Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of bile in lipid digestion?
What is the function of bile in lipid digestion?
- To transport monoglycerides
- To emulsify large fat droplets (correct)
- To absorb fatty acids
- To directly digest triglycerides
Short and medium-chain fatty acids can be directly absorbed into the bloodstream.
Short and medium-chain fatty acids can be directly absorbed into the bloodstream.
True (A)
What substances do long chain fatty acids and monoglycerides reassemble into within the intestinal cell?
What substances do long chain fatty acids and monoglycerides reassemble into within the intestinal cell?
triglycerides
The process of combining triglycerides with cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins creates __________.
The process of combining triglycerides with cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins creates __________.
Match the following components with their role in lipid digestion:
Match the following components with their role in lipid digestion:
Which enzyme helps infants digest the fats in their mother's milk?
Which enzyme helps infants digest the fats in their mother's milk?
The gallbladder produces bile for fat emulsification.
The gallbladder produces bile for fat emulsification.
Name one location in the gastrointestinal tract where no enzymatic digestion occurs.
Name one location in the gastrointestinal tract where no enzymatic digestion occurs.
The _____ is the storage site of bile.
The _____ is the storage site of bile.
Match the following digestive organs with their functions:
Match the following digestive organs with their functions:
Which part of the gastrointestinal tract follows the stomach?
Which part of the gastrointestinal tract follows the stomach?
The pancreas is responsible for producing gastric lipase.
The pancreas is responsible for producing gastric lipase.
What is the primary function of bile in digestion?
What is the primary function of bile in digestion?
Which pancreatic cells produce glucagon?
Which pancreatic cells produce glucagon?
Glycogenolysis is an anabolic process.
Glycogenolysis is an anabolic process.
What is the role of secretin in pancreatic secretions?
What is the role of secretin in pancreatic secretions?
In a catabolic reaction, large molecules are broken down into __________.
In a catabolic reaction, large molecules are broken down into __________.
Match the following pancreatic hormones with their functions:
Match the following pancreatic hormones with their functions:
What structure is formed from triglycerides and cholesterol, allowing for the transport of fats in the body?
What structure is formed from triglycerides and cholesterol, allowing for the transport of fats in the body?
Short and medium-chain fatty acids are absorbed into the lymphatic system.
Short and medium-chain fatty acids are absorbed into the lymphatic system.
What is the primary function of the gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)?
What is the primary function of the gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)?
Chylomicrons travel first into the __________ vessels before entering the bloodstream.
Chylomicrons travel first into the __________ vessels before entering the bloodstream.
Match the following specialized cells in the stomach to their respective secretions and functions:
Match the following specialized cells in the stomach to their respective secretions and functions:
Which component is necessary for the solubility of chylomicrons?
Which component is necessary for the solubility of chylomicrons?
The stomach consists of two major zones: the cardiac zone and the pyloric zone.
The stomach consists of two major zones: the cardiac zone and the pyloric zone.
What substance neutralizes acid in the small intestine?
What substance neutralizes acid in the small intestine?
The end product of digestion in the stomach is called __________.
The end product of digestion in the stomach is called __________.
What is the function of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)?
What is the function of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)?
What is the primary function of chief cells in the stomach?
What is the primary function of chief cells in the stomach?
Ghrelin is responsible for stimulating appetite.
Ghrelin is responsible for stimulating appetite.
Which part of the small intestine is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption?
Which part of the small intestine is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption?
The __________ cells in the stomach inhibit the production of HCl.
The __________ cells in the stomach inhibit the production of HCl.
Which hormone is released by G-cells to increase HCl secretion?
Which hormone is released by G-cells to increase HCl secretion?
Match the following parts of the small intestine with their characteristics:
Match the following parts of the small intestine with their characteristics:
The ileum is shorter than the jejunum.
The ileum is shorter than the jejunum.
What role do secretagogues play in the stomach?
What role do secretagogues play in the stomach?
What enzyme is responsible for digesting lactose?
What enzyme is responsible for digesting lactose?
Bile is necessary for the digestion of fats.
Bile is necessary for the digestion of fats.
What is the primary function of ribonucleases?
What is the primary function of ribonucleases?
___ deficiency can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, and metabolic acidosis due to the inability to digest lactose.
___ deficiency can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, and metabolic acidosis due to the inability to digest lactose.
Match the following enzymes with their respective functions:
Match the following enzymes with their respective functions:
Which pancreatic enzyme cuts at the amino terminal?
Which pancreatic enzyme cuts at the amino terminal?
Genetic lactose deficiency is typically temporary.
Genetic lactose deficiency is typically temporary.
Name one condition that results from lactose intolerance.
Name one condition that results from lactose intolerance.
Fatty acids and monoacylglycerol are absorbed into the body by the ___ after lipid digestion.
Fatty acids and monoacylglycerol are absorbed into the body by the ___ after lipid digestion.
What type of enzyme is cholecystokinin classified as?
What type of enzyme is cholecystokinin classified as?
Enzymes that split triacylglycerol are known as lipases.
Enzymes that split triacylglycerol are known as lipases.
What are nucleoproteins composed of?
What are nucleoproteins composed of?
The primary byproduct of purine metabolism is ___ acid.
The primary byproduct of purine metabolism is ___ acid.
Which of the following substances stimulates the release of histamine in digestion?
Which of the following substances stimulates the release of histamine in digestion?
Flashcards
Lingual Lipase
Lingual Lipase
An enzyme in saliva that helps digest fats, especially in infants.
Fat Digestion
Fat Digestion
The process of breaking down fats into smaller molecules for absorption.
Pancreatic Lipase
Pancreatic Lipase
An enzyme produced by the pancreas, essential for fat digestion.
Gastric Lipase
Gastric Lipase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Production
Bile Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emulsification
Emulsification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gallbladder
Gallbladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical Digestion
Mechanical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to fats in the small intestine?
What happens to fats in the small intestine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chylomicrons
Chylomicrons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short- and Medium-chain Fatty Acids
Short- and Medium-chain Fatty Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long-chain Fatty Acids
Long-chain Fatty Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chylomicron Structure
Chylomicron Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chylomicron Function
Chylomicron Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short/Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Absorption
Short/Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long-Chain Fatty Acid Absorption
Long-Chain Fatty Acid Absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chylomicron Path
Chylomicron Path
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric Zones
Gastric Zones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyloric Zone Divisions
Pyloric Zone Divisions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chyme
Chyme
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Cell Function
Parietal Cell Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide (GIP)
Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide (GIP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What stimulates stomach secretions?
What stimulates stomach secretions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are chief cells?
What are chief cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is pepsin activated?
How is pepsin activated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is gastrin?
What is gastrin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of histamine in stomach acid production?
What is the role of histamine in stomach acid production?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the duodenum?
What is the function of the duodenum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the jejunum?
What is the role of the jejunum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the ileum?
What is the function of the ileum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
-lysis Processes
-lysis Processes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin
Insulin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon
Glucagon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Catabolic
Catabolic
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 2 major parts of digestion?
What are the 2 major parts of digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrin
Gastrin
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 3 main pancreatic enzymes involved in protein digestion?
What are the 3 main pancreatic enzymes involved in protein digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of lactase?
What is the role of lactase?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 3 main brush border enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion?
What are the 3 main brush border enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do pancreatic enzymes affect protein digestion?
How do pancreatic enzymes affect protein digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explain the role of bile in fat digestion.
Explain the role of bile in fat digestion.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of lipase enzymes?
What is the purpose of lipase enzymes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does lactose intolerance occur?
How does lactose intolerance occur?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to carbohydrates in the small intestine?
What happens to carbohydrates in the small intestine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between endopeptidases and exopeptidases?
What is the difference between endopeptidases and exopeptidases?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does protein digestion begin?
Where does protein digestion begin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are nucleic acids digested?
How are nucleic acids digested?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 3 main stages of metabolism?
What are the 3 main stages of metabolism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does lactose intolerance lead to digestive issues?
How does lactose intolerance lead to digestive issues?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
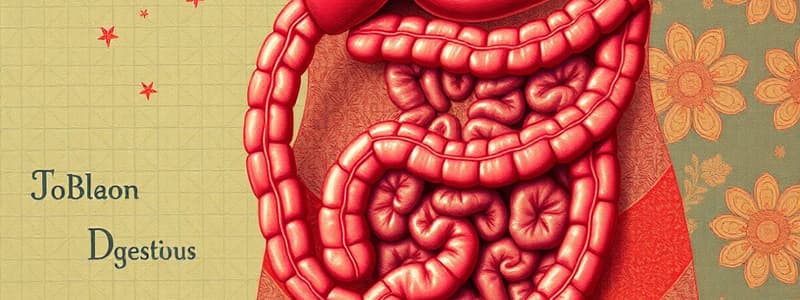
Digestion
- Digestion is the process of breaking down food into absorbable substances
- It starts in the mouth with amylase and lipase
- Food is broken down into smaller pieces, traveling through the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine
- The small intestine is the primary site of digestion
- The process continues through the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and finally the anus
- Most digestion occurs in the small intestine
Digestive Enzymes in Saliva
- Salivary amylase breaks down carbohydrates into smaller molecules (sugars)
- Amylopectin and amylose, large carbohydrates, break down into maltose (a glucose sugar)
- Lingual lipase breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerides, aiding in lipid digestion; works optimally in low pH values, continuing into the stomach.
- Aids in infant digestion
Gastrointestinal Tract
- The mouth is the site for mechanical digestion initially
- The liver produces bile crucial for fat emulsification
- The gallbladder stores bile, a substance vital for fat digestion
- The digestion process requires mechanical and enzymatic actions within the digestive system
Carbohydrate Digestion
- The mouth begins the breakdown of carbohydrates into shorter sugar chains with salivary amylase
- The stomach deactivates salivary amylase where no further carbohydrate digestion occurs
- The small intestine is the major site for starch digestion and sugars
- Disaccharidases (sucrase, lactase, and maltase) break down disaccharides into monosaccharides
- Glucose is stored as glycogen or is transported into the blood
- Carbohydrate digestion occurs mostly in the mouth and small intestine
Protein Digestion
- Protein digestion begins in the stomach, where hydrochloric acid denatures proteins
- Pepsin, an enzyme, breaks down proteins into shorter polypeptide chains
- Enzymatic digestion continues in the small intestine with enzymes like trypsin, chymotrypsin, and peptidases breaking these chains into their constituent amino acids
- These amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream and travel to the liver. If excess protein is present, it is converted to fats, which cannot be stored in the same way as amino acids. Gluconeogenesis occurs to produce glucose if needed as an alternative energy source.
Lipid Digestion and Absorption
- Lipids are emulsified by bile salts in the small intestine
- Pancreatic lipase breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides
- Absorbed into the bloodstream through lacteals (lymph vessels)
- These components reform into triglycerides, combined with proteins, and form chylomicrons (lipid transport particles), which enter lymphatic vessels and eventually the bloodstream
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.