Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is true about modern currency?
Which of the following is true about modern currency?
- It is authorised by the government of the country (correct)
- It is made of precious metals like gold and silver
- It is of everyday use like grains and cattle
- It was used in India since the very early ages
What is the facility that lends demand deposits the essential characteristics of money?
What is the facility that lends demand deposits the essential characteristics of money?
- The deposits being safe with the banks
- The interest earned on the deposits
- The ability to make payments through cheques (correct)
- The provision to withdraw the money as and when required
What is the role of banks in the working of modern forms of money?
What is the role of banks in the working of modern forms of money?
- To withdraw money from demand deposits on behalf of the government
- To refuse payments made in rupees
- To issue currency notes on behalf of the central government
- To accept deposits and pay interest on them (correct)
Which of the following is true about the role of banks in extending loans?
Which of the following is true about the role of banks in extending loans?
What is the difference between formal and informal sector loans?
What is the difference between formal and informal sector loans?
What is the role of the Reserve Bank of India in the functioning of formal sources of loans?
What is the role of the Reserve Bank of India in the functioning of formal sources of loans?
Which group of people in urban areas rely on informal sources for the majority of their loans?
Which group of people in urban areas rely on informal sources for the majority of their loans?
What is the major reason why the poor cannot get bank loans?
What is the major reason why the poor cannot get bank loans?
What is the purpose of a loan sanctioned in the name of a self-help group by a bank?
What is the purpose of a loan sanctioned in the name of a self-help group by a bank?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Banks, Loans, and Credit: Understanding the Mechanisms and Risks
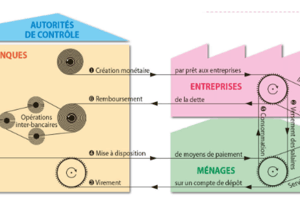
- Banks keep only a small portion of their deposits as cash and use the major portion to extend loans.
- Banks act as intermediaries between depositors and borrowers, charging higher interest rates on loans than what is offered on deposits.
- Credit refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods, or services in return for the promise of future payment.
- Rural areas have a high demand for credit, especially for crop production, but credit can lead to a debt trap if the borrower cannot repay the loan due to crop failure.
- Loan agreements specify an interest rate and may demand collateral (security) against loans.
- The terms of credit vary substantially from one credit arrangement to another, depending on the nature of the lender and the borrower.
- Loans can be obtained from formal sector loans (banks and cooperatives) and informal sector loans (moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, and friends).
- The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans to ensure banks maintain cash balance and give loans to various borrowers.
- Informal lenders charge much higher interest rates on loans compared to formal lenders.
- There is no organization that supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector, which can lead to the use of unfair means to collect loan payments.
- Credit can be useful or not depending on the risks in the situation and whether there is support in case of loss.
- The failure of credit to help borrowers improve their earnings can leave them worse off than before, as seen in the example of Swapna having to sell part of her land to repay the loan.
Access to Credit in India: Formal and Informal Sources
- Higher cost of borrowing reduces the income of borrowers, leading to a debt trap and hindering entrepreneurship.
- Banks and cooperative societies need to lend more to provide affordable credit and boost incomes.
- Poor households in urban areas rely on informal sources for 85% of their loans, while rich households rely on formal sources for 90% of their loans.
- The formal sector only meets half of the credit needs of rural people, leaving the rest dependent on informal sources with high interest rates.
- Banks are not present everywhere in rural India, and getting a loan from a bank requires proper documents and collateral.
- Absence of collateral is a major reason why the poor cannot get bank loans, and informal lenders like moneylenders offer loans without collateral but charge high interest rates.
- Self-help groups (SHGs) have emerged as a newer way of providing loans to the poor, particularly women, by pooling savings and charging lower interest rates than moneylenders.
- A typical SHG has 15-20 members who meet and save regularly, with saving per member varying from Rs 25 to Rs 100 or more.
- Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs and repay with interest.
- After a year or two of regular savings, the group becomes eligible for a loan from the bank, which is sanctioned in the name of the group and meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
- Expanding formal sector loans is necessary, but it is also important to distribute them more equally so that the poor can benefit from cheaper loans.
- Access to affordable credit is crucial for the country's development and reducing dependence on informal sources with high interest rates.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.