Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role does the sympathetic nervous system play in gastric secretion?
What role does the sympathetic nervous system play in gastric secretion?
- It generally inhibits gastric secretion. (correct)
- It enhances stomach contractions.
- It stimulates the release of gastrin.
- It increases gastric juice production.
Which factor primarily triggers the gastric phase of digestion?
Which factor primarily triggers the gastric phase of digestion?
- Release of bile from the gallbladder.
- Presence of fats in the stomach.
- Presence of carbohydrates in the food.
- Presence of food causing stomach distension. (correct)
What is the primary function of gastrin during the gastric phase?
What is the primary function of gastrin during the gastric phase?
- To stimulate the production of pancreatic juices.
- To inhibit gastric secretion.
- To neutralize stomach acid.
- To promote gastric motility. (correct)
What is the approximate pH of pancreatic juice?
What is the approximate pH of pancreatic juice?
Which function of bile is primarily responsible for breaking fat into smaller droplets?
Which function of bile is primarily responsible for breaking fat into smaller droplets?
Which component of pancreatic juice is responsible for neutralizing stomach acid?
Which component of pancreatic juice is responsible for neutralizing stomach acid?
What is the primary storage function of the gallbladder?
What is the primary storage function of the gallbladder?
What triggers the contraction of the gallbladder to release bile?
What triggers the contraction of the gallbladder to release bile?
During what phase of digestion does the stomach prepare for food intake before it arrives?
During what phase of digestion does the stomach prepare for food intake before it arrives?
Which organs are considered accessory organs of the digestive system?
Which organs are considered accessory organs of the digestive system?
Which mechanism is involved in the digestion of fats by increasing their exposure to digestive enzymes?
Which mechanism is involved in the digestion of fats by increasing their exposure to digestive enzymes?
What effect do partially digested proteins have during the gastric phase?
What effect do partially digested proteins have during the gastric phase?
What is the primary function of micelle formation in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the primary function of micelle formation in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which component is typically NOT found in pancreatic juice?
Which component is typically NOT found in pancreatic juice?
What is a key event that occurs during the gastric phase of digestion?
What is a key event that occurs during the gastric phase of digestion?
In what way do bile salts contribute to lipid digestion?
In what way do bile salts contribute to lipid digestion?
What is primarily responsible for chemical digestion in the stomach?
What is primarily responsible for chemical digestion in the stomach?
During the gastric phase, which function is performed by the pyloric sphincter?
During the gastric phase, which function is performed by the pyloric sphincter?
What happens during the intestinal phase of digestion?
What happens during the intestinal phase of digestion?
Which component is NOT typically found in pancreatic juice?
Which component is NOT typically found in pancreatic juice?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder?
Which sphincter regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the small intestine?
Which sphincter regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the small intestine?
What role does the liver play in digestion?
What role does the liver play in digestion?
Which part of the digestive system primarily absorbs water and ions?
Which part of the digestive system primarily absorbs water and ions?
Match the following digestive enzymes with their primary substrate:
Match the following digestive enzymes with their primary substrate:
Match the following major organs of the digestive system with their specific functions:
Match the following major organs of the digestive system with their specific functions:
Match the following accessory organs of the digestive system with their roles:
Match the following accessory organs of the digestive system with their roles:
Match the following salivary glands with their specific locations:
Match the following salivary glands with their specific locations:
Match the following terms related to carbohydrate digestion with their corresponding processes:
Match the following terms related to carbohydrate digestion with their corresponding processes:
Match the following major organs of the digestive system with their primary function:
Match the following major organs of the digestive system with their primary function:
Match the following accessory organs of the digestive system with their role:
Match the following accessory organs of the digestive system with their role:
Match the phases of gastric secretion with their respective triggers:
Match the phases of gastric secretion with their respective triggers:
Match the stomach secretions with their functions:
Match the stomach secretions with their functions:
Match the following components with their associated secretion:
Match the following components with their associated secretion:
Match the following digestive phrases with their descriptions:
Match the following digestive phrases with their descriptions:
Match the following gastrointestinal hormones with their functions:
Match the following gastrointestinal hormones with their functions:
Match the following digestive processes with their definitions:
Match the following digestive processes with their definitions:
Match the following organs of the digestive system with their primary functions:
Match the following organs of the digestive system with their primary functions:
Match the following accessory organs with their roles in digestion:
Match the following accessory organs with their roles in digestion:
Match the phases of gastric secretion with their main triggers:
Match the phases of gastric secretion with their main triggers:
Match the following terms with their definitions related to digestion:
Match the following terms with their definitions related to digestion:
Match the following gastrointestinal processes with their correct duration:
Match the following gastrointestinal processes with their correct duration:
Match the following digestive functions with the corresponding organs:
Match the following digestive functions with the corresponding organs:
Match the parts of the small intestine with their roles:
Match the parts of the small intestine with their roles:
Match the following conditions with their related digestive processes:
Match the following conditions with their related digestive processes:
Match the following digestive organs with their primary functions:
Match the following digestive organs with their primary functions:
Match the digestive phases with their triggers:
Match the digestive phases with their triggers:
Match the components of pancreatic juice with their roles:
Match the components of pancreatic juice with their roles:
Match the gastric phase mechanisms with their explanations:
Match the gastric phase mechanisms with their explanations:
Match the accessory organs of the digestive system with their specific functions:
Match the accessory organs of the digestive system with their specific functions:
Match each phase of digestion with the percentage of gastric secretion it accounts for:
Match each phase of digestion with the percentage of gastric secretion it accounts for:
Match the following substances with their function in digestion:
Match the following substances with their function in digestion:
Match the role of the nervous system with the corresponding action in gastric secretion:
Match the role of the nervous system with the corresponding action in gastric secretion:
Match the following terms related to bile with their correct descriptions:
Match the following terms related to bile with their correct descriptions:
Match the following organs of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) with their primary functions:
Match the following organs of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) with their primary functions:
Match the phases of gastric secretion with their triggers:
Match the phases of gastric secretion with their triggers:
Match the following digestive enzymes with their functions:
Match the following digestive enzymes with their functions:
Match the following terms with their relevance to lipid digestion:
Match the following terms with their relevance to lipid digestion:
Match the following components of the digestive system with their roles:
Match the following components of the digestive system with their roles:
Match the following functions of bile with their purposes in digestion:
Match the following functions of bile with their purposes in digestion:
Match the following digestive processes with their mechanisms:
Match the following digestive processes with their mechanisms:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Bile Release
- The gallbladder contracts, releasing bile into the cystic duct when stimulated by CCK.
- Bile then flows into the common bile duct and into the duodenum.
- Bile is produced in the liver.
- Bile salts have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, making them amphipathic.
Bile's Role in Lipid Absorption & Digestion
- Bile facilitates lipid absorption and digestion through emulsification and micelle formation.
- Emulsification involves bile salts surrounding fat droplets, breaking them down into smaller droplets, called emulsion droplets.
- The hydrophobic side of bile salts binds to fat, while the hydrophilic side interacts with water.
- This process increases the surface area of fat, enhancing exposure to digestive enzymes like pancreatic lipase.
- Bile salts form micelles, transporting digested fats for absorption.
Organs of the Digestive Tract
- Major Organs: Oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum), large intestine (colon, rectum, and anus).
- Accessory Organs: Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas.
Digestive Enzymes & Secretions
- Pancreatic Juice: Contains water, electrolytes, bicarbonate ions, and digestive enzymes.
- Proteases: Break down proteins.
- Lipases: Convert triglycerides into monoglycerides and fatty acids.
- Nucleases: Break down DNA and RNA into nucleotides.
Liver & Gallbladder
- Liver: Secretion of bile, storage of nutrients, and other vital functions.
- Gallbladder: Stores and concentrates bile by absorbing water and electrolytes.
Phases of Gastric Secretion
- Cephalic Phase
- Triggered by sight, smell, taste, and thought of food.
- Stimulates gastric juice production (HCl, pepsinogen), and increases gastric motility.
- Gastric Phase
- Triggered by the presence of food in the stomach, stretching the stomach and activating stretch receptors.
- Partially digested proteins stimulate the release of gastrin.
- Gastrin increases gastric juice (HCl and pepsinogen) production and enhances stomach contractions.
- Intestinal Phase
- Occurs when chyme enters the small intestine.
- Will be discussed in a future lecture.
Nervous System's Role
- The parasympathetic nervous system stimulates gastric secretion.
- The sympathetic nervous system inhibits gastric secretion.
Sphincters
- Upper Esophageal Sphincter: Allows food to pass from the mouth to the esophagus.
- Lower Esophageal Sphincter: Allows food to pass from the esophagus to the stomach and air to escape during burping.
- Pyloric Sphincter: Allows partially digested food to pass from the stomach to the duodenum.
- Ileocecal Sphincter: Separates the small intestine from the large intestine.
- Internal Anal Sphincter: Prevents stool from leaking out (involuntary muscle).
- External Anal Sphincter: Allows voluntary control of stool passage.
Sphincter of Oddi
- Controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the small intestine.
- Ensures the correct amounts are released when food enters the duodenum.
Gastrointestinal System Overview
- The Gastrointestinal (GI) system or Digestive system consists of the Gastrointestinal tract (GIT) or Alimentary Canal, a long, continuous hollow tube that starts at the mouth and ends at the anus.
- The GI system also includes accessory organs that aid in digestion.
- The primary functions are:
- Extracting nutrients from food
- Excreting waste products
Major Organs of the Digestive Tract
- Oral Cavity (Mouth): Ingestion, mechanical digestion with teeth and tongue, moistening, mixing with salivary secretions.
- Pharynx (Throat): Muscular propulsion of materials into the esophagus.
- Esophagus: Moves bolus (food) from the pharynx to the stomach.
- Stomach: Stores and mixes food, begins protein digestion with pepsin, absorbs alcohol and aspirin.
- Small Intestine: Majority of nutrient digestion and absorption occurs here (duodenum, jejunum, ileum).
- Large Intestine: Water and electrolyte absorption, waste processing (colon, cecum/appendix, rectum, anus).
Accessory Organs of the Digestive System
- Teeth: Aid in mechanical breakdown of food in the oral cavity.
- Tongue: Involved in manipulating and mixing food, swallowing.
- Salivary Glands: Secrete saliva containing salivary amylase, which starts starch digestion.
- Liver: Produces bile, which aids in fat digestion and absorption.
- Gallbladder: Stores and concentrates bile, releasing it into the duodenum.
- Pancreas: Secretes pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes (proteases, lipases, amylase, nucleases) and bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid.
- Colon: Absorbs water and electrolytes from the remaining undigested food.
- Rectum: Stores waste before elimination.
Digestion and Absorption Processes
- Oral Cavity:
- Digestion: Carbohydrates (starch)
- Absorption: None
- Salivary amylase in saliva begins breaking down starch into maltose.
- Stomach:
- Digestion: Proteins and fats (minimal)
- Absorption: Alcohol, aspirin (lipid soluble substances)
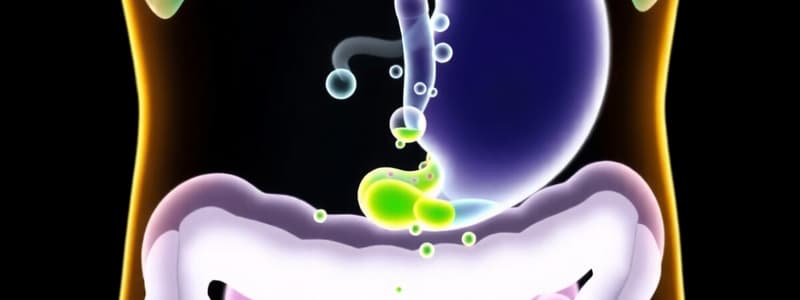
- Gastric secretions:
- HCl: Decreases pH, kills bacteria, denatures proteins, activates pepsin.
- Mucus: Protects stomach lining from acid.
- Gastrin: Regulates digestive activity, stimulating acid production and stomach contractions.
- Digestive Enzymes: Pepsinogen is activated to pepsin by HCl, digesting proteins.
Gastric Secretion Phases
-
Cephalic Phase:
- Triggered by: Sight, smell, taste, or thought of food.
- Mechanism: The brain (hypothalamus and medulla) stimulates the vagus nerve, signaling the stomach to initiate gastric juice production and gastrin release.
- Outcome: Prepares the stomach for digestion by stimulating gastric juice secretion and motility.
-
Gastric Phase:
- Triggered by: Presence of food in the stomach, causing distension and the presence of proteins/amino acids.
- Mechanism: Distension activates stretch receptors, proteins stimulate gastrin release.
- Outcome: Responsible for majority of gastric secretion, ensuring proper food breakdown.
The Pancreas
- Secretes pancreatic juice:
- Watery and alkaline solution (pH 8).
- Contains electrolytes, primarily bicarbonate (HCO3-) for neutralizing stomach acid.
- Produces digestive enzymes:
- Proteases: Break down proteins into peptides.
- Lipases: Break down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol/monoglycerides.
- Amylase: Breaks down starch into maltose.
- Nucleases: Break down DNA/RNA into nucleotides.
The Liver and Gallbladder
- Liver: Produces bile, stored in the gallbladder.
- Gallbladder: Concentrates bile by absorbing water and electrolytes, releasing bile into the duodenum when stimulated by CCK.
- Bile:
- Contains bile salts, amphipathic (hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions).
- Facilitates lipid digestion and absorption:
- Emulsification: Bile salts surround fat droplets, breaking them into smaller droplets.
- Increased Surface Area: Enhances fat exposure to enzymes (e.g., pancreatic lipase).
- Micelle Formation: Bile salts form micelles to transport digested fats for absorption.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.