Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the three essential factors for a successful endodontic treatment?
What are the three essential factors for a successful endodontic treatment?
- Removing all caries, conserving sound tooth structure, and de-roofing the pulp chamber
- Removing coronal pulp tissue, locating canal orifices, and achieving straight-line access
- Cleaning and shaping, disinfection, and three-dimensional obturation (correct)
- Pre-operative assessment, access cavity preparation, and canal shaping
What is the preliminary step that precedes the three essential factors of endodontic treatment?
What is the preliminary step that precedes the three essential factors of endodontic treatment?
- Disinfection of the root canal
- Pre-operative assessment of the tooth
- Shaping and cleaning of the root canal
- Preparation of the access cavity (correct)
What is the primary objective of access cavity preparation?
What is the primary objective of access cavity preparation?
- To remove all coronal pulp tissue
- To conserve sound tooth structure
- To locate all root canal orifices
- To achieve straight-line access to the apical foramen (correct)
What is assessed during the pre-operative assessment stage?
What is assessed during the pre-operative assessment stage?
Why is it important to check the depth of the preparation?
Why is it important to check the depth of the preparation?
What is the purpose of pre-operative radiographs?
What is the purpose of pre-operative radiographs?
What is the purpose of de-roofing the pulp chamber?
What is the purpose of de-roofing the pulp chamber?
What is the objective of removing all caries during access cavity preparation?
What is the objective of removing all caries during access cavity preparation?
What type of bur is used to make the initial entry?
What type of bur is used to make the initial entry?
What is the main purpose of applying a rubber dam?
What is the main purpose of applying a rubber dam?
What is used to taper the walls of the pulp chamber?
What is used to taper the walls of the pulp chamber?
What is used to clear remaining pulp tissue and debris?
What is used to clear remaining pulp tissue and debris?
What is used to flush the access cavity?
What is used to flush the access cavity?
What is used to locate the canal orifices?
What is used to locate the canal orifices?
What is the importance of access in endodontic practice?
What is the importance of access in endodontic practice?
What is the final step in preparing the access cavity?
What is the final step in preparing the access cavity?
What is the primary goal of removing the pulp chamber roof?
What is the primary goal of removing the pulp chamber roof?
What type of bur is used to remove the lip of the pulp horn?
What type of bur is used to remove the lip of the pulp horn?
What is the ideal location of the orifices in the final preparation?
What is the ideal location of the orifices in the final preparation?
What is the purpose of removing the cervical dentin bulges?
What is the purpose of removing the cervical dentin bulges?
What instrument is used to remove the cervical dentin bulges?
What instrument is used to remove the cervical dentin bulges?
What is necessary for files to perform properly?
What is necessary for files to perform properly?
Why is visual inspection of the pulp chamber floor necessary?
Why is visual inspection of the pulp chamber floor necessary?
What is the purpose of using a safety-tip tapered diamond bur?
What is the purpose of using a safety-tip tapered diamond bur?
What shape does the access cavity typically have in the maxillary first molar?
What shape does the access cavity typically have in the maxillary first molar?
What is the main difference between the maxillary first and second molar in terms of canal presence?
What is the main difference between the maxillary first and second molar in terms of canal presence?
What is the shape of the access cavity when only three canals are present in the maxillary second molar?
What is the shape of the access cavity when only three canals are present in the maxillary second molar?
What is unique about the mandibular first premolar compared to its maxillary counterpart?
What is unique about the mandibular first premolar compared to its maxillary counterpart?
Why is buccal extension nearly approaching the tip of the buccal cusp in the mandibular first premolar?
Why is buccal extension nearly approaching the tip of the buccal cusp in the mandibular first premolar?
What is different about the access cavity preparation for the mandibular second premolar compared to the first premolar?
What is different about the access cavity preparation for the mandibular second premolar compared to the first premolar?
What is the typical shape of the access cavity for the mandibular first premolar?
What is the typical shape of the access cavity for the mandibular first premolar?
What is the relationship between the walls of the pulp chamber and the external surface of the tooth at the level of the CEJ?
What is the relationship between the walls of the pulp chamber and the external surface of the tooth at the level of the CEJ?
What is the characteristic of the distance from the external surface of the clinical crown to the wall of the pulp chamber at the level of the CEJ?
What is the characteristic of the distance from the external surface of the clinical crown to the wall of the pulp chamber at the level of the CEJ?
What is the characteristic of the canal orifices in maxillary molars?
What is the characteristic of the canal orifices in maxillary molars?
What is the characteristic of the color of the pulp chamber floor compared to the walls?
What is the characteristic of the color of the pulp chamber floor compared to the walls?
Where are the orifices of the root canals typically located?
Where are the orifices of the root canals typically located?
What is the main cause of errors in access cavity preparation?
What is the main cause of errors in access cavity preparation?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Endodontic Treatment
- A successful outcome in endodontic treatment depends on three factors: cleaning and shaping, disinfection, and three-dimensional obturation of the root canal system.
- However, an error in the preliminary step of preparing the access cavity can compromise all subsequent work.
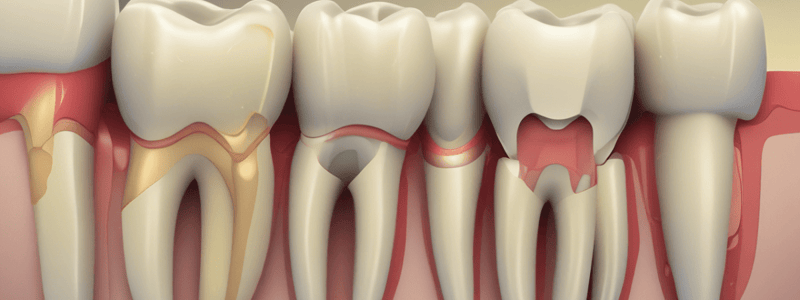
Preparation of the Access Cavity
- The access cavity is the opening in the dental crown that permits localization, cleaning, shaping, disinfection, and three-dimensional obturation of the root canal system.
- Objectives of access cavity preparation:
- Remove all caries when present
- Conserve sound tooth structure
- De-roof the pulp chamber completely
- Remove all coronal pulp tissue (vital or necrotic)
- Locate all root canal orifices
- Achieve straight- or direct-line access to the apical foramen or to the initial curvature of the canal
Pre-Operative Assessment
- An assessment of the following features can be made after visual examination of the tooth and study of a pre-operative periapical radiograph:
- The number of canals present
- The length, direction, and degree of curvature of each canal
- Any branching or division of the main canals
- The relationship of the canal orifice(s) to the pulp chamber and to the external surface of the tooth
- The presence and location of any lateral canals
- The position and size of the pulp chamber and its distance from the occlusal surface
- Any related pathology
The Stages of Access Cavity Preparation
- The initial entry is made with a tungsten carbide or diamond bur in a turbine handpiece and the outline form is completed as required.
- The bur is advanced towards the pulp horns until the roof of the pulp chamber is just penetrated.
- The rubber dam is applied to provide an aseptic operating field, isolate the tooth from oral and salivary contamination, facilitate the use of strong medicaments, and protect the patient from the inhalation or ingestion of endodontic instruments.
- The removal of the entire roof of the pulp chamber, and the tapering of the walls, is carried out with a safe-tipped endodontic access bur.
- The walls of the pulp chamber are gently flared out towards the occlusal surface.
- Any remaining pulp tissue and debris is cleared with an excavator from the floor of the pulp chamber and the canal orifices.
- The access cavity is flushed with a solution of sodium hypochlorite to remove any residual debris.
- The canal orifices are located with an endodontic probe.
- Once the canal orifices have been identified, the preparation of the coronal part of the root canals is commenced.
- Any alteration to the access cavity outline form may be undertaken to ensure a direct line of approach to the canal orifices.
Anterior Teeth
- The bur of choice is used to remove the roof of the pulp chamber completely, including all pulp horns.
- The goal is to funnel the corners of the access cavity directly into the orifices.
- The round bur hooks under the lip of the pulp horn and is rotated and withdrawn in an occlusal direction to remove the lip.
- A safety-tip tapered diamond bur is used to blend and funnel the axial wall from the cavosurface margin to the orifice.
Posterior Teeth
- The access cavity preparation for posterior teeth is more complex due to the presence of cervical dentin bulges.
- The cervical bulges are removed with safety-tip diamond or carbide burs or Gates Glidden burs.
- The instruments are placed at the orifice level and leaned towards the dentin bulge to remove the overhanging shelf.
- The access cavity is shaped to ensure a direct line of approach to the canal orifices.
Identification of All Canal Orifices
- The orifices are located at the corners of the final preparation to facilitate all of the root canal procedures.
- Internally, the access cavity should have all orifices positioned entirely on the pulp floor and should not extend into an axial wall.
Straight-Line Access Determination
- Files must have unimpeded access to the apical foramen or the first point of canal curvature to perform properly.
Visual Inspection of the Pulp Chamber Floor
- The floor and walls must be inspected, using appropriate magnification and illumination, to ensure that all canal orifices are visible and no roof overhangs are present.
Morphology of Specific Teeth
- Maxillary first molar: four canals are present, and the access cavity has a rhomboid shape with the corners corresponding to the four orifices.
- Maxillary second molar: four canals are less likely to be present, and the access cavity has a rhomboid shape and is a smaller version of the access cavity for the maxillary first molar.
- Mandibular first premolar: the access cavity is oval and less slot-shaped, with buccal extension nearly approaching the tip of the buccal cusp to achieve straight-line access.
- Mandibular second premolar: the access cavity form varies in at least two ways in its external anatomy, with less lingual inclination and less extension up the buccal cusp incline.
Errors in Access Cavity Preparation
- Errors can occur in the preparation of an access cavity, often due to failure to follow the access guidelines or a lack of understanding of the internal and external tooth morphology.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.