Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main difference between mechanical and chemical digestion?
What is the main difference between mechanical and chemical digestion?
Mechanical digestion involves physical breakdown of food, while chemical digestion involves the breakdown of food using enzymes.
What is the function of the circulatory system in the digestive process?
What is the function of the circulatory system in the digestive process?
The circulatory system transports digested nutrients from the digestive system to the cells.
What is an example of a simple animal with a digestive sac?
What is an example of a simple animal with a digestive sac?
A jellyfish is an example of a simple animal with a digestive sac.
What are the four main steps of the digestive process?
What are the four main steps of the digestive process?
What type of digestion occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine?
What type of digestion occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine?
What is a characteristic of a complete digestive system?
What is a characteristic of a complete digestive system?
What is the primary function of amylase in the digestion process?
What is the primary function of amylase in the digestion process?
What is the purpose of mucus in saliva?
What is the purpose of mucus in saliva?
What is the term for the process of taking food in and swallowing it?
What is the term for the process of taking food in and swallowing it?
What type of muscle contractions occur in the esophagus to propel food towards the stomach?
What type of muscle contractions occur in the esophagus to propel food towards the stomach?
What is the main function of the stomach in the digestion process?
What is the main function of the stomach in the digestion process?
What is the maximum capacity of the stomach in terms of volume?
What is the maximum capacity of the stomach in terms of volume?
What is the average length of the gastrointestinal tract in humans, and what factors can influence its length?
What is the average length of the gastrointestinal tract in humans, and what factors can influence its length?
What are the two main types of digestion that occur in the mouth, and what are their roles in breaking down food?
What are the two main types of digestion that occur in the mouth, and what are their roles in breaking down food?
What is the role of the accessory organs in the digestion process, and what are some examples of these organs?
What is the role of the accessory organs in the digestion process, and what are some examples of these organs?
What is the primary function of the enzyme amylase in saliva, and how does it contribute to chemical digestion?
What is the primary function of the enzyme amylase in saliva, and how does it contribute to chemical digestion?
What is the relationship between the type of teeth an animal has and its diet, and how do herbivores and carnivores differ in this regard?
What is the relationship between the type of teeth an animal has and its diet, and how do herbivores and carnivores differ in this regard?
What are the six main stops in the journey of digestion, and what is the primary function of each stop?
What are the six main stops in the journey of digestion, and what is the primary function of each stop?
Flashcards
Digestion
Digestion
The process of breaking down nutrients into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body.
Digestive System
Digestive System
A group of organs that work together to break down food and absorb nutrients.
Ingestion
Ingestion
The process of taking food into the mouth.
Digestion
Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Absorption
Absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Egestion
Egestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physical Digestion
Physical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Digestion
Chemical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enzyme
Enzyme
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amylase
Amylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saliva
Saliva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bolus
Bolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophagus
Esophagus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristalsis
Peristalsis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomach
Stomach
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrointestinal Tract (GI tract)
Gastrointestinal Tract (GI tract)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accessory Organs
Accessory Organs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical Digestion
Mechanical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Digestion
Chemical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Digestion
- Digestion is the process of breaking down nutrients and absorbing them into the blood and carrying it to cells.
- The digestive system is a group of organs that work together to carry out digestion.
- Four main steps: ingestion, digestion, absorption, and egestion.
Mouth
- Two types of digestion occur in the mouth: physical and chemical.
- Physical digestion: food is broken down into smaller pieces by teeth.
- Chemical digestion: breaking food down using chemicals, specifically saliva and acid.
- Saliva contains enzymes, which are chemicals that increase the rate of chemical reactions.
- The most important enzyme in saliva is amylase.
Saliva
- Amylase breaks down starch into disaccharides.
- Saliva also dissolves food particles, making it possible to taste food.
- It contains mucus, a protective secretion that acts as a lubricant to aid in swallowing.
- You produce approximately 0.75 to 1.5 L of saliva each day.
The Bolus
- The water in saliva moistens the food and a bolus, or ball of food, is formed from chewing.
- The tongue pushes the bolus to the back of the mouth for swallowing.
- The bolus is then pushed into the pharynx and a soft palate is raised to prevent food from entering the nasal passages.
- At the same time, the larynx is raised against the epiglottis, which covers the entrance to the trachea, preventing the food from entering the lungs.
Esophagus
- Food moves from the mouth to the stomach via the esophagus.
- Long muscular tube with a 2cm diameter.
- The walls stretch because of the food, which activates the smooth muscles, undergoing rhythmic wave-like contractions called peristalsis.
- It takes about 8 s for food to travel down the esophagus to the stomach.
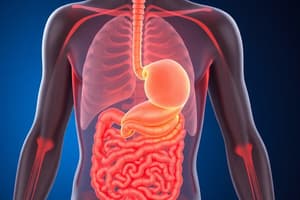
Stomach
- J-shaped, muscular organ.
- Mechanical and chemical digestion.
- The stomach can expand and hold up to 2L.
Gastrointestinal Tract
- The digestive tract is referred to as the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract).
- Approximately 7-9m long, depending on age and size.
- Interaction with other systems: circulatory to transport nutrients, nervous and endocrine system regulates digestion.
- The GI tract consists of: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
- The accessory organs are: salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gall bladder.
Digestive Journey
- Digestion is like a journey down a disassembly line with many stops: mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
- The accessory organs also aid in digestion.
Types of Digestion
- Mechanical digestion: occurs in the mouth and stomach, involves tearing, chewing, grinding, and peristalsis.
- Chemical digestion: occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine, involves coating food with saliva containing digestive enzymes.
Specialized Digestive Systems
- Simple animals have a digestive sac with a single opening into a gastrovascular cavity.
- More complex animals digest food along a tract with two openings, one for intake and one for waste elimination.
- The human system is a complete digestive system.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.