Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main criticism about using speed as a measure of intelligence in animals?
What is the main criticism about using speed as a measure of intelligence in animals?
- It's difficult to determine the motivation of each animal to carry out the task. (correct)
- Speed can be influenced by factors other than intelligence, such as perception and motivation. (correct)
- Animals may have different levels of motor skills, which can influence their performance. (correct)
- Speed is not a reliable indicator of cognitive abilities in animals. (correct)
What did Bitterman's experiments with systematically varied perceptual and motivational demands demonstrate?
What did Bitterman's experiments with systematically varied perceptual and motivational demands demonstrate?
- Perceptual and motivational factors can significantly affect learning outcomes in animals. (correct)
- Animals can learn to associate specific stimuli with rewards or punishments.
- Animals learn best when motivated by a reward.
- The speed of learning is influenced by the complexity of the task.
What was the main finding of Garcia and Koelling's experiment with rats?
What was the main finding of Garcia and Koelling's experiment with rats?
- Rats can learn to associate different stimuli with specific outcomes.
- Rats are more likely to associate taste with illness than visual or auditory stimuli. (correct)
- Rats have a strong aversion to lithium chloride.
- Rats can be trained to avoid certain stimuli through classical conditioning.
What is the main challenge in comparing the intelligence of different animal species?
What is the main challenge in comparing the intelligence of different animal species?
What is the main difference between the concept of 'learning' and 'knowledge'?
What is the main difference between the concept of 'learning' and 'knowledge'?
What is the main reason why the Clark's nutcracker has a remarkable ability to remember food caches?
What is the main reason why the Clark's nutcracker has a remarkable ability to remember food caches?
Vander Wall's research on the Clark's nutcracker highlights what aspect of animal intelligence?
Vander Wall's research on the Clark's nutcracker highlights what aspect of animal intelligence?
What is the main reason why pigeons can learn to peck keys associated with specific photos?
What is the main reason why pigeons can learn to peck keys associated with specific photos?
What was ruled out as the reason for birds finding food through spatial location?
What was ruled out as the reason for birds finding food through spatial location?
What maximum number of items can a subject perform subitizing tasks on?
What maximum number of items can a subject perform subitizing tasks on?
According to Herrnstein et al., what ability do pigeons have?
According to Herrnstein et al., what ability do pigeons have?
Which of the following best describes innate categories?
Which of the following best describes innate categories?
What phenomenon occurs when there is a reduction in responsiveness to a stimulus after repeated presentation?
What phenomenon occurs when there is a reduction in responsiveness to a stimulus after repeated presentation?
What was the result of Whitlow's study on rabbits in response to a loud tone?
What was the result of Whitlow's study on rabbits in response to a loud tone?
What challenge do rats face when navigating a radial maze with more arms?
What challenge do rats face when navigating a radial maze with more arms?
What is receptor fatigue?
What is receptor fatigue?
What concept did Lloyd Morgan argue against regarding animal behavior?
What concept did Lloyd Morgan argue against regarding animal behavior?
Which principle is highlighted by Thorndike's law of effect?
Which principle is highlighted by Thorndike's law of effect?
What did Skinner contribute to the study of animal learning?
What did Skinner contribute to the study of animal learning?
What do fixed interval schedules in operant conditioning entail?
What do fixed interval schedules in operant conditioning entail?
In classical conditioning, what does the CS represent?
In classical conditioning, what does the CS represent?
What is the primary focus of Watson's behaviorism?
What is the primary focus of Watson's behaviorism?
What does the term 'survival of the fittest' relate to in the context of Darwin's theory?
What does the term 'survival of the fittest' relate to in the context of Darwin's theory?
What technique did Thorndike famously use to study animal intelligence?
What technique did Thorndike famously use to study animal intelligence?
What did Beatty & Shavalia (1980) find in their study with rats regarding retroactive interference?
What did Beatty & Shavalia (1980) find in their study with rats regarding retroactive interference?
According to Mackintosh's theory, what type of stimuli are animals most likely to pay attention to?
According to Mackintosh's theory, what type of stimuli are animals most likely to pay attention to?
What role does consolidation play in long-term memory according to Hebb (1949)?
What role does consolidation play in long-term memory according to Hebb (1949)?
What do affective qualities refer to in the context of stimuli?
What do affective qualities refer to in the context of stimuli?
How does LePelley's theory describe the focus of attention in learning?
How does LePelley's theory describe the focus of attention in learning?
What phenomenon occurs when conditioned responding drops off to almost nothing after the conditioned stimulus is presented alone?
What phenomenon occurs when conditioned responding drops off to almost nothing after the conditioned stimulus is presented alone?
What is the re-presentation of the conditioned stimulus alone after a rest period that produces a conditioned response called?
What is the re-presentation of the conditioned stimulus alone after a rest period that produces a conditioned response called?
What does the Pearce-Hall theory suggest about associative learning?
What does the Pearce-Hall theory suggest about associative learning?
What was Duncan's (1949) finding regarding ECS and memory tasks?
What was Duncan's (1949) finding regarding ECS and memory tasks?
In the context of learning, what does a generalisation gradient represent?
In the context of learning, what does a generalisation gradient represent?
What does a lower conditioned responding due to a slight difference between the trained and presented conditioned response indicate?
What does a lower conditioned responding due to a slight difference between the trained and presented conditioned response indicate?
What element does Wagner's theory focus on in terms of learning?
What element does Wagner's theory focus on in terms of learning?
According to the foraging intelligence hypothesis, which brain region is suggested to correlate with certain behaviors in animals?
According to the foraging intelligence hypothesis, which brain region is suggested to correlate with certain behaviors in animals?
What does a higher cephalisation index imply about a species?
What does a higher cephalisation index imply about a species?
What does the principle of proper mass suggest about brain function?
What does the principle of proper mass suggest about brain function?
Which hypothesis posits that social complexity drives the evolution of larger brains and cognitive abilities in animals?
Which hypothesis posits that social complexity drives the evolution of larger brains and cognitive abilities in animals?
What can be concluded about birds learning photographs?
What can be concluded about birds learning photographs?
How do circadian rhythms influence animal behavior?
How do circadian rhythms influence animal behavior?
What was the finding of Bolles & Lorge (1962) regarding rats raised with altered day cycles?
What was the finding of Bolles & Lorge (1962) regarding rats raised with altered day cycles?
What uniquely demonstrates the ability of rats to remember time intervals?
What uniquely demonstrates the ability of rats to remember time intervals?
What was discovered by Pfungst (1908) about Clever Hans?
What was discovered by Pfungst (1908) about Clever Hans?
What major conclusion did Meck & Church (1983) reach regarding rats in their study?
What major conclusion did Meck & Church (1983) reach regarding rats in their study?
What did Brannon & Terrace (2000) demonstrate about monkeys?
What did Brannon & Terrace (2000) demonstrate about monkeys?
What ability was shown by five-day-old chicks in the study by Rugani, Regotin, and Vallortigara (2007)?
What ability was shown by five-day-old chicks in the study by Rugani, Regotin, and Vallortigara (2007)?
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates deductive reasoning?
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates deductive reasoning?
In the context of problem-solving, what is the primary difference between trial and error learning and reasoning?
In the context of problem-solving, what is the primary difference between trial and error learning and reasoning?
How does piloting, as demonstrated by Cartwright and Collett's (1983) experiment with gerbils, differ from dead reckoning in navigation?
How does piloting, as demonstrated by Cartwright and Collett's (1983) experiment with gerbils, differ from dead reckoning in navigation?
What potential flaw did Tolman, Ritchie, and Kalish (1946a) identify in their experiments aimed at demonstrating cognitive maps in rats?
What potential flaw did Tolman, Ritchie, and Kalish (1946a) identify in their experiments aimed at demonstrating cognitive maps in rats?
How did Kohler (1925) challenge Thorndike's assertion that animals learn primarily through trial and error?
How did Kohler (1925) challenge Thorndike's assertion that animals learn primarily through trial and error?
How does the experiment involving Betty the crow bending a wire to retrieve food challenge anthropomorphism?
How does the experiment involving Betty the crow bending a wire to retrieve food challenge anthropomorphism?
What is the key distinction between inductive and deductive reasoning in problem-solving?
What is the key distinction between inductive and deductive reasoning in problem-solving?
Considering Gillan and Premack's (1981) work with the chimpanzee Sarah, how does training an animal to use symbols relate to studying analogical reasoning?
Considering Gillan and Premack's (1981) work with the chimpanzee Sarah, how does training an animal to use symbols relate to studying analogical reasoning?
What key linguistic abilities were demonstrated by the chimpanzee in the language study described?
What key linguistic abilities were demonstrated by the chimpanzee in the language study described?
What was Terrace's (1979) conclusion regarding language acquisition in chimpanzees, based on his analysis of 19,000 utterances?
What was Terrace's (1979) conclusion regarding language acquisition in chimpanzees, based on his analysis of 19,000 utterances?
According to Pepperberg (1992), what aspect of language is equally important as comprehension, as demonstrated by Alex the parrot?
According to Pepperberg (1992), what aspect of language is equally important as comprehension, as demonstrated by Alex the parrot?
In Premack's (1971) experiment, what was Sarah the chimpanzee required to do with symbols representing different words to receive a reward?
In Premack's (1971) experiment, what was Sarah the chimpanzee required to do with symbols representing different words to receive a reward?
What specific abilities did Sarah demonstrate when learning 130 words in Premack's experiment??
What specific abilities did Sarah demonstrate when learning 130 words in Premack's experiment??
How does the waggle dance of honeybees communicate the distance to a food source?
How does the waggle dance of honeybees communicate the distance to a food source?
Which of Hockett's design features of language is best illustrated by a dog barking at an intruder?
Which of Hockett's design features of language is best illustrated by a dog barking at an intruder?
How does evidence from Vervet monkey alarm calls challenge the idea that animal communication is solely instinctive?
How does evidence from Vervet monkey alarm calls challenge the idea that animal communication is solely instinctive?
What aspect of language does Chomsky's Language Acquisition Device (LAD) primarily address?
What aspect of language does Chomsky's Language Acquisition Device (LAD) primarily address?
In the study with Washoe, what primary method was used to teach her American Sign Language (ASL)?
In the study with Washoe, what primary method was used to teach her American Sign Language (ASL)?
Which of Hockett's design features of language is best illustrated by Washoe signing about a cat she had previously?
Which of Hockett's design features of language is best illustrated by Washoe signing about a cat she had previously?
How does the concept of 'arbitrariness' in language, as defined by Hockett, apply to animal communication systems?
How does the concept of 'arbitrariness' in language, as defined by Hockett, apply to animal communication systems?
According to Macphail's view on animal intelligence, how do non-human animals compare to humans?
According to Macphail's view on animal intelligence, how do non-human animals compare to humans?
Flashcards
Darwin's Theory
Darwin's Theory
Explains evolutionary continuity between animals and humans through natural selection.
Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism
Attributing human traits, motivations, and desires to animals.
Lloyd Morgan's Canon
Lloyd Morgan's Canon
Principle stating actions should not be interpreted as higher reasoning if simpler explanations exist.
Thorndike's Law of Effect
Thorndike's Law of Effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Behaviourism
Behaviourism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Operant Conditioning
Operant Conditioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skinner Box
Skinner Box
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pavlovian Conditioning
Pavlovian Conditioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acquisition
Acquisition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extinction
Extinction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spontaneous Recovery
Spontaneous Recovery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Generalisation Gradient
Generalisation Gradient
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stimulus Generalisation
Stimulus Generalisation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Generalisation Decrement
Generalisation Decrement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cephalisation Index
Cephalisation Index
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social Intelligence Hypothesis
Social Intelligence Hypothesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macphail's Theory
Macphail's Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Learning Definition
Learning Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
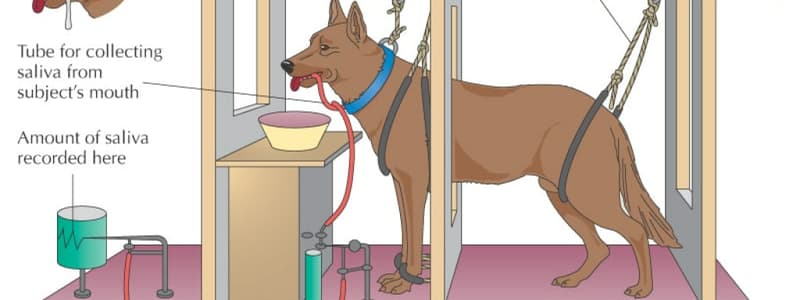
Speed Measurement Issues
Speed Measurement Issues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perceptual Demands
Perceptual Demands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motivational Demands
Motivational Demands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Garcia and Koelling Study
Garcia and Koelling Study
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vander Wall's Nutcracker Example
Vander Wall's Nutcracker Example
Signup and view all the flashcards
Animal Intelligence Measurement
Animal Intelligence Measurement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retroactive Interference
Retroactive Interference
Signup and view all the flashcards
Consolidation
Consolidation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retention
Retention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retrieval
Retrieval
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autoshaping
Autoshaping
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mackintosh's Theory
Mackintosh's Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pearce-Hall Theory
Pearce-Hall Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hebb's Theory
Hebb's Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subitizing
Subitizing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exemplar Learning
Exemplar Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Category Acquisition in Pigeons
Category Acquisition in Pigeons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Habituation
Habituation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effector Fatigue
Effector Fatigue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Receptor Fatigue
Receptor Fatigue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radial Maze
Radial Maze
Signup and view all the flashcards
Innate Categories
Innate Categories
Signup and view all the flashcards
Birds' Memory Capacity
Birds' Memory Capacity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporal Information in Animals
Temporal Information in Animals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circadian Rhythms
Circadian Rhythms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Innate 24-Hour Clock
Innate 24-Hour Clock
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rats and Time Intervals
Rats and Time Intervals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clever Hans Phenomenon
Clever Hans Phenomenon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Numerosity in Monkeys
Numerosity in Monkeys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chicks and Numerical Memory
Chicks and Numerical Memory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reasoning
Reasoning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trial and Error
Trial and Error
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deductive Reasoning
Deductive Reasoning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inductive Reasoning
Inductive Reasoning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Piloting
Piloting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dead Reckoning
Dead Reckoning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insight
Insight
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chimpanzee Language Study
Chimpanzee Language Study
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trial and Error Learning
Trial and Error Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alex the Parrot
Alex the Parrot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarah's Symbol Learning
Sarah's Symbol Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chimpanzee Capabilities
Chimpanzee Capabilities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Waggle Dance
Waggle Dance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Round Dance
Round Dance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vervet Monkey Alarm Calls
Vervet Monkey Alarm Calls
Signup and view all the flashcards
Language Acquisition Device
Language Acquisition Device
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arbitrariness (Language)
Arbitrariness (Language)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Discreteness (Language)
Discreteness (Language)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duality of Patterning
Duality of Patterning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Displacement (Language)
Displacement (Language)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Hebb (1949)
- Consolidation and rehearsal are needed to complete connections
- Memory depends on the virtually permanent formation of circuits of interconnected neurons
Duncan (1949)
- ECS impaired the memory and rehearsal task
Habituation
- Reduction in responsiveness as result of repeated stimuli
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.