Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the outermost layer of Earth called?
What is the outermost layer of Earth called?
Crust
What is the layer located between the liquid outer core and the solid inner core?
What is the layer located between the liquid outer core and the solid inner core?
Lehmann Discontinuity
What type of crust makes up the continents?
What type of crust makes up the continents?
Continental Crust
What type of crust underlies the ocean floor?
What type of crust underlies the ocean floor?
What is the rigid layer that can break under stress called?
What is the rigid layer that can break under stress called?
What is the name of the layer that can be deformed and reshape as a result of the hot, molten mantle?
What is the name of the layer that can be deformed and reshape as a result of the hot, molten mantle?
What phenomenon involves the upward movement from the lower mantle to the cooler upper mantle?
What phenomenon involves the upward movement from the lower mantle to the cooler upper mantle?
What is the term for the system that incorporates continental drift and seafloor spreading theories?
What is the term for the system that incorporates continental drift and seafloor spreading theories?
Who proposed the continental drift theory in 1912?
Who proposed the continental drift theory in 1912?
Who proposed the seafloor spreading theory in the 1960s?
Who proposed the seafloor spreading theory in the 1960s?
What is the shaking of the ground due to the interaction of plates called?
What is the shaking of the ground due to the interaction of plates called?
What is the region of deformed rocks known as?
What is the region of deformed rocks known as?
What is the area that is formed in between two sliding plates called?
What is the area that is formed in between two sliding plates called?
What process describes the forming of mountains and mountain ranges?
What process describes the forming of mountains and mountain ranges?
What is the vast sea or superocean called?
What is the vast sea or superocean called?
What interface exists between the crust and the upper mantle?
What interface exists between the crust and the upper mantle?
What boundary separates the lower mantle from the outer core?
What boundary separates the lower mantle from the outer core?
What is the term for the point of origin of an earthquake?
What is the term for the point of origin of an earthquake?
What is the point directly above the focus of an earthquake called?
What is the point directly above the focus of an earthquake called?
What are the cracks on Earth's crust called?
What are the cracks on Earth's crust called?
What term describes the strength of shaking of an earthquake?
What term describes the strength of shaking of an earthquake?
What term refers to the amount of energy released during an earthquake?
What term refers to the amount of energy released during an earthquake?
What type of plate boundary involves two plates sliding towards each other?
What type of plate boundary involves two plates sliding towards each other?
What type of plate boundary forms rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges?
What type of plate boundary forms rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges?
What theory involves contraction and wrinkling of the planet?
What theory involves contraction and wrinkling of the planet?
Match the following supercontinents:
Match the following supercontinents:
Match the types of evidence for the Continental Drift Theory (CDT):
Match the types of evidence for the Continental Drift Theory (CDT):
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
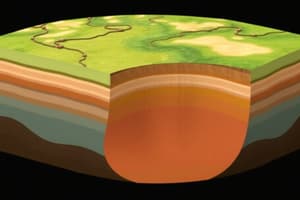
Earth's Structure
- Crust: The outermost layer of the Earth, where life exists.
- Continental Crust: Makes up the continents.
- Oceanic Crust: Underlies the ocean floor.
- Lithosphere: Rigid layer that can break under stress, location of plates.
- Asthenosphere: Deformable layer due to the hot, molten mantle.
- Mantle: Semisolid, rocky, and very hot layer, making up 80% of the Earth.
- Convection Currents: Travel upward from the lower mantle to the cooler upper mantle.
- Outer Core: Liquid layer of Earth.
- Inner Core: Primarily composed of solid iron.
- Mohorovicic Discontinuity: Interface between the crust and upper mantle.
- Gutenberg Discontinuity: Boundary between the lower mantle and the outer core.
- Lehmann Discontinuity: Located between the liquid outer core and the solid inner core.
Plate Tectonics
- Alfred Wegener (1912): Proposed the continental drift theory.
- Harry Hess (1960s): Proposed the seafloor spreading theory.
- Plate Tectonic Theory: Combines continental drift and seafloor spreading.
- Earthquakes: Shaking of the ground caused by the interaction of plates.
Plate Boundaries
- Convergent Plate Boundary: Two plates sliding towards each other.
- Produces the most powerful earthquakes.
- Oceanic-Oceanic: Volcanoes form in the ocean.
- Oceanic-Continental: Volcanoes form on land, mountain ranges form.
- Continental-Continental: Mountains form.
- Divergent Plate Boundary: Two plates moving away from each other.
- Forms rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges.
- Transform Plate Boundary: Plates slide against each other in opposite directions.
Earthquake Characteristics
- Focus (Hypocenter): Point of origin of an earthquake.
- Epicenter: Point directly above the focus.
- Faults: Cracks on Earth's crust.
- Intensity: Strength of shaking of an earthquake.
- Magnitude: Amount of energy released during an earthquake.
- Horst: Crustal blocks that do not slide down.
- Graben: Block that slides down.
Evidence of Continental Drift Theory
- Geographical Evidence: Matching coastlines of South America and Africa.
- Fossil Correlation: Similar fossils found on different continents.
- Rock and Mountain Correlation: Similar rock layers and mountain ranges on different continents.
- Glacial Evidence: Evidence of glaciers in tropical areas.
Other Key Terms
- Orogenic Belt: Region of deformed rocks.
- Shear Zone: Area formed between two sliding plates.
- Orogenesis: Process of forming mountains and mountain ranges.
- Pacific Ring of Fire (Circum-Pacific Belt): Region known for volcanic and seismic activity.
- PHILVOCS: Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology.
Seismic Waves
- Body Waves: Travel through the inner layers of the Earth.
- Primary Waves (P Waves): Fastest waves, travel through solids and liquids.
- Surface Waves: Travel only on the surface of the Earth.
Supercontinents
- Pangaea: Supercontinent where present continents came from.
- Laurasia: Northern part of Pangaea.
- Gondwana: Southern part of Pangaea.
Plates
- Primary Plates: Eurasian, Australian, Pacific, North American, South American, African, Antarctic.
- Secondary Plates: Juan De Fuca, Nazca, Cocos, Caribbean, Philippine Sea, Arabian, Indian, Scotia.
Water Use
- Domestic Use: Most important use of water.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.