Podcast
Questions and Answers
What distinguishes allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) from irritant contact dermatitis (ICD)?
What distinguishes allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) from irritant contact dermatitis (ICD)?
- ICD occurs only in atopic individuals.
- ACD is caused by direct exposure to irritants.
- ACD is a result of hypersensitivity to a sensitizing agent. (correct)
- ICD results from an immunologic reaction.
Which of the following is a common causative agent of irritant contact dermatitis (ICD)?
Which of the following is a common causative agent of irritant contact dermatitis (ICD)?
- Soap (correct)
- Rubber (correct)
- Nickel
- Chromate
When seeking to assess contact dermatitis in a patient, which of the following should a pharmacist inquire about?
When seeking to assess contact dermatitis in a patient, which of the following should a pharmacist inquire about?
- The patient's allergies to medications.
- Whether the patient uses sunscreen.
- The patient's family history of skin conditions.
- The onset of the rash and agents handheld. (correct)
What is a key differentiating feature of dermatitis compared to eczema?
What is a key differentiating feature of dermatitis compared to eczema?
What indicates the need for referral in patients with contact dermatitis?
What indicates the need for referral in patients with contact dermatitis?
Which of the following is least likely to be a common location for irritant contact dermatitis (ICD)?
Which of the following is least likely to be a common location for irritant contact dermatitis (ICD)?
What is the minimum age requirement for prescribing hydrocortisone in the UK?
What is the minimum age requirement for prescribing hydrocortisone in the UK?
Which type of contact dermatitis involves a less important concentration of the substance at the time of exposure?
Which type of contact dermatitis involves a less important concentration of the substance at the time of exposure?
For how long can hydrocortisone be used in Canada?
For how long can hydrocortisone be used in Canada?
What is a possible symptom indicating severe contact dermatitis that would necessitate referral?
What is a possible symptom indicating severe contact dermatitis that would necessitate referral?
What type of skin should hydrocortisone not be applied to?
What type of skin should hydrocortisone not be applied to?
How often can hydrocortisone cream be applied per day?
How often can hydrocortisone cream be applied per day?
What is a fingertip unit used for?
What is a fingertip unit used for?
Which of the following is a known sensitizer that should not be used in topical ointments?
Which of the following is a known sensitizer that should not be used in topical ointments?
What is the effect of hydrocortisone on protein synthesis in human skin?
What is the effect of hydrocortisone on protein synthesis in human skin?
Is the use of hydrocortisone during pregnancy considered safe?
Is the use of hydrocortisone during pregnancy considered safe?
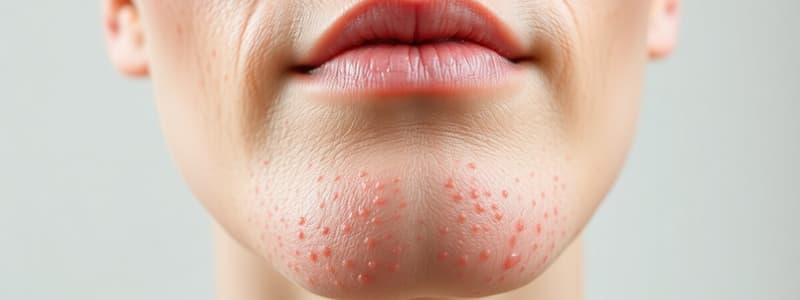
What characterizes mild acne?
What characterizes mild acne?
When should a patient with moderate acne be referred?
When should a patient with moderate acne be referred?
What additional condition is indicative of severe acne?
What additional condition is indicative of severe acne?
Which factor might lead a patient to be referred for acne treatment?
Which factor might lead a patient to be referred for acne treatment?
What is NOT a characteristic of rosacea?
What is NOT a characteristic of rosacea?
Which medication is frequently associated with acne-like lesions?
Which medication is frequently associated with acne-like lesions?
Which of these conditions requires referral to a doctor?
Which of these conditions requires referral to a doctor?
What is a potential cause of occupational acne?
What is a potential cause of occupational acne?
What is the primary purpose of benzoyl peroxide in acne treatment?
What is the primary purpose of benzoyl peroxide in acne treatment?
Which concentration of benzoyl peroxide is recommended to start treatment?
Which concentration of benzoyl peroxide is recommended to start treatment?
What type of skin formulation is generally more suitable for oily skin?
What type of skin formulation is generally more suitable for oily skin?
What should patients be warned about after starting benzoyl peroxide treatment?
What should patients be warned about after starting benzoyl peroxide treatment?
How should benzoyl peroxide be applied to be most effective?
How should benzoyl peroxide be applied to be most effective?
What adverse effect can occur with sensitization to benzoyl peroxide?
What adverse effect can occur with sensitization to benzoyl peroxide?
Which statement about retinoids in acne treatment is accurate?
Which statement about retinoids in acne treatment is accurate?
What risk is associated with using benzoyl peroxide in relation to clothing and bedding?
What risk is associated with using benzoyl peroxide in relation to clothing and bedding?
What percentage of Adapalene is in Differin Gel, which is available over the counter for acne treatment?
What percentage of Adapalene is in Differin Gel, which is available over the counter for acne treatment?
What is essential for patients using Adapalene cream to protect against photoirritation?
What is essential for patients using Adapalene cream to protect against photoirritation?
Which statement regarding diet and acne is accurate?
Which statement regarding diet and acne is accurate?
What is recommended to ensure maximum benefit from acne treatments?
What is recommended to ensure maximum benefit from acne treatments?
What is a common misconception about acne and skin hygiene?
What is a common misconception about acne and skin hygiene?
Why is the use of topical hydrocortisone contraindicated in acne?
Why is the use of topical hydrocortisone contraindicated in acne?
What type of make-up is considered better for individuals with acne?
What type of make-up is considered better for individuals with acne?
Which demographic is primarily affected by scabies?
Which demographic is primarily affected by scabies?
What is the primary method of scabies transmission?
What is the primary method of scabies transmission?
How long can the scabies mite live after leaving its host?
How long can the scabies mite live after leaving its host?
What is the first choice treatment for eradicating scabies infection?
What is the first choice treatment for eradicating scabies infection?
Which of the following is a recommended precaution after treating scabies?
Which of the following is a recommended precaution after treating scabies?
What measure should be taken if there is no visible improvement after 3 months of daily use of benzoyl peroxide?
What measure should be taken if there is no visible improvement after 3 months of daily use of benzoyl peroxide?
What is the recommended timeframe for visible benefits from keratolytic treatments like benzoyl peroxide?
What is the recommended timeframe for visible benefits from keratolytic treatments like benzoyl peroxide?
Which action should be avoided when using benzoyl peroxide?
Which action should be avoided when using benzoyl peroxide?
What should patients be advised regarding the use of benzoyl peroxide at night?
What should patients be advised regarding the use of benzoyl peroxide at night?
Flashcards
Contact Dermatitis
Contact Dermatitis
A skin condition, like eczema, caused by an external irritant or allergic reaction. Characterized by dryness, redness, and itching.
Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD)
Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD)
The most common type. Skin irritation caused by direct damage from a substance, regardless of allergy.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD)
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD)
Skin irritation from an allergic reaction to a substance, resulting in hypersensitivity.
ICD Causative Agents
ICD Causative Agents
Signup and view all the flashcards
ACD Causative Agents
ACD Causative Agents
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duration of Concern
Duration of Concern
Signup and view all the flashcards
Severe Contact Dermatitis
Severe Contact Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient Assessment for Contact Dermatitis
Patient Assessment for Contact Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrocortisone age limit (UK)
Hydrocortisone age limit (UK)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clobetasone age limit (UK)
Clobetasone age limit (UK)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maximum hydrocortisone treatment duration (UK)
Maximum hydrocortisone treatment duration (UK)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cream vs. Ointment for topical steroids
Cream vs. Ointment for topical steroids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrocortisone application frequency
Hydrocortisone application frequency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clobetasone application frequency
Clobetasone application frequency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Topical steroid application amount
Topical steroid application amount
Signup and view all the flashcards
Topical steroid use during pregnancy
Topical steroid use during pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mild Acne Characteristics
Mild Acne Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moderate Acne
Moderate Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Severe Acne
Severe Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne Referral Triggers
Acne Referral Triggers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne Affected Areas
Acne Affected Areas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rosacea vs. Acne
Rosacea vs. Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne-related Occupational Risks
Acne-related Occupational Risks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment Failure Referral
Treatment Failure Referral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benzoyl peroxide use
Benzoyl peroxide use
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benzoyl peroxide side effects
Benzoyl peroxide side effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benzoyl peroxide application
Benzoyl peroxide application
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adapalene treatment
Adapalene treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne skin cleansing
Acne skin cleansing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retinoids for acne
Retinoids for acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne drug progression
Acne drug progression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin irritation from acne treatments
Skin irritation from acne treatments
Signup and view all the flashcards
OTC Acne Treatment
OTC Acne Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adapalene & Sun
Adapalene & Sun
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diet and Acne
Diet and Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne Treatment Time
Acne Treatment Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin Hygiene and Acne
Skin Hygiene and Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrocortisone & Acne
Hydrocortisone & Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Makeup and Acne
Makeup and Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies
Scabies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Mite Lifespan
Scabies Mite Lifespan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Transmission
Scabies Transmission
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies Reinfestation Prevention
Scabies Reinfestation Prevention
Signup and view all the flashcards
First-line Treatment for Scabies
First-line Treatment for Scabies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treating Scabies Itch
Treating Scabies Itch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benzoyl Peroxide Action
Benzoyl Peroxide Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benzoyl Peroxide Application Frequency
Benzoyl Peroxide Application Frequency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benzoyl Peroxide Usage Duration
Benzoyl Peroxide Usage Duration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Eczema/Dermatitis
- Dermatitis and eczema are used interchangeably to describe skin conditions with dryness, redness, itching, and sometimes weeping or crusting.
- Dermatitis is more often used when an external trigger exists (as in contact dermatitis), while eczema usually refers to endogenous causes in individuals (like atopic eczema)
- Contact dermatitis is categorized into irritant and allergic types.
Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD)
- ICD is the most common type of contact dermatitis.
- It is caused by direct exposure to a substance that irritates the skin.
- This can happen with initial or repeated exposures; the substance could be strong or mild.
- Occupational exposures to water or irritant substances are common causes.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD)
- ACD is caused by a hypersensitivity reaction to a sensitizing agent.
- Irritants commonly include water, detergents, solvents, and certain metals (like nickel or chromate).
- ACD often leads to an immunologic reaction.
- Allergens can include metals, rubber, dyes, certain plants and medications.
Contact Dermatitis Patient Assessment
- Work-related exposure: Assess job/hobbies, onset and resolution of the rash, whether symptoms improve when away from work to determine if work is the cause.
- Duration of rash: Rash lasting more than two weeks requires referral to a doctor.
Severity and Referral
- Severe symptoms (fissured/bleeding/infection) require doctor referral
- Failed medication, signs of infection or duration of more than 2 weeks necessitate referral.
Treatment
- Emollients: Regularly used to soothe, hydrate, and provide a protective layer to the skin.
- Topical steroids: Mild to moderate topical steroid creams or ointments are first-line treatments; their use depends on the severity. Hydrocortisone is a mildly potent OTC option, while clobetasone is moderately potent, but not always available as an ointment.
- Other treatments: Antipruritics (e.g., calamine, crotamiton) or topical anesthetics (e.g., benzocaine) can be used, though not recommended for prolonged use due to potential for sensitization.
Acne
- Acne, also known as acne vulgaris, commonly affects young people.
- It results from a combination of factors, with hormonal changes during puberty often playing a role.
- Lesions range from non-inflammatory (comedones - blackheads, whiteheads) to inflammatory (papules, pustules, nodules, cysts).
- Acne can be mild, moderate, or severe based on lesion type and distribution.
Acne assessment
- Age: Acne is rare in infants and young children, thus referral may be necessary.
- Duration: Persistent acne outside the typical teenage years, or after previous treatments have failed, needs assessment.
- Occupation: Long-term contact with oils (in some cases) may lead to specific acne treatment plans.
- Medications: Certain medications (e.g., steroids, lithium, contraceptives) are linked to acne-like skin reactions.
Scabies
- Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei.
- The primary symptom is intense itching, especially at night.
- Affected areas commonly include skin folds and extremities.
- Scabies may affect all ages and is common in vulnerable communities.
Scabies Assessment and Treatment
- Symptom duration: Severe itching may persist even after successful treatment.
- History of infection: Exposure to other infected people.
- Physical examination: Presence of burrows as well as signs of infection (from scratching).
- Treatment Protocol: (Generally) 7-day spaced applications of medication.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.