Podcast
Questions and Answers
The primary center for thermoregulation in the body is located in the:
The primary center for thermoregulation in the body is located in the:
- Hypothalamus (correct)
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
- Cerebellum
- Hippocampus
Heat loss through direct contact, like touching a cold object, is known as:
Heat loss through direct contact, like touching a cold object, is known as:
- Conduction (correct)
- Metabolism
- Convection
- Evaporation
- Radiation
Sweating is a mechanism for cooling the body by:
Sweating is a mechanism for cooling the body by:
- Evaporation (correct)
- Radiation
- Filtration
- Convection
- Conduction
Shivering increases body temperature through:
Shivering increases body temperature through:
In response to cold, the body conserves heat by:
In response to cold, the body conserves heat by:
Vitamin C is important for:
Vitamin C is important for:
A deficiency in vitamin B12 may lead to:
A deficiency in vitamin B12 may lead to:
Which vitamin is essential for calcium absorption in the intestines?
Which vitamin is essential for calcium absorption in the intestines?
The mineral iron is crucial for:
The mineral iron is crucial for:
Vitamin K is necessary for:
Vitamin K is necessary for:
The main function of carbohydrates in the diet is to:
The main function of carbohydrates in the diet is to:
The body's long-term energy reserves are primarily stored as:
The body's long-term energy reserves are primarily stored as:
Proteins are essential in the body for:
Proteins are essential in the body for:
Lipids are essential in the body because they:
Lipids are essential in the body because they:
During a prolonged fast, the body relies primarily on which process for energy?
During a prolonged fast, the body relies primarily on which process for energy?
In the absorptive state, the body primarily:
In the absorptive state, the body primarily:
During the postabsorptive state, the body's main source of glucose is:
During the postabsorptive state, the body's main source of glucose is:
Gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the:
Gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the:
Which process allows the liver to produce glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
Which process allows the liver to produce glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
In the postabsorptive state, which hormone is primarily active to mobilize stored nutrients?
In the postabsorptive state, which hormone is primarily active to mobilize stored nutrients?
Which structure forms the boundary between the oral and nasal cavities?
Which structure forms the boundary between the oral and nasal cavities?
The enteric nervous system is primarily responsible for:
The enteric nervous system is primarily responsible for:
Organs that are completely covered by visceral peritoneum are considered:
Organs that are completely covered by visceral peritoneum are considered:
Which layer of the digestive tract contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics?
Which layer of the digestive tract contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics?
Which cells detect changes in the digestive tract's chemical environment?
Which cells detect changes in the digestive tract's chemical environment?
The labial frenulum connects the:
The labial frenulum connects the:
The serous component of saliva contains which enzyme for carbohydrate digestion?
The serous component of saliva contains which enzyme for carbohydrate digestion?
Saliva provides protection by containing:
Saliva provides protection by containing:
Which salivary gland produces the thickest mucous secretion?
Which salivary gland produces the thickest mucous secretion?
The buccinator muscle primarily aids in:
The buccinator muscle primarily aids in:
The primary function of the canines is to:
The primary function of the canines is to:
In the process of mastication, the masseter and temporalis muscles work to:
In the process of mastication, the masseter and temporalis muscles work to:
Which part of the tooth is highly calcified and covers the crown?
Which part of the tooth is highly calcified and covers the crown?
The mastication reflex is primarily integrated within the:
The mastication reflex is primarily integrated within the:
The pulp cavity of a tooth contains:
The pulp cavity of a tooth contains:
The pharyngeal constrictors are responsible for:
The pharyngeal constrictors are responsible for:
The main function of the epiglottis during swallowing is to:
The main function of the epiglottis during swallowing is to:
The part of the pharynx that only transports air is the:
The part of the pharynx that only transports air is the:
The esophageal hiatus refers to the:
The esophageal hiatus refers to the:
Which part of the esophagus contains only smooth muscle?
Which part of the esophagus contains only smooth muscle?
Peristalsis in the esophagus begins with:
Peristalsis in the esophagus begins with:
The stomach's muscularis layer is unique because it has:
The stomach's muscularis layer is unique because it has:
Parietal cells in the stomach produce:
Parietal cells in the stomach produce:
Pepsinogen, secreted by chief cells, is activated by:
Pepsinogen, secreted by chief cells, is activated by:
Gastrin primarily functions to:
Gastrin primarily functions to:
The majority of digestion and absorption in the small intestine occurs in the:
The majority of digestion and absorption in the small intestine occurs in the:
Which structure in the small intestine significantly increases surface area for absorption?
Which structure in the small intestine significantly increases surface area for absorption?
Brunner's glands, located in the duodenum, secrete:
Brunner's glands, located in the duodenum, secrete:
The small intestine absorbs fats into:
The small intestine absorbs fats into:
The terminal portion of the small intestine is the:
The terminal portion of the small intestine is the:
The main function of bile is to:
The main function of bile is to:
Pancreatic juice neutralizes stomach acid in the small intestine with:
Pancreatic juice neutralizes stomach acid in the small intestine with:
The hormone that stimulates bile release from the gallbladder is:
The hormone that stimulates bile release from the gallbladder is:
The primary liver function is to:
The primary liver function is to:
In the liver, bile is produced by:
In the liver, bile is produced by:
The primary function of the large intestine is to:
The primary function of the large intestine is to:
The first section of the large intestine is the:
The first section of the large intestine is the:
The large intestine produces vitamin K with the help of:
The large intestine produces vitamin K with the help of:
Mass movements in the large intestine are often triggered by:
Mass movements in the large intestine are often triggered by:
Which structure regulates the passage of feces from the large intestine to the rectum?
Which structure regulates the passage of feces from the large intestine to the rectum?
The defecation reflex is primarily initiated by:
The defecation reflex is primarily initiated by:
The internal anal sphincter is controlled by:
The internal anal sphincter is controlled by:
The purpose of the external anal sphincter is to:
The purpose of the external anal sphincter is to:
The final portion of the large intestine where waste is stored before defecation is the:
The final portion of the large intestine where waste is stored before defecation is the:
A key factor that triggers the defecation reflex includes:
A key factor that triggers the defecation reflex includes:
Which enzyme begins carbohydrate digestion in the mouth?
Which enzyme begins carbohydrate digestion in the mouth?
Which enzyme, secreted by the stomach, is essential for protein digestion?
Which enzyme, secreted by the stomach, is essential for protein digestion?
The pancreas produces which enzyme to digest fats in the small intestine?
The pancreas produces which enzyme to digest fats in the small intestine?
Proteins are broken down into amino acids in the small intestine by:
Proteins are broken down into amino acids in the small intestine by:
Lactose intolerance occurs due to a deficiency in the enzyme:
Lactose intolerance occurs due to a deficiency in the enzyme:
Monosaccharides such as glucose are absorbed in the small intestine through:
Monosaccharides such as glucose are absorbed in the small intestine through:
Amino acids are transported across the intestinal mucosa via:
Amino acids are transported across the intestinal mucosa via:
Triglycerides are absorbed into the bloodstream after forming:
Triglycerides are absorbed into the bloodstream after forming:
Fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed:
Fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed:
The primary site of nutrient absorption in the digestive system is the:
The primary site of nutrient absorption in the digestive system is the:
The process of glycolysis occurs in the:
The process of glycolysis occurs in the:
The end products of aerobic respiration are:
The end products of aerobic respiration are:
Beta-oxidation is the metabolic process that breaks down:
Beta-oxidation is the metabolic process that breaks down:
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to:
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to:
Which metabolic process involves the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
Which metabolic process involves the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources?
Carbohydrates primarily provide the body with:
Carbohydrates primarily provide the body with:
Excess glucose in the body is stored as:
Excess glucose in the body is stored as:
Essential amino acids:
Essential amino acids:
The primary role of lipids in the body includes:
The primary role of lipids in the body includes:
During prolonged exercise, the body primarily uses energy from:
During prolonged exercise, the body primarily uses energy from:
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, primarily functions to:
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, primarily functions to:
The hormone glucagon primarily:
The hormone glucagon primarily:
Epinephrine has a metabolic effect by:
Epinephrine has a metabolic effect by:
Cortisol, a hormone released during stress, primarily affects metabolism by:
Cortisol, a hormone released during stress, primarily affects metabolism by:
During fasting, the body relies on which hormone to maintain blood glucose levels?
During fasting, the body relies on which hormone to maintain blood glucose levels?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
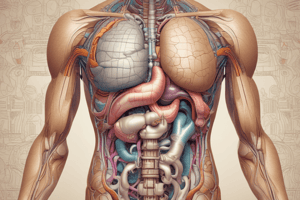
Digestive System Overview
- The hard palate forms the boundary between the oral and nasal cavities.
- The enteric nervous system controls local reflexes regulating digestive tract functions.
- Intraperitoneal organs are completely covered by visceral peritoneum.
- The submucosa layer of the digestive tract contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.
- Enteric sensory neurons detect changes in the digestive tract's chemical environment.
Oral Cavity and Salivary Glands
- The labial frenulum connects the upper lip to the gingiva.
- The serous component of saliva contains amylase for carbohydrate digestion.
- Saliva contains bicarbonate and lysozyme for protection.
- The sublingual salivary gland produces the thickest mucous secretion.
- The buccinator muscle aids in chewing and pushing food against the teeth.
Teeth and Mastication
- Canines tear food.
- The masseter and temporalis muscles close and elevate the jaw during mastication.
- Enamel is the highly calcified outer layer of the tooth crown.
- The mastication reflex is integrated within the medulla oblongata.
- The pulp cavity of a tooth contains nerves and blood vessels.
Pharynx and Swallowing
- The pharyngeal constrictors push food into the esophagus.
- The epiglottis covers the larynx during swallowing to prevent food entry.
- The nasopharynx only transports air.
Esophagus and Peristalsis
- The esophageal hiatus is the passage through the diaphragm for the esophagus.
- The lower third of the esophagus contains only smooth muscle.
- Peristalsis in the esophagus begins with a wave of relaxation followed by contraction.
Stomach Anatomy and Digestion
- The stomach's muscularis layer has an additional oblique layer.
- Parietal cells in the stomach produce hydrochloric acid.
- Pepsinogen is activated by hydrochloric acid to form pepsin.
- Gastrin stimulates hydrochloric acid secretion.
Small Intestine Functions and Structure
- Most digestion and absorption occur in the duodenum and jejunum.
- Villi and microvilli increase surface area for absorption in the small intestine.
- Brunner's glands in the duodenum secrete bicarbonate-rich mucus.
- Fats are absorbed into lacteals within the villi.
- The ileum is the terminal portion of the small intestine.
Accessory Organs: Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas
- Bile emulsifies fats.
- Pancreatic juice neutralizes stomach acid with bicarbonate ions.
- Cholecystokinin (CCK) stimulates bile release from the gallbladder.
- The primary liver function is to produce and secrete bile.
- Hepatocytes in the liver produce bile.
Large Intestine and Absorption
- The primary function of the large intestine is to absorb water and electrolytes.
- The cecum is the first section of the large intestine.
- Bacteria in the colon produce vitamin K.
- Mass movements in the large intestine are often triggered by eating.
- The ileocecal valve regulates the passage of feces from the ileum to the cecum.
Defecation and Rectal Function
- The defecation reflex is initiated by distension of the rectum.
- The internal anal sphincter is controlled by involuntary smooth muscle.
- The external anal sphincter controls voluntary defecation.
- The rectum stores waste before defecation.
- Peristalsis in the rectum triggers the defecation reflex.
Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Digestion
- Amylase begins carbohydrate digestion in the mouth.
- Pepsin is essential for protein digestion in the stomach.
- The pancreas produces lipase to digest fats in the small intestine.
- Trypsin and chymotrypsin break down proteins into amino acids in the small intestine.
- Lactase deficiency causes lactose intolerance.
Absorption of Nutrients
- Monosaccharides are absorbed by active transport.
- Amino acids are transported by active transport mechanisms.
- Triglycerides are absorbed as chylomicrons into the bloodstream.
- Fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed through lymphatic vessels with lipids.
- The small intestine is the primary site of nutrient absorption.
Metabolism and Cellular Respiration
- Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm.
- The end products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.
- Beta-oxidation breaks down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA.
- Lactic acid is formed from pyruvate in the absence of oxygen.
- Gluconeogenesis is the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Energy Balance and Nutrient Use
- Carbohydrates primarily provide quick energy through ATP production.
- Excess glucose is stored as glycogen.
- Essential amino acids must be obtained from the diet.
- Lipids build cell membranes and provide long-term energy storage.
- During prolonged exercise, the body uses energy from lipids and glycogen stores.
Hormonal Regulation of Metabolism
- Insulin lowers blood glucose by promoting glucose uptake in cells.
- Glucagon stimulates glycogen breakdown to increase blood glucose.
- Epinephrine increases glucose availability for energy.
- Cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis to increase blood glucose.
- During fasting, glucagon maintains blood glucose levels.
Thermoregulation and Heat Production
- The hypothalamus is the thermoregulation center.
- Conduction is heat loss through direct contact.
- Evaporation is the mechanism for cooling the body through sweating.
- Shivering increases body temperature by increasing cellular respiration in muscles.
- The body conserves heat by vasoconstriction in cold temperatures.
Vitamin and Mineral Absorption
- Vitamin C is important for collagen synthesis and immune function.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to anemia.
- Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption in the intestines.
- Iron is crucial for hemoglobin synthesis and oxygen transport.
Vitamin K
- Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting.
Macronutrient Functions and Energy Balance
- Carbohydrates are the primary dietary source of energy for cellular processes.
- The body primarily stores long-term energy reserves as triglycerides in adipose tissue.
- Proteins are crucial for building and repairing body tissues.
- Lipids are essential for forming cell membranes and providing insulation.
- During prolonged fasting, the body primarily relies on lipolysis of stored fat for energy.
Absorptive and Postabsorptive States
- The absorptive state is characterized by the body storing excess nutrients as glycogen and fat.
- Liver glycogen is the body's main source of glucose during the postabsorptive state.
- Gluconeogenesis, the process of producing glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, mainly occurs in the liver.
- Glucagon is the primary hormone active in mobilizing stored nutrients during the postabsorptive state.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.