Podcast
Questions and Answers
Quelles sont les différences fondamentales entre les reliefs continentaux et océaniques ?
Quelles sont les différences fondamentales entre les reliefs continentaux et océaniques ?
Les continents présentent des reliefs positifs (altitude moyenne 300m, avec des chaînes de montagnes), tandis que les océans présentent des reliefs négatifs (profondeur moyenne 4000m). Cette différence est liée à la nature des roches : granitique (moins dense) pour les continents et basaltique pour les fonds océaniques.
Quelle est la roche la plus représentative de la croûte continentale ?
Quelle est la roche la plus représentative de la croûte continentale ?
Le granite
Quels sont les trois principaux types de minéraux composant le granite ?
Quels sont les trois principaux types de minéraux composant le granite ?
- Olivine, pyroxène, mica
- Quartz, feldspaths, micas (correct)
- Feldspaths, pyroxène, amphibole
- Quartz, olivine, feldspaths
Le granite est une roche magmatique _____.
Le granite est une roche magmatique _____.
Quelles sont les deux principales roches magmatiques constituant la croûte océanique, sous la couche de sédiments ?
Quelles sont les deux principales roches magmatiques constituant la croûte océanique, sous la couche de sédiments ?
Le basalte a une texture _____ car il est issu du refroidissement _____ d'un magma.
Le basalte a une texture _____ car il est issu du refroidissement _____ d'un magma.
Le gabbro a une texture _____ car il est issu du refroidissement _____ d'un magma en profondeur.
Le gabbro a une texture _____ car il est issu du refroidissement _____ d'un magma en profondeur.
Le basalte et le gabbro ont des compositions chimiques très différentes.
Le basalte et le gabbro ont des compositions chimiques très différentes.
En quels éléments chimiques les roches de la croûte océanique (basalte, gabbro) sont-elles plus riches que le granite de la croûte continentale ?
En quels éléments chimiques les roches de la croûte océanique (basalte, gabbro) sont-elles plus riches que le granite de la croûte continentale ?
Associez chaque roche à sa texture caractéristique et son type magmatique :
Associez chaque roche à sa texture caractéristique et son type magmatique :
Flashcards
Earth's Internal Dynamics
Earth's Internal Dynamics
The study of Earth's internal processes through scientific methods.
Two Major Earth Domains
Two Major Earth Domains
Oceanic and continental domains.
Average Height of Continents
Average Height of Continents
The continents is 300m.
Negative Reliefs
Negative Reliefs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why bimodal topography?
Why bimodal topography?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continental Crust Composition
Continental Crust Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Granite Minerals
Granite Minerals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Granite
Granite
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oceanic Crust Layers
Oceanic Crust Layers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basalt Texture
Basalt Texture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gabbro Texture
Gabbro Texture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basalt
Basalt
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gabbro
Gabbro
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The general question is how current geoscience methods allow constructing a scientific approach to terrestrial dynamics.
Earth's Crust Structure
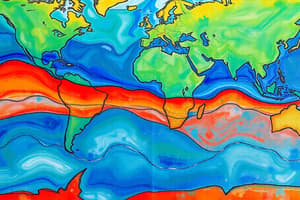
- Observation of Earth's surface distinguishes oceanic and continental domains.
- What are the differences between continental and oceanic crusts?
Contrasts Between Continents and Oceans
Contrasted Reliefs
- Relief observations distinguish two large sets relative to sea level (=level 0).
- Positive reliefs include mountain ranges on continents.
- Average continent altitude is 300m.
- Negative reliefs are ocean floors averaging 4,000 m in depth.
- Bimodal relief distribution is due to the nature of continental and oceanic floor materials.
- Continents are granitic and less dense than basaltic oceanic floors.
Different Rocks
- Continental crust exhibits visible heterogeneity on the surface (magmatic, sedimentary, metamorphic rocks).
- Granite is the most representative rock at depth.
- Granite consists mainly of quartz, feldspars, and mica.
- Granite is entirely crystallized with a granular structure, resulting from slow magma cooling.
- Granite is a plutonic magmatic rock.
- Oceanic crust is covered by a thin sediment layer (0 to 400 m).
- Below, the crust is composed of basalt first, then gabbro.
- These are magmatic rocks from magma cooling.
- Their chemical composition is identical.
- The minerals present are the same, but their cooling mode differs, hence their texture.
- Basalt has a microlithic texture, with rare large minerals or phenocrysts (olivine, pyroxene) embedded in a matrix.
- Basalt contains uncrystallized glass and small crystals (microliths) of plagioclase.
- Basalt results from slow magma cooling, a volcanic magmatic rock.
- Gabbro has a granular texture due to large, jointed minerals.
- Magma cools slowly at depth, a plutonic magmatic rock.
- Both rocks come from the crystallization of the same magma type.
- They are less rich in silica than granite in the continental crust.
- They are rich in ferromagnesian elements (Fe, Mg).
- They contain minerals rich in these elements, such as olivine and pyroxenes, but no quartz.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.