Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which process involves breaking down large food molecules into smaller substances for absorption?
Which process involves breaking down large food molecules into smaller substances for absorption?
- Digestion (correct)
- Absorption
- Metabolism
- Excretion
Absorption refers to the mechanical and chemical processes that convert food into smaller substances.
Absorption refers to the mechanical and chemical processes that convert food into smaller substances.
False (B)
What is the primary form of direct energy derived from carbohydrates during digestion?
What is the primary form of direct energy derived from carbohydrates during digestion?
glucose
Excess energy from carbohydrates, fats, or proteins is converted into ______ for storage within the body.
Excess energy from carbohydrates, fats, or proteins is converted into ______ for storage within the body.
Match the following digestive organs with their primary functions:
Match the following digestive organs with their primary functions:
Which term describes the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in the body?
Which term describes the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in the body?
Catabolism involves building up growth, repair, and storage reserves in the body.
Catabolism involves building up growth, repair, and storage reserves in the body.
What is the small amount of energy produced during anaerobic respiration called?
What is the small amount of energy produced during anaerobic respiration called?
The process of breaking down energy to produce energy or ATP is referred to as ______?
The process of breaking down energy to produce energy or ATP is referred to as ______?
Match the following energy systems with their typical durations:
Match the following energy systems with their typical durations:
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the process of digestion?
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the process of digestion?
The digestive system is a closed system that operates entirely within the body.
The digestive system is a closed system that operates entirely within the body.
What is the approximate length, in feet, of the muscular tube that extends from the pharynx to the rectum in the digestive system?
What is the approximate length, in feet, of the muscular tube that extends from the pharynx to the rectum in the digestive system?
The ______ helps with the movement of food and air (mouth and nasal).
The ______ helps with the movement of food and air (mouth and nasal).
Match the following regions of the pharynx with their corresponding locations:
Match the following regions of the pharynx with their corresponding locations:
What is the primary role of the epiglottis during the swallowing process?
What is the primary role of the epiglottis during the swallowing process?
Peristalsis refers to a constant state of contraction of the esophageal muscles.
Peristalsis refers to a constant state of contraction of the esophageal muscles.
What enzyme, secreted in the stomach, is crucial for the initial digestion of proteins?
What enzyme, secreted in the stomach, is crucial for the initial digestion of proteins?
The mixture of food and gastric secretions in the stomach is known as ______
The mixture of food and gastric secretions in the stomach is known as ______
Match the following sections of the small intestine with their primary functions:
Match the following sections of the small intestine with their primary functions:
What structural feature of the small intestine significantly enhances the surface area for absorption?
What structural feature of the small intestine significantly enhances the surface area for absorption?
The liver primarily stores glycogen and regulates blood sugar by producing insulin
The liver primarily stores glycogen and regulates blood sugar by producing insulin
What digestive fluid, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, aids in the digestion and absorption of fats?
What digestive fluid, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, aids in the digestion and absorption of fats?
The organ that functions in detoxification, and producing bile, is called the ______.
The organ that functions in detoxification, and producing bile, is called the ______.
Match the types of liver disease with their descriptions:
Match the types of liver disease with their descriptions:
Which of the following components is primarily absorbed in the large intestine?
Which of the following components is primarily absorbed in the large intestine?
The rectum has involuntary internal and external sphincters.
The rectum has involuntary internal and external sphincters.
The appendix stores what?
The appendix stores what?
The condition that involves hardened deposits of digestive fluid within the gallbladder is referred to as ______.
The condition that involves hardened deposits of digestive fluid within the gallbladder is referred to as ______.
Match the following regions of the large intestine with their position within the body:
Match the following regions of the large intestine with their position within the body:
Which of the following best describes the function of enzymes in digestion?
Which of the following best describes the function of enzymes in digestion?
Enzymes are consumed during chemical reactions.
Enzymes are consumed during chemical reactions.
What is the primary function of amylase?
What is the primary function of amylase?
[Blank] aids in fat digestion and is produced by the liver.
[Blank] aids in fat digestion and is produced by the liver.
Match the following protein enzymes with their location:
Match the following protein enzymes with their location:
In which organ does the digestion of carbohydrates initially begin?
In which organ does the digestion of carbohydrates initially begin?
Most alcohol is absorbed in the small intestine.
Most alcohol is absorbed in the small intestine.
What is the name of the enzyme found in some fats in the mouth at the beginning of digestion?
What is the name of the enzyme found in some fats in the mouth at the beginning of digestion?
Stress slows down the process of ______.
Stress slows down the process of ______.
Match gut functions with its description:
Match gut functions with its description:
Flashcards
What is metabolism?
What is metabolism?
The sum of all chemical reactions in the body.
What is anabolism?
What is anabolism?
Building up growth, repair, and storage, using energy.
What is catabolism?
What is catabolism?
Breaking down substances to produce energy/ATP.
What is anaerobic respiration?
What is anaerobic respiration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is aerobic respiration?
What is aerobic respiration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the preferred fuel sources of the body?
What are the preferred fuel sources of the body?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is digestion?
What is digestion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Absorption?
What is Absorption?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of Protein?
What is the role of Protein?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of carbohydrates?
What is the role of carbohydrates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of fat?
What is the role of fat?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of vitamins?
What is the role of vitamins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of minerals?
What is the role of minerals?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is 'Gum to Bum'?
What is 'Gum to Bum'?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the mouth?
What is the mouth?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the digestive tract?
What is the digestive tract?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the other organs of the digestive system?
What are the other organs of the digestive system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the pharynx?
What is the pharynx?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the larynx?
What is the larynx?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the epiglottis?
What is the epiglottis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the esophagus?
What is the esophagus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is peristalsis?
What is peristalsis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the cardiac sphincter?
What is the cardiac sphincter?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the pyloric sphincter?
What is the pyloric sphincter?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Chyme?
What is Chyme?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Duodenum?
What is the Duodenum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the jejunum?
What is the jejunum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Ileum?
What is Ileum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of villi and curcular folds?
What is the role of villi and curcular folds?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the liver?
What is the role of the liver?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the pancreas?
What is the role of the pancreas?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of gallbladder?
What is the role of gallbladder?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are gallstones?
What are gallstones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the large intestine?
What is the role of the large intestine?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the rectum?
What is the role of the rectum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the salivary glands?
What is the role of the salivary glands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the stomach?
What is the role of the stomach?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are other functions of the gut?
What are other functions of the gut?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is gut microbiome?
What is gut microbiome?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of Enzymes?
What is the role of Enzymes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Lecture 2 focuses on digestion and absorption
- In class assignments are beginning soon, details are coming next week
Metabolism and Nutrition
- Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body
- Digestion and absorption of food leads to a nutrient pool
- The body uses the nutrient pool for metabolism
- Anabolic activities build up growth, repair, storage, and reserves, leading to energy use
- Catabolic processes break down substances, producing energy/ATP, with 60% lost as heat and 40% as usable energy
- Anaerobic respiration (glycolysis) produces a small amount of energy quickly, without oxygen
- Aerobic respiration (citric acid/krebs cycle and electron transport chain) creates a large amount of energy, 90% of which the body uses
Fuel Sources
- Preferred fuels for the body include phosphocreatine, glucose, and fat
- Phosphocreatine provides energy for 5-10 seconds
- Glucose (glycolysis) provides energy for 10 sec - 2/3 minutes
- Fat (aerobic respiration) provides energy for 2/3 min – hours
- Protein is used during the synthesis process, but it can convert to glucose if needed
Importance of Nutrition
- Humans are continually renewing themselves
- 5% of body weight is replaced each day
- Optimal body function requires proper fuel, i.e. essential nutrients
- Food breaks down so smaller substances can be absorbed into the body and built back up as tissues, organs, and glands
- Macronutrients have energy stored as bonds, and thus, need to all be broken down and then absorbed
- Micronutrients also must be released from food and then absorbed
Digestion and Absorption
- Digestion is the mechanical and chemical process that converts food into smaller substances
- Smaller substances from digestion can be absorbed and used by the body
- Absorption is the process where nutrients and other substances are transferred from the digestive system into body fluids
- Body fluids transport nutrients
- Protein provides energy and amino acid building blocks
- Carbohydrates provide direct energy as glucose/glycogen
- Fat provides stored energy, cell membranes, and hormone synthesis
- Excess protein, carbs, or fats will become stored energy
- Vitamins are fat and water soluble and assist in regulating body processes/function
- Minerals come from the soil and are incorporated into plants, tissues of animals, and in drinking water
- Minerals assist in regulating body processes/function
Gum to Bum
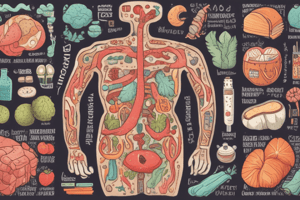
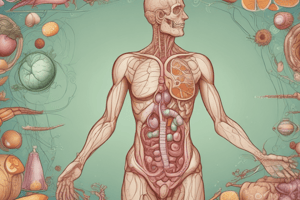
- Digestion occurs in one continuous tunnel from mouth to anus; the body exists outside of this tunnel
- The digestive system is a 30-foot long muscular tube
- Major parts include the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, rectum and anus
- Other supporting digestive organs include the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder, which secrete additional digestive juices
Mouth and Throat
- Includes teeth, tongue, and salivary glands
- The pharynx aids in the movement of both food and air
- Larynx protects the trachea from food aspiration
- Epiglottis seals the windpipe during eating
- Saliva contains enzymes, beginning carb and fat digestion
Esophagus
- A muscular tube, the esophagus transports food/drink to the stomach
- Smooth constrictor/sphincter muscles are present in the esophagus
- Peristalsis moves the food bolus along with relaxation and contraction
Food Bolus
- In the buccal phase, the food bolus is swallowed
- In the pharyngeal phase, the food bolus bypasses airway into the esophagus
- In the esophageal phase, peristaltic waves move the food bolus toward the stomach
- Sphincters that enter the stomach include the upper muscular sphincter and the lower (cardiac) muscular sphincter
Stomach
- The cardiac sphincter opens to the esophagus
- The pyloric sphincter opens to the small intestine
- Structures present are the greater and lesser curvatures
- Chyme is food mixed with gastric secretions (HCl, Pepsin)
- Protein digestion begins, and alcohol absorption occurs (30%)
Small Intestine
- The duodenum is the mixing bowl chyme in the small intestine that mixes with enzymes from pancreas and liver
- The jejunum is the bulk of chemical digestion, water and nutrient absorption in the small intestine
- The ileum has final nutrient absorption, fat soluble vitamins
Absorption
- Intestinal walls contain villi and circular folds to increase surface area for absorption
- The size of the intestinal wall is the size of a baseball infield
- Blood absorbs protein and carbs
- Lymph absorbs fat
Supporting Organs
- The liver is responsible for detoxification, glycogen storage and production of bile for fat digestion
- The pancreas secretes enzymes for carb, protein, fat breakdown and produces insulin for blood sugar regulation
- The gallbladder stores and secretes bile for fat digestion
Liver Diseases
- Cirrhosis of the Liver is the formation of fibrous scarring, which impacts liver function
- A Fatty Liver is a warning sign for Cirrhosis
- Jaundice (yellowish skin and eyes) results from buildup of bilirubin/red blood cell waste in skin that liver normally processes
- Alcohol abuse and genetic factors may cause Cirrhosis
- Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid
- Gallstones can be the size of a grain of sand to a golf ball
- Passing a gallstone through the ducts is painful
- Lasers can break up gallstones
Major Structures
- Large intestine contains the ascending colon, transverse colon, and descending colon
- Water and electrolyte absorption continues, concentrating feces
- Intestinal bacteria aid in digestion, otherwise little digestion occurs
- The appendix stores healthy gut bacteria
- The rectum stores waste products for elimination
- Sphincters include internal (involuntary) and external (voluntary)
- Elimination occurs by holding the rectum closed
The Digestive Process
- Salivary glands produce enzymes that break down starch and fats
- The tongue undergoes mastication and mixing of food with saliva to form bolus
- Esophagus transfers the food bolus to the stomach
- The stomach secretes enzymes that break down proteins and mixes and liquefies food (Chyme = gastric secretions + food)
- The liver produces bile that aids fat digestion
- The gallbladder stores and secretes bile that aids in fat digestion
- The pancreas secretes enzymes that break down carbs, proteins, and fats
- The small intestine is the primary site where enzymes break down carbs, proteins, and fats
- Water/electrolyte reabsorption occur in the large intestine
- The rectum stores waste products for elimination
- The anus holds rectum closed and then opens to allow elimination
- The entire digestive process takes 24 to 72 hours
- Mouth watering, chewing, and swallowing help the digestive process
- Bolus contracts and relaxes as it moves through the esophagus, entering the stomach
- Liquified contents are ejected into the pulse, roughly in the form of 1 to 2 teaspoons
- Then the bolus liquefies its contents at a time until emptied into small intestine (Chyme)
- Intestinal smooth muscle continues to contract/relax to move food along to the small intestine
- The small intestine contains intestinal walls that are lined with finger-like villi
- Majority of nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestine, the exception being 30% alcohol in the stomach
- Lymphatic/circulatory in the blood systems take up nutrients in order for absorption to continue
- Large intestines absorb water, sodium and chloride
- Large intestine compacts substances that cannot be digested/absorbed, e.g. bacteria and cellular waste, as stool
Macronutrient Absorption Rates
- 99% of absorbed carbs turn into glucose, providing direct or stored energy (glycogen or adipose)
- 95% of absorbed fats turn into fatty acids and glycerol
- 92% of absorbed proteins turn into amino acids, to provide materials for building tissue or to provide energy
Lipogenesis
- Excess energy is converted into fat (adipose) stores regardless of the source (carb, fat, or protein)
- It's regulated by insulin and stimulated by simple carbs
- Excess Calories will always be stored
Gut MicroBiome
- Gut microbiome contains beneficial bacteria/gut flora that reside in the large intestine
- This serves as a signal immune system that fights harmful bacteria
- Gut digests parts of fiber to produce energy (and gas)
- Gut produces vit K and biotin (B7)
- Antibiotics use reduces healthy bacteria
Gut as a Second Brain
- Gut is the second brain as it can regulate taste centers (salty, sweet, bitter, sour and rich/savory)
- Gut has either benefits or can be toxic
- Stress slows down digestion
- Digestion is parasympathetic
Gut Diseases
- Constipation occurs with no more than 3 bowel movements per week
- Diarrhea occurs with more than 3 bowel movements per day
- Crohn's and colitis are chronic inflammations of the digestive tract, potentially leading to ulcers and bleeding
- A symptom of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is an irritated large intestine
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.