?
How many eggs does a female produce on average per month during her reproductive years?
What is the purpose of the follicular fluid in a secondary follicle?
What is the purpose of the follicular fluid in a secondary follicle?
What is the result of meiosis I in a primary oocyte?
What is the result of meiosis I in a primary oocyte?
What is the name of the cell that results from meiosis I in a primary oocyte?
What is the name of the cell that results from meiosis I in a primary oocyte?
What triggers ovulation at around day 14 of a 28-day cycle?
What triggers ovulation at around day 14 of a 28-day cycle?
What is the main function of estrogen in females?
What is the main function of estrogen in females?
During which phase of the ovarian cycle does the corpus luteum develop?
During which phase of the ovarian cycle does the corpus luteum develop?
What is the primary function of progesterone during the uterine cycle?
What is the primary function of progesterone during the uterine cycle?
What is the approximate age range during which menopause typically occurs?
What is the approximate age range during which menopause typically occurs?
What is the hormone responsible for milk letdown during nursing?
What is the hormone responsible for milk letdown during nursing?
What is the duration of menstruation cessation required to confirm menopause?
What is the duration of menstruation cessation required to confirm menopause?
What occurs to the endometrium during days 1-5 of a 28-day uterine cycle?
What occurs to the endometrium during days 1-5 of a 28-day uterine cycle?
What is the primary function of a polar body?
What is the primary function of a polar body?
What happens to the endometrium during the proliferative phase of the uterine cycle?
What happens to the endometrium during the proliferative phase of the uterine cycle?
What triggers the secondary oocyte to undergo meiosis II?
What triggers the secondary oocyte to undergo meiosis II?
What is the primary function of the corpus luteum during the uterine cycle?
What is the primary function of the corpus luteum during the uterine cycle?
What is the typical thickness of the endometrium at the end of the secretory phase?
What is the typical thickness of the endometrium at the end of the secretory phase?
What happens to the corpus luteum if the egg is not fertilized?
What happens to the corpus luteum if the egg is not fertilized?
Which hormone from the hypothalamus controls the ovaries' sexual function?
Which hormone from the hypothalamus controls the ovaries' sexual function?
What happens to the corpus luteum if implantation does not occur?
What happens to the corpus luteum if implantation does not occur?
What is the primary hormonal signal that triggers ovulation?
What is the primary hormonal signal that triggers ovulation?
What happens to the estrogen level in the blood during the follicular phase?
What happens to the estrogen level in the blood during the follicular phase?
What is the result of the estrogen spike at the end of the follicular phase?
What is the result of the estrogen spike at the end of the follicular phase?
During which days of the uterine cycle does the endometrium prepare to receive the developing embryo?
During which days of the uterine cycle does the endometrium prepare to receive the developing embryo?
What happens to the anterior pituitary secretion of FSH as the estrogen level in the blood rises?
What happens to the anterior pituitary secretion of FSH as the estrogen level in the blood rises?
Which of the following structures develops from a vesicular follicle after it has lost the oocyte?
Which of the following structures develops from a vesicular follicle after it has lost the oocyte?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Female Reproductive System
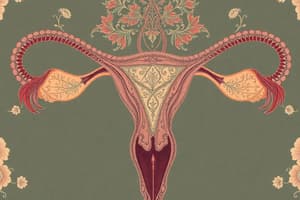
- The female reproductive system is divided into internal reproductive organs and external genital organs.
Internal Reproductive Organs
- Ovaries:
- Produce eggs (ova) and female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone
- Lie in shallow depressions on each side of the upper pelvic cavity
- Oviducts (Uterine or Fallopian Tubes):
- Conduct eggs
- Location of fertilization
- Extend projections called fimbriae that sweep over the ovaries
- Uterus (Womb):
- Houses developing fetus
- Thick-walled, muscular organ about the size and shape of an inverted pear
- Cervix:
- Contains opening to uterus
- Vagina:
- Serves as birth canal and exit for menstrual flow
- Tube that lies at a 45° angle to the small of the back
- Mucosal lining lies in folds and can extend
Ovarian Cycle
- An ovary contains many follicles, each containing an immature egg called an oocyte
- A female is born with 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000 by the time of puberty
- Only a small number of follicles (about 400) ever mature because a female usually produces only one egg per month during her reproductive years
- The ovarian cycle consists of three stages:
- Primary follicle stage
- Secondary follicle stage
- Vesicular (Graafian) follicle stage
- Ovulation:
- The vesicular follicle bursts, releasing the oocyte (egg) surrounded by a clear membrane
- Occurs around day 14 of a 28-day cycle
Oogenesis
- Primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I, resulting in haploid cells with 23 chromosomes each
- One of these cells is called a polar body, which is a sort of cellular "trash can"
- Secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis II, but only if it is first fertilized by a sperm cell
- If the secondary oocyte remains unfertilized, it will die shortly after being released from the ovary
Estrogen and Progesterone
- Estrogen:
- Produced by primary and secondary follicles
- Responsible for secondary sex characteristics in females, such as axillary and pubic hair during puberty and fat distribution
- Affects breast development
- Progesterone:
- Produced by the corpus luteum
- Preparates the uterus to receive a fertilized egg
- Affects breast development
Uterine Cycle
- The uterine cycle is a cyclical series of events caused by the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone
- 28-day cycle consists of:
- Days 1-5: Low estrogen and progesterone levels cause the endometrium to disintegrate and its blood vessels to rupture
- Days 6-13: Increased estrogen production causes the endometrium to thicken and become vascular and glandular (proliferative phase)
- Days 14-28: Increased progesterone production causes the endometrium to double or triple in thickness and prepare for implantation (secretory phase)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.