Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following best describes the relationship between a habitat and a niche?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between a habitat and a niche?
- A habitat and niche are essentially the same thing, referring to where an organism lives and what it does there.
- A habitat describes the non-living parts of an organism's environment, while a niche describes the living parts.
- A habitat is the physical environment where an organism lives, while a niche is the role the organism plays in that environment. (correct)
- A habitat is the role an organism plays in its environment, while a niche is the physical space it occupies.
A forest ecosystem experiences a prolonged drought. Which ecosystem is MOST likely to be more resilient to this change?
A forest ecosystem experiences a prolonged drought. Which ecosystem is MOST likely to be more resilient to this change?
- A forest with a monoculture of pine trees.
- A forest with a simple food web and few species.
- A newly planted forest with young, developing trees.
- A forest with high biodiversity, including various tree species, insects, and fungi. (correct)
Which of the following is NOT considered an abiotic factor within an ecosystem?
Which of the following is NOT considered an abiotic factor within an ecosystem?
- Water availability.
- Soil composition.
- Amount of sunlight.
- Decomposers. (correct)
How are photosynthetic organisms crucial to the survival of an ecosystem?
How are photosynthetic organisms crucial to the survival of an ecosystem?
Which of the following is the MOST comprehensive definition of biodiversity?
Which of the following is the MOST comprehensive definition of biodiversity?
What could be a likely consequence of reduced biodiversity in an ecosystem?
What could be a likely consequence of reduced biodiversity in an ecosystem?
Which of the following is NOT a direct value of biodiversity to humans?
Which of the following is NOT a direct value of biodiversity to humans?
How would the removal of a keystone species MOST likely affect an ecosystem?
How would the removal of a keystone species MOST likely affect an ecosystem?
Which of the following BEST exemplifies the concept of an ecological niche?
Which of the following BEST exemplifies the concept of an ecological niche?
How does the role of a producer differ from that of a consumer in an ecosystem?
How does the role of a producer differ from that of a consumer in an ecosystem?
Why is it important to understand the niche of a species when trying to conserve it?
Why is it important to understand the niche of a species when trying to conserve it?
An ecosystem is experiencing a decline in its primary producer population. What is the MOST likely short-term consequence?
An ecosystem is experiencing a decline in its primary producer population. What is the MOST likely short-term consequence?
Some species of plants are known to produce chemicals that inhibit the growth of other plants around them. How would you best describe this phenomenon?
Some species of plants are known to produce chemicals that inhibit the growth of other plants around them. How would you best describe this phenomenon?
How do food chains and food webs relate to the concept of energy flow in an ecosystem?
How do food chains and food webs relate to the concept of energy flow in an ecosystem?
Which of the following human activities would MOST likely lead to a decrease in biodiversity in a forest ecosystem?
Which of the following human activities would MOST likely lead to a decrease in biodiversity in a forest ecosystem?
Flashcards
Population
Population
A group of organisms of the same species living in the same area.
Community
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area.
Ecosystem
Ecosystem
A community of living organisms (biotic) interacting with their non-living environment (abiotic).
Habitat
Habitat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niche
Niche
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biodiversity
Biodiversity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Biodiversity
Importance of Biodiversity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotic Factors
Biotic Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abiotic Factors
Abiotic Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Producers
Producers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sunlight
Sunlight
Signup and view all the flashcards
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Threats to Biodiversity
Threats to Biodiversity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Producers
Primary Producers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biodiversity Definition
Biodiversity Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- All of an organism's needs must be met in its ecosystem, including food, water, and shelter
- Some needs are met by biotic factors, which are living components
- Example: Squirrels get food and shelter from trees
- Abiotic factors consist of thee nonliving components in an ecosystem
- Example: Water, oxygen, rock, and soil
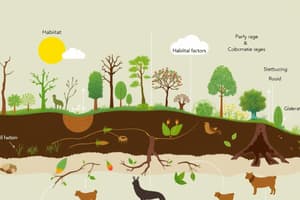
Habitats
- An organism's habitat is its physical location in an ecosystem
- Habitats are defined by features, including amount of precipitation, temperature range, and soil quality
- A habitat must provide all the needs of the organisms that live there
- Organisms live in different habitats because they have different needs
- Example: A roadrunner obtains its food and shelter from the desert
- A roadrunner cannot survive in a tropical forest or Antarctica
- A toucan cannot survive in the desert
- A penguin cannot survive in a tropical forest
Niches
- An organism's niche is the role it plays within an ecosystem
- Trees in a forest can fulfill roles like providing shelter for squirrels and birds, food for insects, and shade for animals.
Biodiversity
- Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms on earth
- Biodiversity is defined as the variability within species, between species, and between ecosystems
- Ecosystems with higher biodiversity are healthier and recover more rapidly from disturbances
- High biodiversity means a wider variety of living organisms, each with a unique capacity to withstand disturbances
- A high level of biodiversity increases the chance that at least a few organisms will survive an adversity
- Biodiversity is threatened by extinction due to harmful human activities
- Maintaining biodiversity and preserving the variety of species has direct and indirect benefits for humans
- Commercial products like vegetables, fruits, fibers, beeswax, and seaweed are provided by the different species in the environment
- Hunting and fishing are ways humans obtain food
- Crops like wheat, rice, and corn provide food for living organisms, including people
- Many prescription drugs come from living organisms
- Efficient anticancer drugs are extracted from tropical plants
- Penicillin is derived from a fungus
- Different species play roles in providing fresh water, recycling wastes, preventing soil erosion, regulating climate, and promoting ecotourism
- Living organisms enact a role in the biogeochemical cycles of nutrients, including water, nitrogen, and carbon cycles.
- Maintaining biodiversity is important to humans and other living organisms
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
- The sun is the main source of energy input
- Plants and photosynthetic organisms such as protists and bacteria capture sunlight, which is converted and stored in organic molecules through photosynthesis
- Photosynthetic organisms, or primary producers, secure energy and nutrients for the ecosystem in which they grow
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.