Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term for the interaction between all biotic and abiotic factors in a geographic area?
What is the term for the interaction between all biotic and abiotic factors in a geographic area?
- Population
- Habitat
- Niche
- Ecosystem (correct)
Which of the following is the BEST description of a habitat?
Which of the following is the BEST description of a habitat?
- The role an organism plays in its environment
- The place where an organism lives and finds food, water, and shelter (correct)
- The interaction of all living things
- A group of organisms of the same species
What term defines the unique role an organism plays within its ecosystem?
What term defines the unique role an organism plays within its ecosystem?
- Ecosystem
- Population
- Habitat
- Niche (correct)
In the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem, wildebeests primarily eat:
In the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem, wildebeests primarily eat:
Which of the following animals hunts smaller, faster prey like gazelles in the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem?
Which of the following animals hunts smaller, faster prey like gazelles in the Serengeti-Mara ecosystem?
What is the definition of population density?
What is the definition of population density?
Which of these is an example of a density-dependent factor affecting population size?
Which of these is an example of a density-dependent factor affecting population size?
Which of the following is an abiotic factor that can affect population density?
Which of the following is an abiotic factor that can affect population density?
Herons and egrets can coexist because:
Herons and egrets can coexist because:
What is a key characteristic of a healthy ecosystem regarding niches?
What is a key characteristic of a healthy ecosystem regarding niches?
Flashcards
Ecosystem
Ecosystem
Interaction between all biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors within a geographic area.
Habitat
Habitat
Natural home within an ecosystem that provides food, water, shelter, and space for an organism to survive.
Niche
Niche
The specific role an organism plays within its ecosystem.
Serengeti-Mara Ecosystem
Serengeti-Mara Ecosystem
Signup and view all the flashcards
Animal Niche
Animal Niche
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population
Population
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Density
Population Density
Signup and view all the flashcards
Density-Dependent Factors
Density-Dependent Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Density-Independent Factors
Density-Independent Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
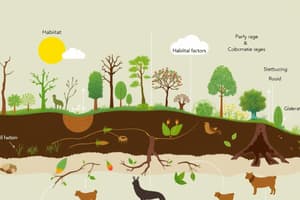
Ecosystem, Habitat, and Niche
- An ecosystem is the interaction between all biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors within a specific geographic area.
- Ecosystems are dynamic and vary greatly in size, location, and diversity.
- A habitat is an organism's natural home within an ecosystem, providing food, water, shelter, and living space.
- Habitats are suitable dwellings for different groups of organisms, such as forests, deserts, grasslands, or marine environments.
- A niche is the unique role an organism plays within its ecosystem or the specific conditions it utilizes.
- Niches relate to how an organism obtains essentials like food, water, and shelter.
- Different species typically occupy different niches within an ecosystem, minimizing competition for resources.
Ecosystem vs. Habitat vs. Niche
- A habitat is simply where an animal or organism lives.
- An ecosystem accounts for the interactions of living organisms with each other and their environment.
- Ecosystems can encompass multiple habitats or be a small part of one.
- A niche is an organism's unique role or job within its ecosystem.
The Serengeti-Mara Ecosystem
- The Serengeti-Mara is an open, wooded grassland savanna in east-central Africa (Tanzania and Kenya).
- Its climate is seasonally tropical, with temperatures from 15°C (59°F) to 27°C (81°F).
- It experiences a dry season for most of the year, with rains from March to May and November to December, totaling 21-41 inches depending on location.
- The soil is volcanic ash-based, ideal for supporting various grasses.
- Fire maintains healthy, nutrient-rich grasslands.
- Animals in the Serengeti-Mara each have a specific niche.
- Each species possesses specialized needs for food, water, space, and shelter, along with the capabilities to acquire them.
Animal Niche
- All organisms need a habitat that provides for their survival.
- Within any habitat, each species interacts in its unique way, defining its niche.
- Species in an ecosystem typically do not share niches.
- Organisms with identical needs will compete, potentially leading to one species dying off or adapting.
- Healthy ecosystems have niches that replenish or make way for others.
- The niche an animal occupies depends on its living habits, including how, what, when, and where it eats, shelters, raises young, and finds water.
- Herbivores on the Serengeti have specific food preferences, such as wildebeests eating short grasses, while zebras, gazelles, and antelopes prefer herbs, shrubs, leaves, or long grasses.
- Giraffes can access food others cannot reach.
- Predators on the Serengeti also have their own niches.
- Lions hunt larger prey like wildebeest, while cheetahs hunt smaller, faster prey like antelope or gazelles.
- Herons and egrets coexist by feeding at slightly different depths in the water and breeding at different times.
- Night herons are most active in the evening.
Population Density
- A population is a group of organisms of the same species living in an area.
- Population density is the number of species within a specific area size.
- Factors such as disease, competition for resources, predation, and environmental degradation are density-dependent.
- Extreme weather, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, drought, seasonal changes, fire, and pollution are examples of density-independent factors.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.