Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary advantage of using electron microscopes over light microscopes?
What is the primary advantage of using electron microscopes over light microscopes?
- They require less specialized training.
- They can visualize smaller objects with greater detail. (correct)
- They are more affordable to operate.
- They can use natural light to illuminate specimens.
Which characteristic is specific to Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM)?
Which characteristic is specific to Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM)?
- They only provide surface images of specimens.
- Electrons pass through the specimen to create images. (correct)
- They require specimens to be coated with metal.
- They measure deflected electrons to form images.
What is a typical challenge associated with the use of electron microscopes?
What is a typical challenge associated with the use of electron microscopes?
- They produce images in color naturally.
- They are inexpensive and accessible.
- They require little to no specimen preparation.
- Specimen preparation is time-consuming and complex. (correct)
In which type of setting are electron microscopes most commonly found?
In which type of setting are electron microscopes most commonly found?
What does the term 'color-enhanced image' refer to in scanning electron microscopy?
What does the term 'color-enhanced image' refer to in scanning electron microscopy?
Which step in the sample preparation process for electron microscopy involves encasing the specimen within a resin?
Which step in the sample preparation process for electron microscopy involves encasing the specimen within a resin?
What is a major limitation of electron microscopy related to specimen characteristics?
What is a major limitation of electron microscopy related to specimen characteristics?
Which advantage of electron microscopy allows for the observation of 3-dimensional structures?
Which advantage of electron microscopy allows for the observation of 3-dimensional structures?
What is the purpose of using heavy metal stains in electron microscopy specimen preparation?
What is the purpose of using heavy metal stains in electron microscopy specimen preparation?
Which of the following statements about the costs associated with electron microscopes is true?
Which of the following statements about the costs associated with electron microscopes is true?
Which field commonly uses electron microscopy for studying microstructures of materials?
Which field commonly uses electron microscopy for studying microstructures of materials?
In which application is electron microscopy NOT typically utilized?
In which application is electron microscopy NOT typically utilized?
What role does scanning electron microscopy (SEM) play in forensic investigations?
What role does scanning electron microscopy (SEM) play in forensic investigations?
How does electron microscopy contribute to advancements in nanotechnology?
How does electron microscopy contribute to advancements in nanotechnology?
What is a common method used to prepare specimens for SEM?
What is a common method used to prepare specimens for SEM?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of electron microscopy in life sciences?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of electron microscopy in life sciences?
Which of the following types of samples would be analyzed using electron microscopy in forensic science?
Which of the following types of samples would be analyzed using electron microscopy in forensic science?
What aspect of cellular structures is often studied using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)?
What aspect of cellular structures is often studied using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)?
Flashcards
Electron Microscope
Electron Microscope
A microscope that uses a beam of electrons to create images, providing much higher magnification and resolution than light microscopes.
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
A type of electron microscope where electrons pass through the specimen, revealing internal structures.
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A type of electron microscope that scans the surface of a specimen with an electron beam, creating a 3D image.
Specimen Preparation for Electron Microscopy
Specimen Preparation for Electron Microscopy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resolving Power
Resolving Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specimen Fixation
Specimen Fixation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specimen Dehydration
Specimen Dehydration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specimen Embedding
Specimen Embedding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specimen Sectioning
Specimen Sectioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specimen Staining
Specimen Staining
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)?
What is Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)?
What is Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the core principle of electron microscopy?
What is the core principle of electron microscopy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a key requirement for TEM specimen preparation?
What is a key requirement for TEM specimen preparation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a common preparation step for SEM?
What is a common preparation step for SEM?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are electron microscopes important in research?
Why are electron microscopes important in research?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is electron microscopy used in material science?
How is electron microscopy used in material science?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is electron microscopy used in life sciences?
How is electron microscopy used in life sciences?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Electron Microscopes
- Electron microscopes offer greater magnification and resolution than light microscopes
- Create images by exposing specimens to an electron beam, not light
- Used in medical research, particularly pathology and virology
- Capable of viewing objects as small as 0.001 mm, too small for light microscopes
- Two main types: transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
- Visualizes objects by passing an electron beam through the specimen
- The image is displayed on a phosphorescent screen or projected onto a monitor
- Enables viewing of minute cell details, including nuclear structure
- An example of a TEM image is shown in Figure 1-64
- Allows viewing of details inside a cell (e.g., nuclear structure)
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Scans the specimen's surface with an electron beam
- The deflected electrons are measured to create a 3D image
- The specimen is coated with a metal to allow electron bounce-off
- Similar to a television screen image in outcome
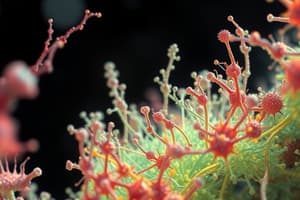
- An example of an SEM image is shown in Figure 1-65
- Can create a color-enhanced image
Applications and Considerations
- Electron microscopes are expensive and require specialized operation
- Specimen preparation can take several hours or days using special instruments and chemicals
- High-quality specimen preparation requires skill and experience
- Typically found in reference laboratories, medical schools, and large hospitals
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.