Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the gizzard in the digestive tube of an earthworm?
What is the primary function of the gizzard in the digestive tube of an earthworm?
- It provides temporary storage for food.
- It facilitates sucking in food.
- It aids in cutting food into smaller bits. (correct)
- It secretes enzymes for digestion.
Which enzyme is responsible for digesting carbohydrates in the earthworm's intestinal system?
Which enzyme is responsible for digesting carbohydrates in the earthworm's intestinal system?
- Lipase
- Amylopsin (correct)
- Pepsin
- Cellulase
In mollusks, where does the absorption of nutrients primarily take place?
In mollusks, where does the absorption of nutrients primarily take place?
- Anus
- Mouth
- Intestine (correct)
- Stomach
What unique characteristic is associated with the stomach of echinoderms?
What unique characteristic is associated with the stomach of echinoderms?
How are the mouth parts of arthropods adapted?
How are the mouth parts of arthropods adapted?
What is the primary function of digestion?
What is the primary function of digestion?
Which process involves the passage of simple food from the digestive tract to the blood?
Which process involves the passage of simple food from the digestive tract to the blood?
Which of the following invertebrate groups has an incomplete digestive tube?
Which of the following invertebrate groups has an incomplete digestive tube?
What is the role of the scolex in tapeworms?
What is the role of the scolex in tapeworms?
Which of the following statements about Nemathelminthes is true?
Which of the following statements about Nemathelminthes is true?
Which digestive process is responsible for incorporating absorbed food into protoplasm?
Which digestive process is responsible for incorporating absorbed food into protoplasm?
How do tapeworms obtain nutrients?
How do tapeworms obtain nutrients?
Which process is the final step in the digestion sequence described?
Which process is the final step in the digestion sequence described?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Digestion Overview
- Digestion transforms food from insoluble to soluble forms for easier absorption and transport by blood.
- Key processes involved in digestion:
- Ingestion: Intake of food via the mouth.
- Digestion: Conversion of solid food into a liquid state.
- Absorption: Transfer of simple nutrients from the digestive tract into blood and lymph.
- Circulation: Movement of absorbed nutrients to body tissues.
- Assimilation: Incorporation of absorbed nutrients into body cells.
- Egestion: Excretion of undigested waste through the anus.
Invertebrate Digestive Systems
- Protozoa: Digestion occurs within food vacuoles; is intercellular.
- Porifera: Digestion occurs intracellularly with specialized choanocytes.
- Coelenterata: Utilizes a gastrovascular cavity for digestion, featuring:
- Incomplete digestive tube: Single opening for food intake and waste expulsion.
- Intracellular: Smaller food particles absorbed by gastrodermis cells.
- Extracellular: Enzymes secreted into cavity for larger particle digestion.
Platyhelminthes
- Have an incomplete branched digestive tube; exception: tapeworms lack digestive tracts.
- Tapeworm Features:
- Scolex: Head with suckers and hooks for attachment to host's intestinal wall.
- Notable Species:
- Diphylobothrium lutum (fish tapeworm)
- Hymenolopis nana (dwarf tapeworm)
- Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm)
- Taenia solium (pork tapeworm)
- Echinococcus granulosus (hydatid cyst disease)
- Echinococcus multilocularis (alveolar cyst disease)
Nemathelminthes
- Possess a complete digestive tube with distinct mouth and anus.
- Common example: Roundworms like Ascaris.
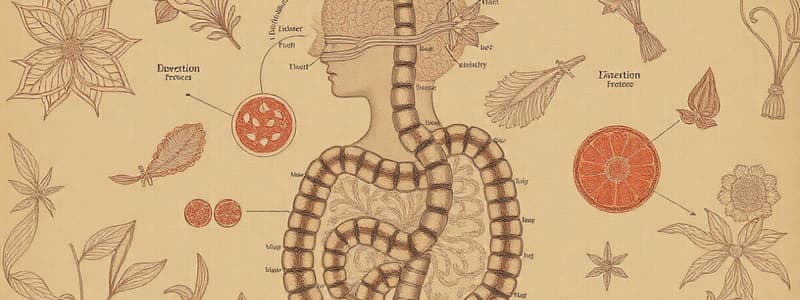
Annelida
- Exhibits a complete digestive tube with extracellular digestion.
- Digestive tract includes:
- Mouth: Anterior opening with prostomium for food grasping.
- Buccal Cavity: Initial food processing area.
- Pharynx: Muscle structure aiding in food suction.
- Crop: Temporary food storage.
- Gizzard: Muscular organ for grinding food with abrasive sand.
- Intestine: Site of digestion aided by enzyme secretion from intestinal glands.
- Enzymes:
- Amylopsin (carbohydrates)
- Pepsin (proteins)
- Lipase (fats)
- Cellulase (cellulose)
- Enzymes:
- Anus: Exit point for waste.
Mollusca
- Possess a complete digestive tube; some species have specialized mouthparts.
- Digestion occurs in the stomach and absorption in the intestine.
Echinodermata
- Generally features a complete digestive tube; some may be incomplete.
- Stomach can evert over food, mucus is secreted, then retracted after digestion.
- Intestine primarily serves excretion purposes.
Arthropoda
- Characterized by a complete digestive tube, with modified mouthparts based on feeding habits (e.g., chewing, piercing, lapping, sucking).
- Enzymatic digestion similar to Annelida; enzymes include amylopsin, pepsin, lipase, and cellulase.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.