Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which factor contributes to the formation of climate zones?
Which factor contributes to the formation of climate zones?
- Industrialization
- Altitude (correct)
- Population density
- Longitude
Which climate zone is characterized by high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and dense vegetation?
Which climate zone is characterized by high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and dense vegetation?
- Tropical Dry Forests
- Polar Climate
- Desert Climate
- Tropical Rainforests (correct)
How do mountains impact climate zones?
How do mountains impact climate zones?
- By creating their own climate zones (correct)
- By reducing altitude
- By decreasing precipitation
- By increasing ocean currents
Which region is likely to have year-round growth due to its climate zone?
Which region is likely to have year-round growth due to its climate zone?
How do climate zones impact agriculture?
How do climate zones impact agriculture?
What role do climate zones play in shaping human societies?
What role do climate zones play in shaping human societies?
How are climate zones related to the distribution of plant and animal species?
How are climate zones related to the distribution of plant and animal species?
What is the significance of understanding climate zones for farmers?
What is the significance of understanding climate zones for farmers?
Why are climate zones described as a fundamental aspect of geography?
Why are climate zones described as a fundamental aspect of geography?
How do climate zones contribute to the development of species in diverse environments?
How do climate zones contribute to the development of species in diverse environments?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Exploring Climate Zones: The Geographic Landscape
Climate zones, a fundamental concept in geography, help us understand the diverse weather patterns and ecosystems that shape our planet. As we delve into this topic, we'll examine how climate zones form and the fascinating ways they influence natural environments and human societies.
Defining Climate Zones
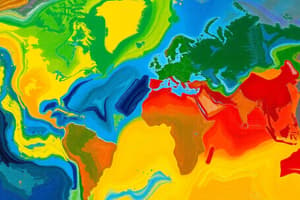
A climate zone is a region that shares similar temperature and precipitation patterns, contributing to distinct ecosystems and natural environments. These zones are determined by factors such as latitude, altitude, and ocean currents.
Formation of Climate Zones
- Latitude: Zones near the poles experience colder temperatures and longer winter seasons, while equatorial regions are warmer and have year-round growth.
- Altitude: As elevation increases, temperature decreases, and precipitation patterns change. Mountains create their own climate zones due to their height.
- Ocean currents: Warm and cold water currents can create distinct climates, such as the Gulf Stream influencing the mild climate of the eastern United States.
Major Climate Zones
- Tropical Rainforests (Equatorial Climate): These regions are characterized by high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and dense vegetation.
- Tropical Dry Forests and Savannas (Tropical Savanna Climate): Particularly in Africa, these zones experience distinct dry and wet seasons.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests (Humid Subtropical Climate): These forests are found in the mid-latitudes and experience distinct seasons.
- Temperate Grasslands (Steppe Climate): Grassy prairies and steppes are found in semi-arid areas, such as the Great Plains.
- Wetlands and Tundras (Polar Climate): These cold climates are characterized by short growing seasons and harsh weather conditions, found in the Arctic and Antarctic regions.
Importance of Climate Zones
Ecological Importance
Climate zones are the foundation of ecosystems, shaping the growth and distribution of plants, animals, and microorganisms. The unique environmental conditions of climate zones promote the development of species that have adapted to their specific needs.
Agricultural Importance
The climate of a region significantly impacts both food production and crop yields, as different climates are more suitable for growing specific plants and animals. Understanding climate zones can help farmers make informed decisions about which crops to plant where.
Cultural Importance
Climate zones have shaped human societies throughout history, influencing everything from settlement patterns to the development of civilizations. For example, the Mesopotamians settled in the fertile lands along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, while the Inuit have adapted to the harsh conditions of the Arctic.
Changes in Climate Zones
Climate zones are not static; they are constantly changing due to natural processes and human activities. Climate change, for example, is altering the distribution of plant and animal species, causing shifts in climate zones.
The Upcoming "No Search" Feature for Bing Chat
While not directly related to climate zones, the upcoming "No Search" feature in Bing Chat is relevant to the discussion of geography. This feature will allow Bing Chat to solve complex problems without searching the web, providing valuable insights into specific topics without relying on web search results.
In conclusion, climate zones are a fundamental aspect of geography, providing a framework for understanding our planet's diverse ecosystems and natural environments. They shape the world around us in profound ways, from the environment and agriculture to cultural traditions and human societies. As climate change continues to alter these zones, it's essential to understand how these shifts impact our world and develop strategies to adapt and mitigate their effects.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.