Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is cleavage in the context of embryology?
What is cleavage in the context of embryology?
- The termination of blastocyst formation
- The fusion of chimaeras and duplication of embryos
- The initial series of rapid mitotic divisions dividing the zygote into blastomeres (correct)
- The process of cell differentiation leading to specialized cell types
What is the significance of the morula in embryonic development?
What is the significance of the morula in embryonic development?
- It marks the beginning of cell differentiation
- It is the precursor to the blastocyst stage (correct)
- It leads to the formation of blastomeres
- It is the stage where cleavage terminates
What role does the trophoblast play in embryonic development?
What role does the trophoblast play in embryonic development?
- Becoming part of the inner cell mass
- Contributing to the formation of extraembryonic membranes (correct)
- Formation of the blastomeres
- Differentiation into specialized cell types
What is the main mechanism of cellular differentiation?
What is the main mechanism of cellular differentiation?
What is the starting place for understanding the process of differentiation?
What is the starting place for understanding the process of differentiation?
What is the role of proteins synthesis in cell differentiation?
What is the role of proteins synthesis in cell differentiation?
What makes a liver cell different from a skin or muscle cell?
What makes a liver cell different from a skin or muscle cell?
What do maternal genes gradually activate during embryonic development?
What do maternal genes gradually activate during embryonic development?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in prokaryotic cells?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in prokaryotic cells?
What does epigenomics study in a specific cell type?
What does epigenomics study in a specific cell type?
What defines the range of different cell types a cell can become?
What defines the range of different cell types a cell can become?
At what stage are cells totipotent, having the potential to develop into a complete organism?
At what stage are cells totipotent, having the potential to develop into a complete organism?
What is the process by which more specialized cells develop from less specialized cell types called?
What is the process by which more specialized cells develop from less specialized cell types called?
What ultimately regulates cell differentiation through differential gene expression?
What ultimately regulates cell differentiation through differential gene expression?
Which type of cells can differentiate into a variety of tissues but not all?
Which type of cells can differentiate into a variety of tissues but not all?
What describes the range of different cell types that a cell can become?
What describes the range of different cell types that a cell can become?
Which stage is characterized by a stable change in cell organization and irreversible fate for determined cells?
Which stage is characterized by a stable change in cell organization and irreversible fate for determined cells?
What describes the process of progressive restrictions in the developmental potentials of cells?
What describes the process of progressive restrictions in the developmental potentials of cells?
What is ultimately responsible for forming all the embryo structures during differentiation?
What is ultimately responsible for forming all the embryo structures during differentiation?
What term is used to describe the reversible state of being committed to a certain fate before cell determination?
What term is used to describe the reversible state of being committed to a certain fate before cell determination?
What describes the process by which proteins are gradually specialized within a common genome during differentiation?
What describes the process by which proteins are gradually specialized within a common genome during differentiation?
At which stage does fertilization occur in the oviduct?
At which stage does fertilization occur in the oviduct?
What type of cleavage pattern is present in bird eggs?
What type of cleavage pattern is present in bird eggs?
What is the main characteristic of a hatched mammalian blastocyst?
What is the main characteristic of a hatched mammalian blastocyst?
What is the result of mammalian blastomeres dividing asynchronously?
What is the result of mammalian blastomeres dividing asynchronously?
What influences the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
What influences the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
In which stage does the blastodisc transform into a two-layered blastula in birds?
In which stage does the blastodisc transform into a two-layered blastula in birds?
What type of embryo is produced by reptiles and birds due to meroblastic cleavage?
What type of embryo is produced by reptiles and birds due to meroblastic cleavage?
At what stage does the mammalian blastocyst release from the zona pellucida?
At what stage does the mammalian blastocyst release from the zona pellucida?
What happens to hatched blastocysts before implantation in mammals?
What happens to hatched blastocysts before implantation in mammals?
What is the characteristic of reptile and bird embryos produced due to meroblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of reptile and bird embryos produced due to meroblastic cleavage?
Where does fertilization occur in mammals?
Where does fertilization occur in mammals?
What type of cleavage produces blastomeres of approximately equal size?
What type of cleavage produces blastomeres of approximately equal size?
What determines the pattern and speed of cleavage?
What determines the pattern and speed of cleavage?
What happens to blastomeres with each successive division?
What happens to blastomeres with each successive division?
What is the result of meroblastic cleavage?
What is the result of meroblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the outcome of unequal holoblastic cleavage?
What is the outcome of unequal holoblastic cleavage?
What is the result of compaction in the morula stage?
What is the result of compaction in the morula stage?
What is the characteristic of holoblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of holoblastic cleavage?
What is the primary mechanism of cellular differentiation?
What is the primary mechanism of cellular differentiation?
Which stage marks the termination of cleavage in mammals?
Which stage marks the termination of cleavage in mammals?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the outcome of unequal holoblastic cleavage?
What is the outcome of unequal holoblastic cleavage?
During which stage does the blastodisc transform into a two-layered blastula in bird embryos?
During which stage does the blastodisc transform into a two-layered blastula in bird embryos?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What happens to hatched mammalian blastocysts before implantation?
What happens to hatched mammalian blastocysts before implantation?
What is the result of meroblastic cleavage?
What is the result of meroblastic cleavage?
What type of cleavage produces blastomeres of approximately equal size?
What type of cleavage produces blastomeres of approximately equal size?
What is responsible for influencing the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
What is responsible for influencing the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
Where does fertilization occur in mammals?
Where does fertilization occur in mammals?
What is the main characteristic of a hatched mammalian blastocyst?
What is the main characteristic of a hatched mammalian blastocyst?
"At what stage are cells totipotent, having the potential to develop into a complete organism?"
"At what stage are cells totipotent, having the potential to develop into a complete organism?"
"What determines the pattern and speed of cleavage?"
"What determines the pattern and speed of cleavage?"
"What role does the trophoblast play in embryonic development?"
"What role does the trophoblast play in embryonic development?"
"What is ultimately responsible for forming all the embryo structures during differentiation?"
"What is ultimately responsible for forming all the embryo structures during differentiation?"
Which process involves the gradual specialization of the protein contents of a cell, eventually leading to the development of a specialized cell type?
Which process involves the gradual specialization of the protein contents of a cell, eventually leading to the development of a specialized cell type?
At which stage are cells totipotent, capable of developing into a complete organism, including the placenta?
At which stage are cells totipotent, capable of developing into a complete organism, including the placenta?
What term describes the irreversible stage in cell development, implying a stable change in cell organization?
What term describes the irreversible stage in cell development, implying a stable change in cell organization?
What plays a role in regulating cell differentiation through differential gene expression?
What plays a role in regulating cell differentiation through differential gene expression?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in eukaryotic cells?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in eukaryotic cells?
What is indicated by the fate of cells, as observed by labeling and observing which structures they become part of?
What is indicated by the fate of cells, as observed by labeling and observing which structures they become part of?
What is the process where less specialized cells develop into more specialized cell types?
What is the process where less specialized cells develop into more specialized cell types?
What do totipotent stem cells originate from?
What do totipotent stem cells originate from?
What can gradual specialization of the protein contents of a cell lead to?
What can gradual specialization of the protein contents of a cell lead to?
What is the process that is controlled by mechanisms promoting or stopping cell divisions at specific moments?
What is the process that is controlled by mechanisms promoting or stopping cell divisions at specific moments?
What determines the potential of individual cells as development proceeds?
What determines the potential of individual cells as development proceeds?
What is the result of differences in the production and suppression of genes during embryonic development?
What is the result of differences in the production and suppression of genes during embryonic development?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in eukaryotic cells?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in eukaryotic cells?
Which type of genes are essential for determining the anatomical identity of different body parts along the anterior/posterior axis?
Which type of genes are essential for determining the anatomical identity of different body parts along the anterior/posterior axis?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation and embryo development through epigenetic modifications?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation and embryo development through epigenetic modifications?
What is the outcome of unequal holoblastic cleavage?
What is the outcome of unequal holoblastic cleavage?
Which genes control the gene expression during the early stages of pattern formation in the embryo?
Which genes control the gene expression during the early stages of pattern formation in the embryo?
What regulates the expression of specific proteins by controlling the activation/repression of genes?
What regulates the expression of specific proteins by controlling the activation/repression of genes?
Which process involves the irreversible commitment of a cell to a specific fate before cell determination?
Which process involves the irreversible commitment of a cell to a specific fate before cell determination?
What controls gene expression by affecting the development of an organism from embryonic stages to adult life?
What controls gene expression by affecting the development of an organism from embryonic stages to adult life?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation through modifications such as histone acetylation?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation through modifications such as histone acetylation?
Which type of cleavage produces blastomeres of approximately equal size?
Which type of cleavage produces blastomeres of approximately equal size?
What type of genes are responsible for forming the basic three-dimensional layout of the early embryo's body?
What type of genes are responsible for forming the basic three-dimensional layout of the early embryo's body?
In eukaryotic cells, what process involves controlling gene expression at multiple levels such as pre-transcriptional, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational regulation?
In eukaryotic cells, what process involves controlling gene expression at multiple levels such as pre-transcriptional, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational regulation?
What type of cleavage is the complete division of the egg, producing blastomeres of approximately equal size?
What type of cleavage is the complete division of the egg, producing blastomeres of approximately equal size?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What stage ends with the formation of a blastocyst or blastula, which is a hollow structure with a central cavity?
What stage ends with the formation of a blastocyst or blastula, which is a hollow structure with a central cavity?
What defines the range of different cell types a cell can become?
What defines the range of different cell types a cell can become?
What is responsible for influencing the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
What is responsible for influencing the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
What is the result of compaction in the morula stage?
What is the result of compaction in the morula stage?
Which type of development is characterized by the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells, leading to the disappearance of cell totipotence?
Which type of development is characterized by the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells, leading to the disappearance of cell totipotence?
What is the term for the process where cytoplasmic determinants are equally distributed in newly created cells, as observed in some animals?
What is the term for the process where cytoplasmic determinants are equally distributed in newly created cells, as observed in some animals?
What characteristic is exhibited by the future embryo in mosaic development due to the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants?
What characteristic is exhibited by the future embryo in mosaic development due to the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants?
What effect does the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants have on the cell totipotence during segmentation in mosaic development?
What effect does the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants have on the cell totipotence during segmentation in mosaic development?
What are morphogens?
What are morphogens?
How do morphogens act in creating concentration gradients?
How do morphogens act in creating concentration gradients?
What does the formation of chimaeras involve?
What does the formation of chimaeras involve?
Which type of twins are formed when a single fertilized egg splits into two?
Which type of twins are formed when a single fertilized egg splits into two?
What is the characteristic of conjoined identical twins?
What is the characteristic of conjoined identical twins?
What determines the success of surgical separation of conjoined twins?
What determines the success of surgical separation of conjoined twins?
What are monozygotic twins also known as?
What are monozygotic twins also known as?
What is the characteristic of different types of union in conjoined twins?
What is the characteristic of different types of union in conjoined twins?
What determines the potential of individual cells as development proceeds?
What determines the potential of individual cells as development proceeds?
What defines the range of different cell types a cell can become?
What defines the range of different cell types a cell can become?
What ultimately forms all the embryo structures during differentiation?
What ultimately forms all the embryo structures during differentiation?
Which genes control the gene expression during the early stages of pattern formation in the embryo?
Which genes control the gene expression during the early stages of pattern formation in the embryo?
What term describes the process in which one embryonic region influences another through secreted substances, causing cellular differentiation and tissue development?
What term describes the process in which one embryonic region influences another through secreted substances, causing cellular differentiation and tissue development?
Which factor is responsible for numerous fundamental inductions and is mediated by signaling factors such as Fgf, Wnt, Tgf, and Hh families?
Which factor is responsible for numerous fundamental inductions and is mediated by signaling factors such as Fgf, Wnt, Tgf, and Hh families?
What role do organizer centers play in developmental biology?
What role do organizer centers play in developmental biology?
Which structure in amphibian embryos is responsible for the formation of the notochord and neural tube?
Which structure in amphibian embryos is responsible for the formation of the notochord and neural tube?
What term describes the development of shape and the organization of functional groups of organs, achieved through complex interactions of cells during pattern formation?
What term describes the development of shape and the organization of functional groups of organs, achieved through complex interactions of cells during pattern formation?
Which process defines the specific spatial organization of organs and tissues?
Which process defines the specific spatial organization of organs and tissues?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in prokaryotic cells?
What is the primary method to control what type and how much of each protein is expressed in prokaryotic cells?
Which type of genes are essential for determining the anatomical identity of different body parts along the anterior/posterior axis?
Which type of genes are essential for determining the anatomical identity of different body parts along the anterior/posterior axis?
Which stage is characterized by a stable change in cell organization and irreversible fate for determined cells?
Which stage is characterized by a stable change in cell organization and irreversible fate for determined cells?
What is the result of compaction in the morula stage?
What is the result of compaction in the morula stage?
What happens to hatched blastocysts before implantation in mammals?
What happens to hatched blastocysts before implantation in mammals?
What is responsible for influencing the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
What is responsible for influencing the cleavage pattern in bird eggs?
What is the term for fraternal twins who develop independently during the same pregnancy?
What is the term for fraternal twins who develop independently during the same pregnancy?
What is the term for the condition where there are adhesions between the placentas of dizygotic twins in cows?
What is the term for the condition where there are adhesions between the placentas of dizygotic twins in cows?
What is the term for asymmetrical or unequal identical twins that occur when one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other?
What is the term for asymmetrical or unequal identical twins that occur when one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other?
What do parasitic twins represent in terms of the processes that also produce vanishing and conjoined twins?
What do parasitic twins represent in terms of the processes that also produce vanishing and conjoined twins?
What is the term for the process where a twin embryo begins developing in utero but does not fully separate?
What is the term for the process where a twin embryo begins developing in utero but does not fully separate?
What is the term for identical or monozygotic twins that may or may not share the same amniotic sac?
What is the term for identical or monozygotic twins that may or may not share the same amniotic sac?
What is the term for a rudimentary twin that is usually found sharing the same placenta with a normal twin?
What is the term for a rudimentary twin that is usually found sharing the same placenta with a normal twin?
What is the term for a condition where conjoined twins begin developing in utero and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other?
What is the term for a condition where conjoined twins begin developing in utero and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other?
What is the primary effect of uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells during segmentation?
What is the primary effect of uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells during segmentation?
What is the term for the type of development in which cytoplasmic determinants are equally distributed in the newly created cells?
What is the term for the type of development in which cytoplasmic determinants are equally distributed in the newly created cells?
What happens to cell totipotence if cytoplasmic determinants become unevenly distributed into the daughter cells from the first divisions?
What happens to cell totipotence if cytoplasmic determinants become unevenly distributed into the daughter cells from the first divisions?
What is the consequence of mosaic development due to the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells?
What is the consequence of mosaic development due to the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells?
In which type of species are fraternal twins more commonly found?
In which type of species are fraternal twins more commonly found?
What is the result of differences in the production and suppression of genes during embryonic development?
What is the result of differences in the production and suppression of genes during embryonic development?
What is the term for identical or monozygotic twins that may or may not share the same amniotic sac?
What is the term for identical or monozygotic twins that may or may not share the same amniotic sac?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the characteristic of superficial meroblastic cleavage?
What is the term for a rudimentary twin that is usually found sharing the same placenta with a normal twin?
What is the term for a rudimentary twin that is usually found sharing the same placenta with a normal twin?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation and embryo development through epigenetic modifications?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation and embryo development through epigenetic modifications?
What stage marks the termination of cleavage in mammals?
What stage marks the termination of cleavage in mammals?
What do parasitic twins represent in terms of the processes that also produce vanishing and conjoined twins?
What do parasitic twins represent in terms of the processes that also produce vanishing and conjoined twins?
What is the term for the process in which one embryonic region influences another through secreted substances, causing cellular differentiation and tissue development?
What is the term for the process in which one embryonic region influences another through secreted substances, causing cellular differentiation and tissue development?
Which factor is responsible for forming concentration gradients and mediating numerous fundamental inductions in embryonic development?
Which factor is responsible for forming concentration gradients and mediating numerous fundamental inductions in embryonic development?
What is the term for the group of cells with the ability to instruct adjacent cells into specific states, playing a crucial role in developmental biology?
What is the term for the group of cells with the ability to instruct adjacent cells into specific states, playing a crucial role in developmental biology?
What is the term for the process that defines the specific spatial organization of organs and tissues?
What is the term for the process that defines the specific spatial organization of organs and tissues?
What is the term for a substance secreted by one group of cells altering the development of another group, often leading to instructive changes in cellular commitments?
What is the term for a substance secreted by one group of cells altering the development of another group, often leading to instructive changes in cellular commitments?
What plays a crucial role in the formation of the notochord and neural tube in amphibian embryos?
What plays a crucial role in the formation of the notochord and neural tube in amphibian embryos?
What type of cells have the ability to become inducing tissues, leading to a cascade of embryonic inductions that shape the body plan?
What type of cells have the ability to become inducing tissues, leading to a cascade of embryonic inductions that shape the body plan?
"Cytoplasmic determinants" affect cell fate decisions through gene activities in specific cells. What are cytoplasmic determinants?
"Cytoplasmic determinants" affect cell fate decisions through gene activities in specific cells. What are cytoplasmic determinants?
"Morphogenesis" is achieved through complex interactions of cells during pattern formation. What is morphogenesis?
"Morphogenesis" is achieved through complex interactions of cells during pattern formation. What is morphogenesis?
"Regulative development" means that cells in early stages can lead to complete individuals when separated or fused. What is regulative development?
"Regulative development" means that cells in early stages can lead to complete individuals when separated or fused. What is regulative development?
What does cytoplasmic determinants affect through gene activities in specific cells?
What does cytoplasmic determinants affect through gene activities in specific cells?
What are morphogens?
What are morphogens?
What is the consequence of mosaic development due to the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells?
What is the consequence of mosaic development due to the uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants into distinct daughter cells?
What term is used to describe the reversible state of being committed to a certain fate before cell determination?
What term is used to describe the reversible state of being committed to a certain fate before cell determination?
What is the characteristic of different types of union in conjoined twins?
What is the characteristic of different types of union in conjoined twins?
What is the term for a condition where conjoined twins begin developing in utero and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other?
What is the term for a condition where conjoined twins begin developing in utero and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation through modifications such as histone acetylation?
What contributes to gene expression and plays a role in cell differentiation through modifications such as histone acetylation?
What is the characteristic of conjoined identical twins?
What is the characteristic of conjoined identical twins?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
-
Maternal proteins and mRNAs control early embryonic cleavages in the zygote.
-
Cleavage divisions are rapid mitotic divisions, increasing the number of cells without increasing cytoplasmic mass.
-
The blastomeres become smaller with each successive division, resulting in a collection of average size cells.
-
The amount and distribution of yolk in the egg determine the pattern and speed of cleavage.
-
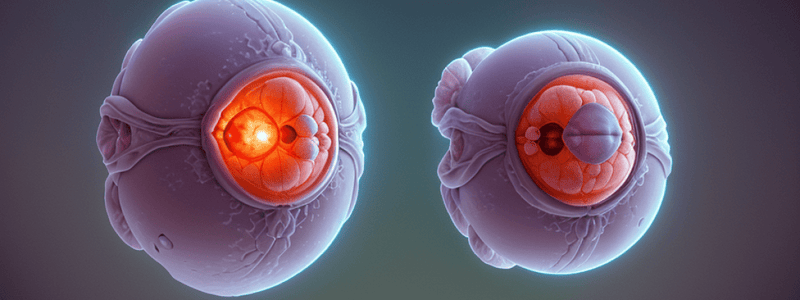
Holoblastic cleavage is the complete division of the egg, producing blastomeres of approximately equal size.
-
Unequal holoblastic cleavage produces blastomeres of unequal size due to the presence of a large yolk mass.
-
Meroblastic cleavage is incomplete division due to the presence of yolk and results in the formation of a discoidal morula.
-
Superficial meroblastic cleavage produces a layer of cells around a central mass of yolk.
-
The morula is a solid collection of cells that undergoes compaction, resulting in surface blastomeres becoming flattened and forming tight junctions.
-
The morula stage ends with the formation of a blastocyst or blastula, which is a hollow structure with a central cavity.
-
The nucleus of a mature organism's cell contains all the genetic instructions (DNA) to make all the cell types, and the process of differentiation involves the activation or inactivation of specific genes to produce the unique protein collection for each cell type.
-
Cells in a complex multicellular organism contain the same DNA, but different cell types are distinguished by the combination of genes that are expressed or repressed.
-
Gene expression is regulated by both internal and external cues, which affect the development of an organism from embryonic stages to adult life.
-
The formation of cells, tissues, and organs is under the control of various types of genes, including maternal genes, segmentation genes, and homeotic genes.
-
The early embryo's body has a basic three-dimensional layout with dorsal, ventral, cranial, and caudal axes, and a similar family of genes, such as Hox genes, controls the gene expression during the early stages of pattern formation.
-
Homeotic genes are essential for determining the anatomical identity of different body parts along the anterior/posterior axis and include a nearly identical DNA sequence called the homeobox region.
-
In eukaryotic cells, the control of gene expression is a multi-level process that involves pre-transcriptional, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational regulation.
-
Transcription factors that activate/repress genes are crucial for controlling the expression of specific proteins.
-
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNA, contribute to gene expression and thus play a role in cell differentiation and embryo development.
-
Maternal proteins and mRNAs control early embryonic cleavages in the zygote.
-
Cleavage divisions are rapid mitotic divisions, increasing the number of cells without increasing cytoplasmic mass.
-
The blastomeres become smaller with each successive division, resulting in a collection of average size cells.
-
The amount and distribution of yolk in the egg determine the pattern and speed of cleavage.
-
Holoblastic cleavage is the complete division of the egg, producing blastomeres of approximately equal size.
-
Unequal holoblastic cleavage produces blastomeres of unequal size due to the presence of a large yolk mass.
-
Meroblastic cleavage is incomplete division due to the presence of yolk and results in the formation of a discoidal morula.
-
Superficial meroblastic cleavage produces a layer of cells around a central mass of yolk.
-
The morula is a solid collection of cells that undergoes compaction, resulting in surface blastomeres becoming flattened and forming tight junctions.
-
The morula stage ends with the formation of a blastocyst or blastula, which is a hollow structure with a central cavity.
-
Mammals undergo regulative development, meaning that cells in early stages can lead to complete individuals when separated or fused.
-
Cytoplasmic determinants are components in the egg or zygote's cytoplasm that affect cell fate decisions through gene activities in specific cells.
-
Induction refers to the process of one embryonic region influencing another through secreted substances, causing cellular differentiation and tissue development.
-
Responding tissues can become inducing tissues, leading to a cascade of embryonic inductions that shape the body plan.
-
The dorsal blastopore lip in amphibian embryos is an example of an organiser centre responsible for the formation of the notochord and neural tube.
-
Organizer centres are groups of cells with the ability to instruct adjacent cells into specific states, playing a crucial role in developmental biology.
-
Morphogenesis, the development of shape and the organization of functional groups of organs, is achieved through complex interactions of cells during pattern formation. This process defines the specific spatial organization of organs and tissues.
-
Numerous fundamental inductions are mediated by signalling factors, such as those in the Fgf, Wnt, Tgf, and Hh families.
-
Induction involves a substance secreted by one group of cells altering the development of another group, often leading to instructive changes in cellular commitments.
-
Target cells only respond to induction signals when they express suitable receptors, which can vary in response to developmental time.
-
Organizer activity is often associated with structures like the primitive node in birds and mammals.
-
Morphogenesis, the development of shape and organization of tissues and organs, is a complex process involving pattern formation that drives the spatial arrangement of tissues and organs into a defined body plan.
-
During pattern formation in embryonic development, cells need to know their relative positions within the body plan.
-
Morphogens are intercellular molecular signals that provide positional information to target cells.
-
Morphogens act according to concentration gradients, with high concentrations near the source and low concentrations farther away.
-
Depending on the concentration of morphogens, cells receive different threshold levels and develop different cell fates.
-
Morphogens are often involved in creating concentration gradients in developing systems, such as the formation of limbs.
-
Animals can be composed of two or more genetically distinct cell populations, forming chimaeras or mosaics.
-
Chimaeras can be produced from the exchange of cells and genetic material during development, resulting in individuals with different genotypes.
-
Chimaeras are distinguished from hybrids, which are composed of genetically identical cell populations.
-
Twin chimaeras can be produced when two zygotes do not undergo fusion but share genetic material.
-
Identical twins are formed when a single fertilized egg splits into two, resulting in two genetically identical individuals.
-
Conjoined identical twins occur when blastomeres only partially separate, resulting in physically connected twins.
-
Success of surgical separation of conjoined twins depends on the degree of union and the skill of the surgical team.
-
Monozygotic twins are also known as identical twins and are formed from a single fertilized egg that splits into two.
-
Conjoined twins, also known as Siamese twins, are monozygotic twins with varying degrees of physical connection.
-
Different types of union in conjoined twins are named based on the region of connection (e.g., craniopagus for head connection).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.