Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which landform region is described as having flat land suited to farming and is where the majority of Canadian fossil fuels are found?
Which landform region is described as having flat land suited to farming and is where the majority of Canadian fossil fuels are found?
- Interior Plains (correct)
- Western Cordillera
- Canadian Shield
- Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands
Which landform region is described as having many lakes, lumpy irregular land, and rivers that are not straight?
Which landform region is described as having many lakes, lumpy irregular land, and rivers that are not straight?
- Canadian Shield (correct)
- Western Cordillera
- Appalachian Mountains
- Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands
Which landform region is characterized by tall, young mountains, pointed peaks, and v-shaped valleys with green vegetation?
Which landform region is characterized by tall, young mountains, pointed peaks, and v-shaped valleys with green vegetation?
- Innuitian Mountains
- Western Cordillera (correct)
- Appalachian Mountains
- Canadian Shield
Which landform region forms the core of the continent and is composed of a large area of Precambrian rock?
Which landform region forms the core of the continent and is composed of a large area of Precambrian rock?
What are the three ways constructive forces can push up the land to create mountains/highlands?
What are the three ways constructive forces can push up the land to create mountains/highlands?
Which type of mountain is formed when crustal plates move together forcing the land between to buckle and fold?
Which type of mountain is formed when crustal plates move together forcing the land between to buckle and fold?
What type of weathering involves the disintegration of rock by changing its composition?
What type of weathering involves the disintegration of rock by changing its composition?
Which landform is described as very low, near sea level, flat, and swampy?
Which landform is described as very low, near sea level, flat, and swampy?
What type of mountain is created by parallel cracks in the crust allowing the center portion of land to rise or fall, forming flat-topped mountains?
What type of mountain is created by parallel cracks in the crust allowing the center portion of land to rise or fall, forming flat-topped mountains?
Which force allows magma to reach the surface and cool and harden to become volcanic mountains?
Which force allows magma to reach the surface and cool and harden to become volcanic mountains?
Which type of weathering involves the disintegration of rock without changing its composition?
Which type of weathering involves the disintegration of rock without changing its composition?
What is the process of wearing away and breaking down the surface called?
What is the process of wearing away and breaking down the surface called?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
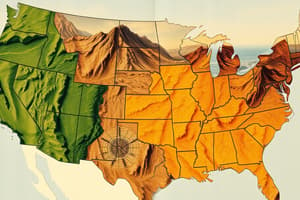
Landform Regions of Canada
- The Prairies region is characterized by flat land suited to farming and is where the majority of Canadian fossil fuels are found.
- The Canadian Shield region is described as having many lakes, lumpy irregular land, and rivers that are not straight.
- The Cordillera region is characterized by tall, young mountains, pointed peaks, and v-shaped valleys with green vegetation.
- The Canadian Shield region forms the core of the continent and is composed of a large area of Precambrian rock.
Mountain Formation
- Constructive forces can push up the land to create mountains/highlands through volcanic activity, folding, and uplift.
- Fold mountains are formed when crustal plates move together, forcing the land between to buckle and fold.
- Block mountains are created by parallel cracks in the crust, allowing the center portion of land to rise or fall, forming flat-topped mountains.
Weathering and Erosion
- Chemical weathering involves the disintegration of rock by changing its composition.
- Physical weathering involves the disintegration of rock without changing its composition.
- Volcanic activity is the force that allows magma to reach the surface and cool and harden to become volcanic mountains.
- Erosion is the process of wearing away and breaking down the surface.
Landform Features
- Lowlands are very low, near sea level, flat, and swampy.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.