Podcast
Questions and Answers
What forms the lens, cornea outer epithelium, and palpebrae epithelium in embryology?
What forms the lens, cornea outer epithelium, and palpebrae epithelium in embryology?
- Ectoderm (correct)
- Endoderm
- Neuroectoderm
- Mesoderm
Which layer of the eye is composed of the retina and pigment epithelium?
Which layer of the eye is composed of the retina and pigment epithelium?
- Outer fibrous tunic
- Inner retinal tunic
- Middle vascular tunic
- Optic cup (correct)
What is the term for the supporting structures of the eye?
What is the term for the supporting structures of the eye?
- Adnexa (correct)
- Lens
- Sclera
- Retina
What is the order of eye color, from least pigmented to most pigmented?
What is the order of eye color, from least pigmented to most pigmented?
What forms the optic nerve in embryology?
What forms the optic nerve in embryology?
What is the term for the boney socket in the skull that contains the eyeball?
What is the term for the boney socket in the skull that contains the eyeball?
What is the location of the ciliary processes?
What is the location of the ciliary processes?
What is the significance of knowing the eye layers in ocular diagnosis?
What is the significance of knowing the eye layers in ocular diagnosis?
What type of cells are responsible for forming the aqueous humor?
What type of cells are responsible for forming the aqueous humor?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the drainage pathway of aqueous humor?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the drainage pathway of aqueous humor?
What is the role of Amacrine cells in the optical retina?
What is the role of Amacrine cells in the optical retina?
What is the primary function of the aqueous humor?
What is the primary function of the aqueous humor?
What is the composition of the sclera?
What is the composition of the sclera?
Which of the following tunics is NOT part of the eye?
Which of the following tunics is NOT part of the eye?
What is the pathway of light through the retina?
What is the pathway of light through the retina?
What is the primary function of the adenosine triphosphatase and carbonic anhydrase pumps in the cornea?
What is the primary function of the adenosine triphosphatase and carbonic anhydrase pumps in the cornea?
What is the main reason for the transparency of the cornea?
What is the main reason for the transparency of the cornea?
What is the function of the posterior limiting membrane (Descemet's membrane)?
What is the function of the posterior limiting membrane (Descemet's membrane)?
Which layer of the cornea is composed primarily of Type 1 collagen?
Which layer of the cornea is composed primarily of Type 1 collagen?
What is the primary function of the limbus?
What is the primary function of the limbus?
What is the primary function of the choroid?
What is the primary function of the choroid?
Which part of the retina is responsible for sending visual images to the brain?
Which part of the retina is responsible for sending visual images to the brain?
What is the result of the lack of melanin pigment in the eyes of individuals with albinism?
What is the result of the lack of melanin pigment in the eyes of individuals with albinism?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the choroid?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the choroid?
What is the function of the iridocorneal angle?
What is the function of the iridocorneal angle?
What is the composition of the stroma in the iris?
What is the composition of the stroma in the iris?
What is the role of the vitreous body in the eye?
What is the role of the vitreous body in the eye?
What is the function of the ciliary muscle during accommodation?
What is the function of the ciliary muscle during accommodation?
What is the sensory innervation of the cornea?
What is the sensory innervation of the cornea?
What is the composition of the iridocorneal angle?
What is the composition of the iridocorneal angle?
What is the function of the ciliary body?
What is the function of the ciliary body?
What does the boxed section of this image represent?
What does the boxed section of this image represent?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is number 5 referring to?
What is number 5 referring to?
What is this an image of?
What is this an image of?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
What is letter "D" referring to?
What is letter "D" referring to?
What is letter "E" referring to?
What is letter "E" referring to?
What is letter "F" referring to?
What is letter "F" referring to?
What is letter "G" referring to?
What is letter "G" referring to?
What is letter "H" referring to?
What is letter "H" referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is number 5 referring to?
What is number 5 referring to?
What is the circled part of this image referring to?
What is the circled part of this image referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is number 4 referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 1 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 2 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is number 3 referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
What is letter "D" referring to?
What is letter "D" referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "A" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "B" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
What is letter "C" referring to?
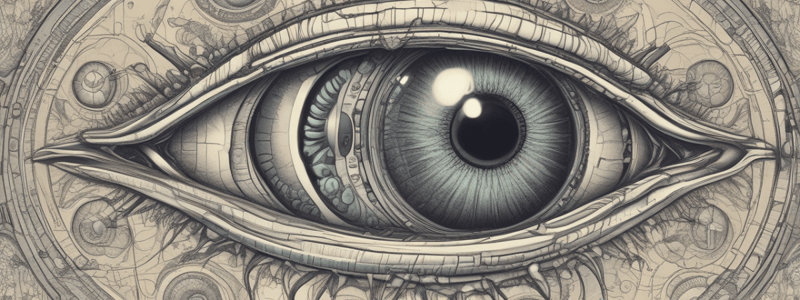
The sclera is the posterior portion of the eye, while the cornea is the anterior portion of the eye.
The sclera is the posterior portion of the eye, while the cornea is the anterior portion of the eye.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Eye Development (Embryology)
- Ectoderm forms the lens, cornea outer epithelium, and palpebrae epithelium (eyelids)
- Mesoderm forms the corneal stroma, sclera, extraocular muscles, ciliary muscles, and tunica vasculosa
- Neuroectoderm of diencephalon forms the optic cup, which remains connected to the optic stalk
- Optic cup has two layers: retina and pigment epithelium
- Optic stalk forms the optic nerve
Eye: General Info
- The eyeball (globe) is located in the skull's boney socket, known as the orbit
- The eye is composed of a lens, and three layers: outer fibrous tunic, middle vascular (uveal) tunic, and inner retinal (neuroepithelial) tunic
- Adnexa (accessory ocular structures) are the supporting structures, including palpebrae (eyelids), third eyelid and conjunctiva, and the lacrimal apparatus
- Knowing the eye layers is important for clinical diagnosis, such as determining the severity of a corneal ulcer
Eye Color
- Eye color follows the trend: blue, gray, green, brown iris, with blue iris having minimal pigment in the stroma of the iris
Ciliary Processes
- Ciliary processes are located at the base of the iris
- Epithelial surface of ciliary processes has two layers of low columnar epithelium, which can be pigmented or nonpigmented
- Nonpigmented epithelium forms aqueous humor, while pigmented epithelium forms zonular fibers that suspend the lens
Aqueous Humor
- Aqueous humor occupies the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye, nourishing the cornea and lens
- Aqueous humor maintains the intraocular pressure and is formed by non-pigmented cells of the ciliary processes
- Aqueous humor requires constant drainage at the iridocorneal angle
Drainage Pathway of Aqueous Humor
- Aqueous humor drains from the posterior chamber, through the pupil, to the anterior chamber, to the iridocorneal angle, past the pectinate ligaments, to the scleral venous plexus
Optical Retina
- Light passes through layers of the retina, stimulating photoreceptor cells (rods and cones)
- Impulse is passed to bipolar neurons, then to ganglion cells
- Axons of ganglionic cells form the nerve fiber layer, where these layers converge at the optic disk (papilla) and leave the eye as the optic nerve (cranial nerve 2)
- Additional cells with supporting roles include Amacrine cells (interneurons), horizontal cells (regulate input from photoreceptor cells), and Muller cells (glial cells)
Eye: Tunics
- The eye tunics include the: fibrous tunic, vascular (uveal) tunic, and neuroepithelial (retinal) tunic
Fibrous Tunic
- The fibrous tunic is composed of the sclera, cornea, and limbus
- Sclera is the posterior portion of the eye, composed of a white opaque layer of dense irregular connective tissue
- Sclera functions include eye protection, maintaining eye shape, and providing insertion point for extraocular muscle tendons
- Cornea is the anterior portion of the eye, avascular and transparent
- Cornea is richly supplied with sensory nerves (from the ophthalmic branch of cranial nerve 5)
- Cornea is highly capable of regenerating
- Cornea is composed of five layers: anterior corneal epithelium, anterior limiting lamina/subepithelial basement membrane, substantia propria, posterior limiting membrane (Descemet's membrane), and posterior epithelium (corneal endothelium)
Limbus (Corneoscleral Junction)
- Limbus is where the opaque sclera overlaps the transparent cornea
- Limbus has small blood vessels
- Nutrition from the cornea comes from the microvasculature of the limbus and aqueous humor
- Epithelium of the limbus is continuous with the conjunctiva that lines the eyelids
Vascular (Uveal) Tunic
- The vascular tunic is composed of the iridocorneal angle, iris, ciliary body, and choroid
- Iris contains the stroma, which is a pigment of loose connective tissue
- Iridial melanin is present in the stromal cells, determining the eye's color
- Iris has dilators and sphincter pupillae muscles
- Posterior epithelium of the iris contains iridic granules (corpora nigra), present in equids and ruminants at the dorsal ventral pupillary margins
- Iridocorneal angle is also known as the filtration angle or drainage angle
- Iridocorneal angle is located at the convergence of corneoscleral junction (limbus), ciliary body, and the iris
- Iridocorneal angle is composed of pectinate ligament, trabecular meshwork, and trabecular (aqueous) veins
- Iridocorneal angle functions as a drainage point for aqueous humor
Ciliary Body
- Ciliary body is the anterior expansion of the choroid at the level of the lens, containing mechanical and secretory functions
- Ciliary body houses the ciliary muscle, which is composed of smooth muscle, surrounded by loose connective tissue (elastic fibers, vessels, and melanocytes)
- Ciliary muscle contracts during accommodation, reducing the tension of the zonular fibers of the lens
- Ciliary muscle receives innervation from cranial nerve 3 (oculomotor nerve)
- Posterior pigmented epithelium of the iris is continuous with the nonpigmented epithelium of the ciliary body
Choroid
- Choroid is highly vascularized, functioning as the nutritional source for the retina
- Choroid contains four parts: anterior, external, internal, and internal to vascular layer (tapetum lucidum)
Neuroepithelial (Retinal) Tunic
- Retina has three parts: sensory/optic, non-sensory/ciliary, and non-sensory/iridal
- Sensory/optic part contacts the choroid, sending visual images to the brain, and is composed of 10 layers held in place by the vitreous body
- Combined nerve fiber layers converge on the optic disk to form the optic nerve
- Non-sensory/ciliary part consists of inner nonpigmented and outer pigmented ciliary epithelium "pars ciliaris retinae"
- Non-sensory/iridal part consists of posterior pigmented epithelium "pars iridica retinae"
Albinism
- Albinism is an inherited congenital disorder, characterized by a partial or total lack of melanin pigment in the eyes, skin, and hair
- Albinos have melanocytes, which produce melanin, but lack genes for tyrosinase
- Albinism results from inheritance of recessive alleles
- Red-colored eyes are a result of the lack of melanin pigment in the eyes, including the iris
- The red coloration is due to hemoglobin in the red blood cells
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.