Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary objective of endodontic therapy?
What is the primary objective of endodontic therapy?
Restoration of the treated tooth to its proper form and function in the masticatory apparatus in a healthy state.
What are the two main components of the root canal system?
What are the two main components of the root canal system?
Pulp chamber and root canal.
What is the term for the aperture at or near the apex of the root?
What is the term for the aperture at or near the apex of the root?
Apical foramen.
What is the scope of endodontics in terms of diagnosis?
What is the scope of endodontics in terms of diagnosis?
What is the result of secondary dentin deposition on the pulp chamber?
What is the result of secondary dentin deposition on the pulp chamber?
What is the purpose of obturation in endodontics?
What is the purpose of obturation in endodontics?
What is the term for the treatment of teeth that have previously undergone endodontic therapy?
What is the term for the treatment of teeth that have previously undergone endodontic therapy?
What is the focus of the pre-clinical aspect of endodontic course?
What is the focus of the pre-clinical aspect of endodontic course?
What is the mechanism by which tertiary dentin is deposited?
What is the mechanism by which tertiary dentin is deposited?
What is the term for any branch of the main pulp canal or chamber that communicates with the external surface of the root?
What is the term for any branch of the main pulp canal or chamber that communicates with the external surface of the root?
What is the definition of an Apical Foramen?
What is the definition of an Apical Foramen?
What is the term for the narrow, ribbon-shaped communication between two root canals that contains pulp or pulpally derived tissue?
What is the term for the narrow, ribbon-shaped communication between two root canals that contains pulp or pulpally derived tissue?
What is the classification system of root canal anatomy developed by Weine?
What is the classification system of root canal anatomy developed by Weine?
What is the definition of Type I root canal anatomy according to Weine's classification?
What is the definition of Type I root canal anatomy according to Weine's classification?
What is the term for the narrowest diameter of the root canal short of the apical foramina or radiographic apex?
What is the term for the narrowest diameter of the root canal short of the apical foramina or radiographic apex?
What is the term for the canal that is located in the coronal or middle third of the root and extends horizontally from the main root canal?
What is the term for the canal that is located in the coronal or middle third of the root and extends horizontally from the main root canal?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Endodontics
- Endodontics is the branch of Dentistry that deals with the etiology, prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of diseases of the pulp and periapical tissues.
Objectives of Endodontics
- The objective of endodontic therapy is to restore the treated tooth to its proper form and function in the masticatory apparatus in a healthy state.
Scope of Endodontics
- Differential diagnosis of oral pain of pulpal and/or periradicular origin
- Vital pulp therapy
- Nonsurgical treatment of root canal systems of pulpal origin
- Obturation of root canal systems
- Endodontic Surgery
- Retreatment of teeth previously treated endodontically
- Treatment procedures related to coronal restorations by means of post and/or cores involving the root canal space.
Endodontic Course Outline
- Morphology and Access Cavity
- Endodontic Instruments
- Cleaning and Shaping
- Root Canal Obturation
Pulp Space Morphology
- Components of root canal system
- Classifications of Root Canal System (Classes and Types)
- Pulp space Morphology of Different teeth
- Principles of Coronal Access Cavity Preparation
- Errors during endodontic cavity preparation
- Problem solving in endodontic cavity preparation.
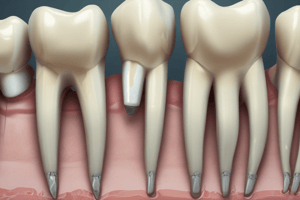
Components of the Root Canal System
- Pulp Chamber: The portion of the pulp within the crown
- Root Canal: The portion of the pulp within the root
- Apical foramen: an aperture at or near the apex of the root
Morphological Features of the Pulp Cavity
- Roof of pulp chamber
- Wall of pulp chamber
- Floor of pulp chamber
- Size of the pulp chamber decreases by age and irritation of the pulp.
Pulp Horns
- Accessory canal: any branch of the main pulp canal or chamber that communicates with the external surface of the root
- Lateral canal: an accessory canal located in the coronal or middle third of the root
- Furcation canal
Apical Root Anatomy
- Apical Constriction (Minor Diameter): the narrowest diameter short of apical foramina or radiographic apex
- Apical Foramen (Major Diameter): the main apical opening on the surface of root canal through which blood vessels enter the canal
- Isthmus: a narrow, ribbon-shaped communication between two root canals that contains pulp or pulpally derived tissue.
Classifications of Root Canal System
- Weine Classified root canal anatomy into six types
- Type I: A single canal extends from the pulp chamber to the apex
- Type II: Two separate canals leave the pulp chamber and join short of the apex to form one canal
- Type III: One canal leaves the pulp chamber and divides into two then merge to exit as one canal
- Type IV: Two separate distinct canals extend from the pulp chamber to the apex
- Vertucci Classification
- Type I: Two or three canals with no communications
- Type II: Two canals with a definite connection between them
- Type III: Three canals with a definite connection between them
- Type IV: Canals extend into the isthmus area
- Type V: A true connection or corridor throughout the section
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.