Podcast
Questions and Answers
What characteristic differentiates the layers of the atmosphere?
What characteristic differentiates the layers of the atmosphere?
- Chemical composition variation
- Humidity levels
- Variation in pressure
- Temperature gradients (correct)
Which of the following best describes mechanical weathering?
Which of the following best describes mechanical weathering?
- Physical disintegration of rocks (correct)
- Accumulation of sediment over time
- Erosion by water only
- Chemical alteration of minerals
What is the primary measure of energy released during an earthquake?
What is the primary measure of energy released during an earthquake?
- Geological intensity scale
- Californian seismic scale
- Richter scale (correct)
- Moment magnitude scale
How do glaciers and ice sheets influence global sea levels?
How do glaciers and ice sheets influence global sea levels?
Which of the following describes the role of oceans in Earth's climate system?
Which of the following describes the role of oceans in Earth's climate system?
What is the study of fossils and extinct life termed?
What is the study of fossils and extinct life termed?
Which factor contributes to erosion by water, wind, and ice?
Which factor contributes to erosion by water, wind, and ice?
Which statement best reflects the importance of understanding geological hazards?
Which statement best reflects the importance of understanding geological hazards?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the mantle's characteristics?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the mantle's characteristics?
What occurs at convergent plate boundaries?
What occurs at convergent plate boundaries?
Which rock type forms through the cooling and solidification of molten rock?
Which rock type forms through the cooling and solidification of molten rock?
In what way does the geologic time scale relate to Earth's history?
In what way does the geologic time scale relate to Earth's history?
What drives the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates?
What drives the movement of Earth's lithospheric plates?
Which best describes the outer core of the Earth?
Which best describes the outer core of the Earth?
What is the outcome of the rock cycle?
What is the outcome of the rock cycle?
Which of the following gases is NOT a major component of Earth's atmosphere?
Which of the following gases is NOT a major component of Earth's atmosphere?
Flashcards
Earth's layers
Earth's layers
The four main parts of Earth: crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics
The theory that Earth's lithosphere is divided into moving plates.
Rock types
Rock types
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, formed in different ways.
Plate boundaries (divergent)
Plate boundaries (divergent)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plate boundaries (convergent)
Plate boundaries (convergent)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Geologic time
Geologic time
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earth's atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mantle
Mantle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earth's atmosphere layers
Earth's atmosphere layers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earth's hydrosphere
Earth's hydrosphere
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earthquake
Earthquake
Signup and view all the flashcards
Volcano
Volcano
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weathering
Weathering
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erosion
Erosion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fossil
Fossil
Signup and view all the flashcards
Natural resources
Natural resources
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
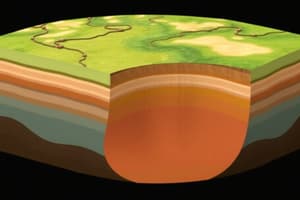
Earth's Structure
- Earth is composed of four major layers: crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
- The crust is the outermost solid shell, varying in thickness from 5 to 70 kilometers.
- The mantle is a thick layer of mostly solid rock beneath the crust.
- The outer core is a liquid layer of mostly iron and nickel.
- The inner core is a solid sphere of mostly iron and nickel.
- Earth's internal heat drives processes like plate tectonics and volcanic activity.
Plate Tectonics
- The Earth's lithosphere is divided into numerous rigid plates that move slowly over the asthenosphere.
- Plate movement is driven by convection currents in the mantle.
- Plate boundaries are classified as divergent, convergent, or transform.
- Divergent boundaries occur where plates move apart, resulting in seafloor spreading and volcanic activity.
- Convergent boundaries occur where plates collide, leading to mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
- Transform boundaries occur where plates slide past each other, producing earthquakes.
- Plate tectonics shapes Earth's surface by creating mountains, valleys, and ocean basins.
Rocks and Minerals
- Rocks are aggregates of one or more minerals.
- Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic solids with a definite chemical composition and crystal structure.
- There are three major rock types: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
- Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of molten rock (magma or lava).
- Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments.
- Metamorphic rocks are formed from existing rocks that have been changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
- The rock cycle describes the continuous transformations among these three rock types.
Geologic Time
- Earth's history is divided into eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
- The geologic time scale is a system of chronological dating that relates strata to time.
- Major events in Earth's history, such as mass extinctions and the evolution of life, are recorded in the rock layers.
Earth's Atmosphere
- The atmosphere is a mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth.
- Major components include nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide.
- The atmosphere protects life by absorbing harmful solar radiation and regulating Earth's temperature through the greenhouse effect.
- Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude.
- Different layers, characterized by temperature gradients, exist within the atmosphere (troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere).
Earth's Water
- Earth's hydrosphere encompasses all of its water, in various forms (oceans, lakes, rivers, ice caps, groundwater).
- The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water between Earth's surface and atmosphere.
- Oceans play a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate and supporting marine life.
- Groundwater is an important source of freshwater for human use.
- Glaciers and ice sheets impact global sea level and regional climates.
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
- Earthquakes are vibrations of the Earth's surface caused by the sudden release of energy within the Earth's crust.
- The energy released by an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale.
- Volcanoes are openings in the Earth's surface through which molten rock (magma) and gases escape.
- Volcanic eruptions can have significant impacts on the environment and human populations.
- Understanding the causes, processes, and potential hazards of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions is crucial for disaster preparedness.
Weathering and Erosion
- Weathering is the process by which rocks are broken down into smaller pieces.
- Erosion is the process by which weathered material is transported from one location to another.
- Mechanical weathering involves physical disintegration of rocks, while chemical weathering involves chemical alteration of rocks.
- Factors like water, wind, and ice contribute to erosion.
- Weathering and erosion shape landscapes over long periods of time.
Fossils and Paleontology
- Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of organisms from the past.
- Paleontology is the study of fossils and extinct life.
- Fossils provide evidence for the evolution of life on Earth.
- Fossils can reveal information about past environments and climates.
- Different types of fossils provide insight into past ecosystems.
Natural Resources
- Earth contains various natural resource deposits, such as minerals, fossil fuels, groundwater, and fertile soils.
- Sustainable practices are essential for responsible resource management.
- Mining and extraction of resources can have environmental and societal impacts.
- Understanding geological conditions is crucial for locating and extracting resources.
Hazards
- Geological hazards include earthquakes, volcanoes, landslides, floods, tsunamis, and droughts.
- Understanding causes and potential impacts of geological hazards is important for mitigation and preparedness.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.