Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which stage of holozoic nutrition involves taking up soluble digestion products into the body's cells?
Which stage of holozoic nutrition involves taking up soluble digestion products into the body's cells?
- Absorption (correct)
- Egestion
- Ingestion
- Digestion
The process of __________ is the elimination of undigested material from the body.
The process of __________ is the elimination of undigested material from the body.
Egestion
What are the two main groups of organs in the digestive system?
What are the two main groups of organs in the digestive system?
- Respiratory system and digestive system
- Alimentary canal and accessory organs (correct)
- Nervous system and endocrine system
- Excretory system and circulatory system
What happens to food in the mouth?
What happens to food in the mouth?
The esophagus is responsible for digestion of food.
The esophagus is responsible for digestion of food.
What role does the epiglottis play during swallowing?
What role does the epiglottis play during swallowing?
What is the pH level of hydrochloric acid in the stomach?
What is the pH level of hydrochloric acid in the stomach?
Which type of teeth are also known as baby teeth?
Which type of teeth are also known as baby teeth?
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Digestion Stages
- Holozoic nutrition includes ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion/defecation.
- Ingestion involves taking large food pieces into the body.
- Digestion consists of mechanical and chemical breakdown of food.
- Absorption is the uptake of soluble digestion products by body cells.
- Assimilation refers to the utilization of absorbed materials.
- Egestion is the elimination of undigested material from the body cavity.
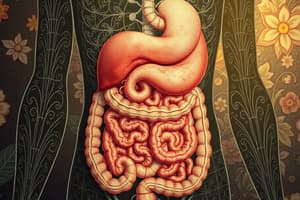
Organs of the Digestive System
- Divided into two main groups: alimentary canal and accessory organs.
- Alimentary Canal includes:
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Anus
- Accessory Organs include:
- Liver
- Teeth
- Pancreas
- Salivary glands
- Gall bladder
Mouth and Its Functions
- Teeth and tongue physically break down food, forming a bolus.
- Salivary glands secrete saliva, containing:
- Water for dissolving substances
- Mucus for lubrication
- Lysozymes to kill bacteria
- Amylase for starch digestion
- The epiglottis prevents food entry into the trachea during swallowing.
Teeth Structure and Types
- Deciduous Teeth: 20 milk teeth form by age two.
- Permanent Teeth: 32 teeth replace deciduous teeth from age 6-12; some may lack wisdom teeth.
- Tooth regions:
- Crown: Exposed part covered with enamel, dentin, and pulp.
- Neck: Connects crown to root, contacts the gum.
- Root: Contains the periodontal membrane and root canal for blood vessels and nerves.
Pharynx Functions
- Acts as a passage for air and food.
- Food is propelled to the esophagus by alternating muscle contractions (peristalsis) from two layers:
- Longitudinal inner layer
- Circular outer layer
Esophagus Characteristics
- Simple tube connecting the mouth to the stomach; no digestion occurs.
- Comprised of a thin epithelium with no villi and a few mucus-secreting glands.
- Thick muscle layer moves food via peristalsis into the stomach.
- Differentiates from the trachea, which remains open by cartilage.
Stomach Anatomy and Function
- Food exits the esophagus through the cardioesophageal sphincter into the stomach.
- Functions as an expandable storage for food, processing it into chyme with three muscle layers.
- Gradually releases chyme into the small intestine via the pyloric sphincter, which regulates flow.
- Stomach wall mucosa has gastric pits leading to gastric glands that secrete gastric juice containing:
- Hydrochloric acid (pH 1) to kill bacteria.
- Mucus to lubricate food and protect mucosal lining from acid.
- Enzymes like pepsin and rennin for protein digestion.
Specialized Mucosa of the Stomach
- Composed of simple columnar epithelium with:
- Mucous neck cells producing alkaline mucus to neutralize HCl.
- Gastric glands responsible for gastric juice secretion.
- Chief cells producing protein-digesting enzymes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.