Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a common cause of thyroglossal fistula?
What is a common cause of thyroglossal fistula?
- Always acquired (correct)
- Congenital defect
- Infection during infancy
- Genetic predisposition
Weight loss despite a good appetite is a characteristic feature of hyperthyroidism.
Weight loss despite a good appetite is a characteristic feature of hyperthyroidism.
True (A)
What medication is commonly used to inhibit the thyroid peroxidase enzyme in hyperthyroidism treatment?
What medication is commonly used to inhibit the thyroid peroxidase enzyme in hyperthyroidism treatment?
Carbimazole
In a thyroid scan, Graves' disease typically shows __________ uptake.
In a thyroid scan, Graves' disease typically shows __________ uptake.
Match the following hyperthyroidism causes with their uptake characteristics on a thyroid scan:
Match the following hyperthyroidism causes with their uptake characteristics on a thyroid scan:
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism overall?
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism overall?
Plummer's disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
Plummer's disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
What is a clinical feature of hypothyroidism?
What is a clinical feature of hypothyroidism?
What percentage of retrosternal goitre cases are classified as 2° (Retrosternal/Plunging)?
What percentage of retrosternal goitre cases are classified as 2° (Retrosternal/Plunging)?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is primarily an __________ condition.
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is primarily an __________ condition.
The Pemberton sign indicates facial congestion due to blockage of venous drainage when the patient raises their hand.
The Pemberton sign indicates facial congestion due to blockage of venous drainage when the patient raises their hand.
What is the common management procedure for removing a goitre?
What is the common management procedure for removing a goitre?
Match the condition with its characteristics:
Match the condition with its characteristics:
The site of a 1° Mediastinal goitre is __________.
The site of a 1° Mediastinal goitre is __________.
Match the type of retrosternal goitre with its corresponding description:
Match the type of retrosternal goitre with its corresponding description:
What is the risk of mutation associated with exon 918?
What is the risk of mutation associated with exon 918?
Prophylactic thyroidectomy should be considered for all first-degree relatives regardless of mutation risk.
Prophylactic thyroidectomy should be considered for all first-degree relatives regardless of mutation risk.
What gene is associated with MEN 4 Syndrome?
What gene is associated with MEN 4 Syndrome?
The recommended timing for prophylactic thyroidectomy for individuals with a low risk of mutation is up to _____ years.
The recommended timing for prophylactic thyroidectomy for individuals with a low risk of mutation is up to _____ years.
Match the following conditions to their corresponding features:
Match the following conditions to their corresponding features:
Which of the following is a sentinel event for De Quervain's thyroiditis?
Which of the following is a sentinel event for De Quervain's thyroiditis?
Riedel's thyroiditis is characterized by painful enlargement of the gland.
Riedel's thyroiditis is characterized by painful enlargement of the gland.
What are the clinical features of postpartum thyroiditis?
What are the clinical features of postpartum thyroiditis?
De Quervain's thyroiditis is also known as __________ thyroiditis.
De Quervain's thyroiditis is also known as __________ thyroiditis.
Match the following types of thyroiditis with their associated features:
Match the following types of thyroiditis with their associated features:
What is the primary reason autoantibodies attack the thyroid gland in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis?
What is the primary reason autoantibodies attack the thyroid gland in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis?
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis typically results in hyperthyroidism in the initial stages.
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis typically results in hyperthyroidism in the initial stages.
Name one type of cancer that long-standing cases of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis can lead to.
Name one type of cancer that long-standing cases of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis can lead to.
Management of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis often includes a low dose of __________.
Management of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis often includes a low dose of __________.
Match the features of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis with their descriptions:
Match the features of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis with their descriptions:
Which type of goitre is associated with long-standing iodine deficiency?
Which type of goitre is associated with long-standing iodine deficiency?
Males have a lower risk of thyroid malignancy compared to females.
Males have a lower risk of thyroid malignancy compared to females.
What is the common procedure used to diagnose thyroid swellings?
What is the common procedure used to diagnose thyroid swellings?
A branch of goitre characterized by a single palpable nodule and the rest of the gland is not palpable is called __________.
A branch of goitre characterized by a single palpable nodule and the rest of the gland is not palpable is called __________.
Match the types of thyroiditis with their pain characteristics:
Match the types of thyroiditis with their pain characteristics:
What is the primary reason for the formation of a lingual thyroid?
What is the primary reason for the formation of a lingual thyroid?
A thyroglossal cyst typically presents as a neck swelling that does not move during swallowing or tongue protrusion.
A thyroglossal cyst typically presents as a neck swelling that does not move during swallowing or tongue protrusion.
What procedure is commonly performed to manage a thyroglossal cyst?
What procedure is commonly performed to manage a thyroglossal cyst?
A __________ thyroid is situated just below the tongue and is caused by undescended thyroid tissue.
A __________ thyroid is situated just below the tongue and is caused by undescended thyroid tissue.
Match the clinical findings with their corresponding stage or procedure:
Match the clinical findings with their corresponding stage or procedure:
What is the main advantage of administering nadolol before surgery in hyperthyroidism management?
What is the main advantage of administering nadolol before surgery in hyperthyroidism management?
Thyroid storm can only occur following surgical trauma.
Thyroid storm can only occur following surgical trauma.
What are the common features of thyroid storm?
What are the common features of thyroid storm?
Graves disease is primarily caused by __________ antibodies that stimulate the thyroid.
Graves disease is primarily caused by __________ antibodies that stimulate the thyroid.
Match the following treatment strategies with their purpose in managing thyroid storm:
Match the following treatment strategies with their purpose in managing thyroid storm:
Which of the following is a clinical feature associated with thyroid conditions?
Which of the following is a clinical feature associated with thyroid conditions?
Thyroid acropachy is characterized by hair loss.
Thyroid acropachy is characterized by hair loss.
Name one autoimmune disease that can be associated with thyroid conditions.
Name one autoimmune disease that can be associated with thyroid conditions.
The sign characterized by eyelid retraction is called __________.
The sign characterized by eyelid retraction is called __________.
Match the eye signs with their descriptions:
Match the eye signs with their descriptions:
What is the recommended surgery for patients with extensive eye signs?
What is the recommended surgery for patients with extensive eye signs?
Moebius sign is indicative of mild toxicity.
Moebius sign is indicative of mild toxicity.
What type of thyroid dysfunction is characterized by exophthalmos?
What type of thyroid dysfunction is characterized by exophthalmos?
Presence of autoantibodies is important for diagnosing __________.
Presence of autoantibodies is important for diagnosing __________.
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typical of hyperthyroidism?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typical of hyperthyroidism?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Thyroglossal vs Branchial Fistula
- Thyroglossal fistulas are always acquired and occur in the midline of the neck.
- Branchial fistulas can be either congenital or acquired and occur along the lower third of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Hyperthyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism is characterized by a thin, irritable patient with weight loss despite good appetite, tachycardia, diarrhea, tremors, heat intolerance, and oligomenorrhea in females.
- Graves' disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, causing a diffuse increase in uptake on a thyroid scan.
- Other causes include solitary toxic nodules (Plummer's disease), toxic nodular goiter, factitious hyperthyroidism, Jod Basedow phenomenon, TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma, and Struma ovarii.
- Propylthiouracil (PTU) and Carbimazole are medications for hyperthyroidism that inhibit the thyroid peroxidase enzyme and the conversion of T4 to T3.
- Both drugs are safe during the first trimester of pregnancy and lactation, but can cause agranulocytosis, with sore throat as the first sign.
Retrosternal Goitre
- Retrosternal goiters are classified into two types: primary mediastinal and secondary retrosternal/plunging.
- Primary mediastinal goiters occur in 10% of cases and involve ectopic thyroid tissue in the mediastinum.
- Secondary retrosternal goiters occur in 90% of cases and start in the neck before plunging into the mediastinum.
- The lower limit of a retrosternal goiter is not palpable, and they can cause pressure symptoms like dyspnea and stridor.
- The Pemberton sign occurs when raising the arms causes facial congestion due to pressure on the thoracic inlet, blocking venous drainage.
- Investigations for retrosternal goiters include a CECT (computed tomography) of the neck and thorax and a chest X-ray.
- Management involves removing the goiter with a neck/cervical incision, with median sternotomy reserved for recurrent mediastinal goiters, primary mediastinal goiters, goiters larger than the thoracic inlet, and malignant retrosternal goiters.
Plummer's Disease & Solitary Toxic Nodule
- Plummer's disease is a type of toxic nodular goiter, with a female to male ratio of 5:1 and occurring most commonly in the second decade of life.
- Solitary toxic nodules are the fifth most common cause of hyperthyroidism, typically occurring in the fifth decade of life with a higher incidence in females.
- Plummer's disease is characterized by multiple hot and cold nodules on a thyroid scan, while solitary toxic nodules are associated with a single hot nodule.
- Management for Plummer's disease typically involves a total thyroidectomy after drug therapy, while solitary toxic nodules are managed with radioactive iodine ablation (RIA) after drug therapy
Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism can be caused by iodine deficiency, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Wolff-Chaikoff effect, non-functioning pituitary adenoma, Sheehan syndrome, dyshormonogenesis, euthyroid sick syndrome, and Refetoff syndrome.
- Associated clinical features include lethargy, alopecia, bradycardia, weight gain, cold intolerance, menorrhagia, and constipation.
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis/Lymphocytic Thyroiditis
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition with a higher incidence in females and a strong hereditary component.
- It's often associated with HLA DR3/88, Down's syndrome, and Turner's syndrome.
RET Testing for 1st Degree Relatives
- Individuals with RET mutations, specifically in exons 768, 790, 618, 634, and 918, are at varying risks for developing medullary thyroid carcinoma.
- Prophylactic thyroidectomy is recommended at different time points depending on the mutation and risk level: up to 80 years for low-risk mutations, up to 5-6 years for medium-risk mutations, and before one year for high-risk mutations.
- Testing for medullary thyroid carcinoma includes pentagastrin stimulation tests and calcitonin levels.
MEN 4 Syndrome
- MEN 4 syndrome is caused by mutations in the CDKN1B gene on chromosome 12.
- Features include pituitary, parathyroid, renal, adrenal, and reproductive organ tumors.
SUBACUTE THYROIDITIS
- De Quervain's thyroiditis, also known as viral or granulomatous thyroiditis, is associated with HLA B35.
- Following an upper respiratory tract infection (URTI), it presents with painful neck enlargement, a spike in hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism, and ultimately resolves with euthyroidism.
- Management is primarily symptomatic, with elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and steroids used for treatment.
- Postpartum thyroiditis, the second most common cause of thyroiditis, occurs in 2-12 months postpartum in 10% of women.
- It presents with similar features to Hashimoto's thyroiditis, including positive anti-TPO antibodies and a 10-fold increased risk of Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
- It's typically self-limiting and resolved with correction of hypothyroidism.
RIEDEL'S/FIBROSING THYROIDITIS
- Riedel's thyroiditis is associated with IgG4, Peyronie's disease, and Dupuytren's contracture.
- It involves fibrosis within the thyroid gland, presenting with painless enlargement, a firm, woody texture, pressure symptoms, hoarseness due to recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement, and stridor.
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition where autoantibodies attack thyroid receptors, leading to inflammation and destruction of the thyroid gland.
- It involves lymphocytic infiltration, destruction of follicles, release of stored hormones, and a brief spike in hyperthyroidism known as hashitoxicosis, followed by prolonged hypothyroidism.
- Other features include diffuse goiter, an increased risk of lymphoma, follicular thyroid cancer, and papillary thyroid cancer.
- Investigations include measuring autoantibody levels and performing fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) to identify lymphocytic infiltration and Hurthle cells.
- Management involves low-dose thyroxine replacement therapy to normalize TSH levels, with total thyroidectomy considered for goiter.
THYROID: Part 3
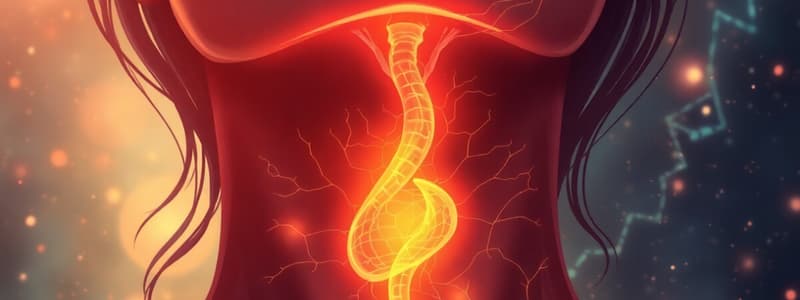
- The thyroid gland develops from the foramen caecum of the tongue, with the thyroglossal tract connecting the tongue to the thyroid.
- Thyroglossal cysts arise from a persistent thyroglossal tract, typically presenting as a midline neck swelling that moves with deglutition and tongue protrusion.
- Lingual thyroid is an undescended thyroid tissue located just below the tongue.
- Complications of thyroglossal cysts include thyroglossal fistulas, which are managed with a Sistrunk's procedure, and papillary thyroid carcinoma in long-standing cases.
- Anaplastic cancer is a possible differential diagnosis for thyroglossal cyst, and US-guided core biopsy is used for diagnosis.
Goitre
- Goiters are classified into diffuse and multinodular types.
- Diffuse goiter is caused by iodine deficiency, pregnancy, puberty, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, and untreated goiter leading to multinodular goiter.
- Multinodular goiter develops from prolonged iodine deficiency.
- Solid thyroid swellings have twice the risk of malignancy compared to cystic ones, and males have four times greater risk than females.
- Management of goiters may involve steroids and tamoxifen.
Graves Disease
- Graves' disease is an autoimmune condition with a higher incidence in females.
- It's the most common cause of hyperthyroidism and is characterized by thyroid receptor antibodies (TRAB).
- It's associated with pretibial myxedema, a V-shaped pattern on a thyroid scan, and eye signs like von Graefe's sign, Dalrymple's sign, Joffroy's sign, Moebius sign, and Stellwag's sign.
- Exophthalmos, a characteristic feature, is associated with lid lag, lid retraction, absence of forehead wrinkling when looking up, loss of accommodation reflex, and infrequent blinking/staring look.
- Management involves drugs, radioactive iodine ablation (RIA), and surgery, with the choice depending on age, presence of goiter, comorbidities, and the severity of eye signs.
- Total thyroidectomy is preferred over subtotal/near total thyroidectomy.
Endocrine System
- Radioactive iodine ablation (RIA) is commonly used for hyperthyroidism management, particularly after drug therapy.
- RIA utilizes iodine-131 (131I), a radioactive isotope, which acts via beta rays with a half-life of 7-8 days.
- Prior to RIA, patients require preparation with antithyroid drugs, beta blockers, and fluid therapy to prevent thyroid storm.
- Thyroid storm, uncontrolled thyrotoxicosis, is often triggered by inadequately prepared patients, interventions like FNAC or surgery, and anesthetic agents.
- It is characterized by dehydration, hyperthermia, hypertension crisis, palpitations, and arrhythmias (leading cause of death).
- Management of thyroid storm involves aggressive IV fluid therapy, cooling measures, IV steroids and antibiotics, large doses of beta blockers, antithyroid drugs, and avoidance of aspirin.
GRAVES DISEASE
- Graves' disease is characterized by stimulating thyroid receptor antibodies (TRAB), formerly known as Long-acting thyroid stimulating antibodies (LATS).
- The disease is associated with pretibial myxedema and a V-shaped pattern on a thyroid scan.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.